Adoptive cell therapy (ACT) has shown promising results in cancer treatment, however, achieving effective ex vivo expansion of potent, functionally active, and cytotoxic T cells remains challenging. To overcome this, we loaded the engineered cytokine Neoleukin-2/15 (Neo2/15) on our recently established artificial antigen-presenting scaffolds (Ag-scaffolds) to expand antigen-specific T cells. Neo2/15 selectively binds to IL-2Rβ/γ receptors, enhancing CD8 + T cell proliferation while limiting regulatory T cell expansion. Our study assessed the efficacy of Neo2/15-loaded Ag-scaffolds (Ag-Neo2/15 scaffolds) in expanding antigen-specific T cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of healthy donors. We optimized Ag-scaffold configurations by varying the number of Neo2/15 molecules loaded on Ag-scaffolds and evaluated their impact on T-cell expansion and functionality. We showed that Ag-Neo2/15 scaffolds promoted significant T-cell expansion, with a comparable frequency of antigen-specific CD8 + T cells compared to IL-2/IL-21-loaded Ag-scaffolds (Ag-IL2/21 scaffolds). The CD8 + T cells expanded with Ag-Neo2/15 scaffolds exhibited potent TNFα and IFNγ production and expressed high levels of α4β7 integrin, a homing molecule which is important for directing T cells to specific tissues, potentially enhancing their therapeutic potential. T cells expanded with Ag-Neo2/15 scaffolds had superior and durable cytotoxicity against tumor target cells compared to T cells expanded with Ag-IL2/21 scaffolds. These findings were further supported by our single-cell analysis revealing that T cells expanded with Ag-Neo2/15 scaffolds had higher cytotoxic scores and lower dysfunctionality scores compared to T cells expanded with Ag-IL2/21 scaffolds. The single-cell analysis also indicated increased expression of genes linked to cell division and enhanced proliferative capacity in Ag-Neo2/15 expanded T cells. Furthermore, TCR clonality analysis demonstrated that Ag-Neo2/15 scaffolds promoted the expansion of functionally superior T-cell clones. The top clones of CD8 + T cells expanded with Ag-Neo2/15 scaffolds exhibited a favorable phenotype, essential for effective antigen recognition and sustained T-cell mediated cytotoxicity. Our findings suggest that Ag-Neo2/15 scaffolds represent an advancement in ACT by producing high-quality, functional antigen-specific T cells. This method has the potential to improve clinical outcomes in cancer therapy by generating large numbers of highly functional T cells, thereby optimizing the balance between cytotoxicity and proliferation capacity with less exhausted T-cells in expansion protocols.
Product Citations: 59
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 20 April 2025 by Ormhøj, M., Munk, K. K., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Temperature-based MHC class-I multimer peptide exchange for human HLA-A, B and C
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 23 December 2024 by Pothast, C. R., Derksen, I., et al.
T cell recognition of specific antigens presented by major histocompatibility complexes class-I (MHC-I) can play an important role during immune responses against pathogens and cancer cells. Detection of T cell immunity is based on assessing the presence of antigen-specific cytotoxic CD8+ T cells using MHC class-I (MHC-I) multimer technology. Previously we have designed conditional peptides for HLA-A*02:01, H-2K b and HLA-E that form stable peptide-MHC-I-complexes at low temperatures and dissociate when exposed to a defined elevated temperature. The resulting conditional MHC-I complex can easily and without additional handling be exchanged with a peptide of interest, allowing to exchange peptides in a ready-to-use multimer and a high-throughput manner. Here we present data that this peptide-exchange technology is a general applicable, ready-to-use and fast approach to load many different peptides in MHC-I multimers for alleles of the HLA-A, HLA-B and HLA-C loci. We describe the development of conditional peptides for HLA-A*03:01, HLA-A*11:01, HLA-B*07:02 and HLA-C*07:02 that only form stable peptide-MHC-I complexes at low temperatures, allowing peptide exchange at higher defined temperature. We document the ease and flexibility of this technology by monitoring CD8+ T cell responses to virus-specific peptide-MHC complexes in patients. Graphical abstract Highlights T cell immunity relies on antigen-specific CD8+ T cells recognizing peptide MHC-I complexes. Establishing temperature-based peptide exchange across multiple HLA alleles, resulting in a robust, easy, and fast system to generate peptide MHC-I complexes. Temperature-based MHC class-I multimer demonstrate applicability across major MHC-I gene families for monitoring CD8+ T cell responses. Easy high-throughput peptide exchange potential, enhancing clinical utility of MHC multimer technology.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer on 9 December 2024 by Fuchs, K. J., Göransson, M., et al.
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation (alloSCT) provides a curative treatment option for hematological malignancies. After HLA-matched alloSCT, donor-derived T cells recognize minor histocompatibility antigens (MiHAs), which are polymorphic peptides presented by HLA on patient cells. MiHAs are absent on donor cells due to genetic differences between patient and donor. T cells targeting broadly expressed MiHAs induce graft-versus-leukemia (GvL) reactivity as well as graft-versus-host disease (GvHD), while T cells for MiHAs with restricted or preferential expression on hematopoietic or non-hematopoietic cells may skew responses toward GvL or GvHD, respectively. Besides tissue expression, overall strength of GvL and GvHD is also determined by T-cell frequencies against MiHAs.Here, we explored the use of DNA barcode-labeled peptide-MHC multimers to detect and monitor antigen-specific T cells for the recently expanded repertoire of HLA-I-restricted MiHAs. In 16 patients who experienced an immune response after donor lymphocyte infusion, variable T-cell frequencies up to 30.5% of CD8+ T cells were measured for 49 MiHAs. High T-cell frequencies above 1% were measured in 12 patients for 19 MiHAs, with the majority directed against mismatched MiHAs, typically 6-8 weeks after donor lymphocyte infusion and at the onset of GvHD. The 12 patients included 9 of 10 patients with severe GvHD, 2 of 3 patients with limited GvHD and 1 of 3 patients without GvHD.In conclusion, we demonstrated that barcoded peptide-MHC multimers reliably detect and allow monitoring for MiHA-specific T cells during treatment to investigate the kinetics of immune responses and their impact on development of GvL and GvHD after HLA-matched alloSCT.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology on 15 July 2024 by Cao, Y., Li, P. P., et al.
In the quest to manage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the focus has shifted to a more holistic approach encompassing both data analytics and innovative treatments. Analyzing rich data resources, such as the cancer genome atlas (TCGA), and examining progressive therapies can potentially reshape the trajectory of HCC treatment.
To elucidate the immunological genes and the underlying mechanism of the combined Kombo knife and sorafenib regimen for HCC by analyzing data from TCGA and machine learning data.
Immune attributes were evaluated via TCGA's postablation HCC RNA sequencing data. Using weighted gene coexpression network analysis and machine learning, we identified genes with high prognostic value. The therapeutic landscape and safety metrics of the integrated treatment were critically evaluated across cellular and animal models.
Immune genes-specifically, peptidylprolyl isomerase A and solute carrier family 29 member 3-emerged as significant prognostic markers. Enhanced therapeutic outcomes, such as prolonged progression-free survival and an elevated overall response rate, characterize the combined approach, with peripheral blood mononuclear cells displaying potent effects on HCC dynamics.
The combination of Kombo knife with sorafenib is an innovative HCC treatment modality anchored in immune-centric strategies.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research : CR on 20 March 2024 by Cavalluzzo, B., Viuff, M. C., et al.
We have recently shown extensive sequence and conformational homology between tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) and antigens derived from microorganisms (MoAs). The present study aimed to assess the breadth of T-cell recognition specific to MoAs and the corresponding TAAs in healthy subjects (HS) and patients with cancer (CP).
A library of > 100 peptide-MHC (pMHC) combinations was used to generate DNA-barcode labelled multimers. Homologous peptides were selected from the Cancer Antigenic Peptide Database, as well as Bacteroidetes/Firmicutes-derived peptides. They were incubated with CD8 + T cells from the peripheral blood of HLA-A*02:01 healthy individuals (n = 10) and cancer patients (n = 16). T cell recognition was identified using tetramer-staining analysis. Cytotoxicity assay was performed using as target cells TAP-deficient T2 cells loaded with MoA or the paired TuA.
A total of 66 unique pMHC recognized by CD8+ T cells across all groups were identified. Of these, 21 epitopes from microbiota were identified as novel immunological targets. Reactivity against selected TAAs was observed for both HS and CP. pMHC tetramer staining confirmed CD8+ T cell populations cross-reacting with CTA SSX2 and paired microbiota epitopes. Moreover, PBMCs activated with the MoA where shown to release IFNγ as well as to exert cytotoxic activity against cells presenting the paired TuA.
Several predicted microbiota-derived MoAs are recognized by T cells in HS and CP. Reactivity against TAAs was observed also in HS, primed by the homologous bacterial antigens. CD8+ T cells cross-reacting with MAGE-A1 and paired microbiota epitopes were identified in three subjects. Therefore, the microbiota can elicit an extensive repertoire of natural memory T cells to TAAs, possibly able to control tumor growth ("natural anti-cancer vaccination"). In addition, non-self MoAs can be included in preventive/therapeutic off-the-shelf cancer vaccines with more potent anti-tumor efficacy than those based on TAAs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
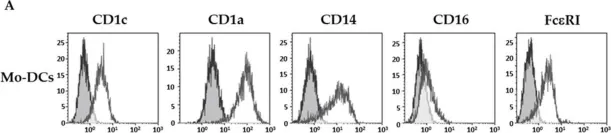
In Cells on 2 July 2021 by Coutant, F., Pin, J. J., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1