FMS-related tyrosine kinase 3 ligand (FLT3L), encoded by FLT3LG, is a hematopoietic factor essential for the development of natural killer (NK) cells, B cells, and dendritic cells (DCs) in mice. We describe three humans homozygous for a loss-of-function FLT3LG variant with a history of various recurrent infections, including severe cutaneous warts. The patients' bone marrow (BM) was hypoplastic, with low levels of hematopoietic progenitors, particularly myeloid and B cell precursors. Counts of B cells, monocytes, and DCs were low in the patients' blood, whereas the other blood subsets, including NK cells, were affected only moderately, if at all. The patients had normal counts of Langerhans cells (LCs) and dermal macrophages in the skin but lacked dermal DCs. Thus, FLT3L is required for B cell and DC development in mice and humans. However, unlike its murine counterpart, human FLT3L is required for the development of monocytes but not NK cells.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 20
FLT3L governs the development of partially overlapping hematopoietic lineages in humans and mice.
In Cell on 23 May 2024 by Momenilandi, M., Levy, R., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
In Heliyon on 1 April 2022 by Townsend, L., Dyer, A. H., et al.
SARS-CoV-2 infection causes a wide spectrum of disease severity. Identifying the immunological characteristics of severe disease and the risk factors for their development are important in the management of COVID-19. This study aimed to identify and rank clinical and immunological features associated with progression to severe COVID-19 in order to investigate an immunological signature of severe disease. One hundred and eight patients with positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR were recruited. Routine clinical and laboratory markers were measured, as well as myeloid and lymphoid whole-blood immunophenotyping and measurement of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and soluble CD25. All analysis was carried out in a routine hospital diagnostic laboratory. Univariate analysis demonstrated that severe disease was most strongly associated with elevated CRP and IL-6, loss of DLA-DR expression on monocytes and CD10 expression on neutrophils. Unbiased machine learning demonstrated that these four features were strongly associated with severe disease, with an average prediction score for severe disease of 0.925. These results demonstrate that these four markers could be used to identify patients developing severe COVID-19 and allow timely delivery of therapeutics.
© 2022 The Author(s).
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Neutrophil Activation/Maturation Markers in Chronic Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction.
In Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland) on 9 February 2022 by Prausmüller, S., Spinka, G., et al.
Neutrophils are critically involved in the immune response. Inflammatory stimuli alter the expression status of their surface molecule toolset, while inflammation-stimulated granulopoiesis might also influence their maturation status. Data on neutrophil status in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) are scarce. The present study aims to evaluate the role of neutrophil CD11b, CD66b and CD64 expression in HFrEF.
A total of 135 HFrEF patients and 43 controls were recruited. Mean fluorescence intensity of the activation/maturation markers CD11b, CD66b and CD64 was measured on neutrophils by flow cytometry. CD10 (neprilysin) expression was simultaneously determined.
Neutrophil CD64 expression was higher in HFrEF compared with controls, while CD11b/CD66b levels were similar. Neutrophil CD11b and CD66b showed a significant direct correlation to neutrophil CD10 expression (rs = 0.573, p < 0.001 and rs = 0.184, p = 0.033). Neutrophil CD11b and CD66b correlated inversely with heart failure severity reflected by NT-proBNP and NYHA class (NT-proBNP: rs = -0.243, p = 0.005 and rs = -0.250, p = 0.004; NYHA class: p = 0.032 and p = 0.055), whereas no association for CD64 could be found. Outcome analysis did not reveal a significant association between the expression of CD11b, CD66b and CD64 and all-cause mortality (p = ns).
The results underline the potential role of neutrophils in HFrEF disease pathophysiology and risk stratification and should stimulate further research, characterizing subpopulations of neutrophils and searching for key molecules involved in the downward spiral of inflammation and heart failure.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cardiovascular biology
Relevance of Neutrophil Neprilysin in Heart Failure.
In Cells on 28 October 2021 by Prausmüller, S., Spinka, G., et al.
Significant expression of neprilysin (NEP) is found on neutrophils, which present the transmembrane integer form of the enzyme. This study aimed to investigate the relationship of neutrophil transmembrane neprilysin (mNEP) with disease severity, adverse remodeling, and outcome in HFrEF. In total, 228 HFrEF, 30 HFpEF patients, and 43 controls were enrolled. Neutrophil mNEP was measured by flow-cytometry. NEP activity in plasma and blood cells was determined for a subset of HFrEF patients using mass-spectrometry. Heart failure (HF) was characterized by reduced neutrophil mNEP compared to controls (p < 0.01). NEP activity on peripheral blood cells was almost 4-fold higher compared to plasma NEP activity (p = 0.031) and correlated with neutrophil mNEP (p = 0.006). Lower neutrophil mNEP was associated with increasing disease severity and markers of adverse remodeling. Higher neutrophil mNEP was associated with reduced risk for mortality, total cardiovascular hospitalizations, and the composite endpoint of both (p < 0.01 for all). This is the first report describing a significant role of neutrophil mNEP in HFrEF. The biological relevance of neutrophil mNEP and exact effects of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ARNi) at the neutrophil site have to be determined. However, the results may suggest early initiation of ARNi already in less severe HF disease, where effects of NEP inhibition may be more pronounced.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Cell Biology
In Nature Communications on 17 September 2021 by Heydt, Q., Xintaropoulou, C., et al.
The specific niche adaptations that facilitate primary disease and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALL) survival after induction chemotherapy remain unclear. Here, we show that Bone Marrow (BM) adipocytes dynamically evolve during ALL pathogenesis and therapy, transitioning from cellular depletion in the primary leukaemia niche to a fully reconstituted state upon remission induction. Functionally, adipocyte niches elicit a fate switch in ALL cells towards slow-proliferation and cellular quiescence, highlighting the critical contribution of the adipocyte dynamic to disease establishment and chemotherapy resistance. Mechanistically, adipocyte niche interaction targets posttranscriptional networks and suppresses protein biosynthesis in ALL cells. Treatment with general control nonderepressible 2 inhibitor (GCN2ib) alleviates adipocyte-mediated translational repression and rescues ALL cell quiescence thereby significantly reducing the cytoprotective effect of adipocytes against chemotherapy and other extrinsic stressors. These data establish how adipocyte driven restrictions of the ALL proteome benefit ALL tumours, preventing their elimination, and suggest ways to manipulate adipocyte-mediated ALL resistance.
© 2021. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
In PLoS One on 2 October 2014 by Martinez-Torres, F., Nochi, T., et al.
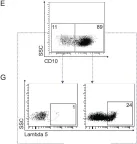
Fig.3.E

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1