The efficacy of immunotherapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains limited. The tumor microenvironment (TME), characterized by the accumulation of suppressive myeloid cells including neutrophils, attributes to immunotherapy resistance in PDAC. IgA monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) can activate neutrophils to kill tumor cells; this can be further enhanced by blocking the myeloid immune checkpoint CD47. In this study, we investigated the potential of this therapeutic strategy for PDAC. We determined the expression of tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) on PDAC cell lines and fresh patient samples, and the results showed that the TAAs epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), trophoblast cell surface antigen 2 (TROP2) and mucin-1 (MUC1), as well as CD47 were consistently expressed on PDAC. In line with this, we showed that IgA mAbs against EpCAM can activate neutrophils to lyse various PDAC cell lines and tumor cells, which can be augmented by addition of CD47 blockade. In addition, we observed that neutrophils were present in patient tumors and expressed the receptor for IgA. In conclusion, our results indicate that a combination of IgA mAb with CD47 blockade is a promising preclinical treatment strategy for PDAC, which merits further investigation.
Product Citations: 32
The Efficacy of Targeted Monoclonal IgA Antibodies Against Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.
In Cells on 24 April 2025 by Raymakers, L., Passchier, E. M., et al.
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
In Scientific Reports on 23 April 2025 by Bodiou, V., Cristini, N., et al.
The use of microcarriers (MCs) is currently the most promising method for scaling up bovine satellite cell (bSC) cultures for cultivated meat production. Thanks to the inherent ability of the cells to migrate from one MC to another, also known as bead-to-bead transfer, the need for cell detachment is limited to a minimum, leading to a seamless seeding train. With this study, we aim to intensify the bioprocessing of bSCs in serum-free medium, by exploring the parameters influencing bead-to-bead transfer and cell growth and by optimising the seeding conditions and the MC addition strategy. Keeping production scale bioprocessing requirements into consideration, such as maximisation of fold increase within the same system, we have grown bSCs in up to 80 cm2/ml MC concentrations, using seeding cell densities of 1,000 to 4,750 cells/cm2. We also demonstrated optimisation of the MC addition strategy by determining an optimal confluence range (15,000 to 25,000 cells/cm2) for MC additions and by maximising the MC expansion ratio to 10, without impairing growth. Finally, to ensure scalability of these findings, we successfully applied them at a 3 L bioreactor scale.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Bos taurus (Bovine)
Drone pupae extract enhances Hanwoo myosatellite cell function for cultivated meat production.
In Journal of Animal Science and Technology on 1 January 2025 by Choi, N., Park, S., et al.
In this study, we analyzed effects of drone pupae aqueous extract powder (DEP) on proliferation and differentiation of Hanwoo myosatellite cells (HSC). Results of amino acid, vitamin, and mineral analysis of drone pupae revealed the presence of branched-chain amino acids, Glu, essential amino acids, vitamins B6, C and Mg, K, and so on. Additionally, drone pupae were shown to have an antioxidant ability. HSC were cultured for proliferation by adding 0, 10, 100, 200, and 400 μg/mL DEP to the medium. As a result of MTS analysis, DEP increased the proliferation capacity of HSC, with cell viability being significantly higher after treatment with DEP, especially when DEP was used at 100 μg/mL (p < 0.05). To measure the differentiation ability of HSC, 0 and 100 μg/mL DEP (CON, D100) were added to the medium, and cells were cultured. Myotube formation was confirmed through images using immunofluorescence staining. Fusion index and myotube area in the D100 were higher than those in the CON (p < 0.01). DEP promoted differentiation ability and myotube formation by increasing the expression of MYH2, MYOG, and DES genes and MYH2 and DES proteins in HSC. Additionally, in HSC differentiation culture, proteome expression intensity was higher in D100 than in CON. Proteins upregulated in the D100 group included Myosin, IL18, MYO1D, and so on. In conclusion, characteristics of various components present in DEP could improve the proliferation and differentiation ability of HSC. This suggests that drone pupae can be used as a functional substance to enhance muscle growth.
© Copyright 2025 Korean Society of Animal Science and Technology.
-
Veterinary Research
In Animals : An Open Access Journal From MDPI on 3 December 2024 by Han, J. H., Jang, S. W., et al.
Cultured meat produced using satellite cells has emerged to address issues such as overpopulation, the ethical conundrums associated with the breeding environment, and the methane gas emissions associated with factory farming. To date, however, the challenges of maintaining satellite cells in vitro and reducing the costs of the culture media are still substantial. Gelatin, collagen, and fibronectin are commonly used extracellular matrices (ECMs) that facilitate signal integration with the cells and promote cell adhesion. In this study, we compared the proliferation, cell cycle, immunocytochemistry, and expression levels of Pax7, Pax3, Myf5, MyoD1, and MyoG genes in bovine satellite cells (BSCs) cultured on gelatin-, collagen- and fibronectin-coated dishes as part of short- and long-term cultures. We observed that BSCs cultured on gelatin-coated dishes showed higher levels of Pax7 expression than BSCs cultured on collagen- and fibronectin-coated dishes in both short- and long-term cultures, indicating that BSCs cultured on gelatin effectively maintained the satellite cell population in both the short- and long-term cultures. Our study highlights that gelatin is an effective ECM for the maintenance of BSCs and the production of cultured meat.
-
FC/FACS
-
Bos taurus (Bovine)
-
Veterinary Research
In Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology on 18 November 2024 by Bodiou, V., Kumar, A. A., et al.
To bring cultivated beef to the market, a scalable system that can support growth of bovine satellite cells (bSCs) in a serum-free and preferably also animal-free medium is of utmost importance. The use of microcarriers (MCs) is, at the moment, one of the most promising technologies for scaling up. MCs offer a large surface to volume ratio, they can be used in scalable stirred tank bioreactors, where the culture conditions can be tightly controlled to meet the cells' requirements (temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen). The inherent capacity of the cells to migrate from one MC to another, also known as bead-to-bead transfer, facilitates a scale-up strategy involving MCs. Previous studies have shown growth of bSCs on three commercially available MCs in serum containing media. Unfortunately there is currently no information available regarding their growth on MCs in serum-free conditions.
In this study, we aimed to find suitable serum-free media, MCs and attachment promoting compounds (APCs) supporting the growth of bSCs. Initially, six commercial MCs and three serum-free media were evaluated. The effects of three APCs were compared (vitronectin, laminin and fibronectin). Subsequently, the effects of different concentrations and modes of addition of the best performing APC were investigated.
Our results showed that Cytodex 1, Synthemax II and CellBIND supported bSCs' growth in all serum-free media. Overall, better growth was observed with Cytodex 1 in serum-free proliferation media. We showed that the use of laminin or vitronectin with Cytodex 1 can significantly improve cell growth and purity. Laminin also allowed attachment and growth of bSCs on Plastic MCs which had been previously unsuccessful without APCs. Finally, we optimized the use of vitronectin from a sustainability and process perspective, and showed that it can be used solely as a coating for Cytodex 1 (16-100 ng/cm2) MCs, instead of as a medium supplement, enhancing cell attachment and proliferation.
Copyright © 2024 Bodiou, Kumar, Massarelli, van Haaften, Post and Moutsatsou.
-
Veterinary Research
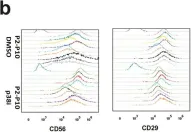
In Sci Rep on 17 July 2018 by Ding, S., Swennen, G. N. M., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Bos taurus (Bovine)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1