VEXAS (Vacuoles, E1 enzyme, X-linked, Autoinflammatory, Somatic) syndrome is caused by inactivating somatic mutations in the UBA1 gene. Here, we characterize the immunological landscape of VEXAS syndrome by performing multi-omics single-cell RNA analysis, cytokine multiplex assays, and in vitro functional assays on patients' peripheral blood. Our data reveals a broad immune system activation with upregulation of multiple inflammatory response pathways and proinflammatory cytokines. Unexpectedly, we find that monocytes have dysfunctional features irrespective of UBA1 mutation status, exhibiting impaired efferocytosis and blunted cytokine production in vitro. In contrast, UBA1-mutated NK cells show an upregulation of the inflammation pathways and enhanced cytotoxicity. Within the lymphocyte subsets, predominantly UBA1 wild-type, we identify clonal expansion of effector memory CD8+ T cells and skewed B cell differentiation with loss of transitional B cells and expansion of plasmablasts. Thus, our analysis indicates that VEXAS syndrome is characterized by profound alterations in both adaptive and innate immune systems, accounting for the complex pathophysiology of the disease, and provides a basis to understand the marked clinical heterogeneity and variable disease course.
© 2025. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Product Citations: 17
In Nature Communications on 20 May 2025 by Mizumaki, H., Gao, S., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Developmental Cell on 6 May 2024 by Fowler, J. L., Zheng, S. L., et al.
The developmental origin of blood-forming hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) is a longstanding question. Here, our non-invasive genetic lineage tracing in mouse embryos pinpoints that artery endothelial cells generate HSCs. Arteries are transiently competent to generate HSCs for 2.5 days (∼E8.5-E11) but subsequently cease, delimiting a narrow time frame for HSC formation in vivo. Guided by the arterial origins of blood, we efficiently and rapidly differentiate human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) into posterior primitive streak, lateral mesoderm, artery endothelium, hemogenic endothelium, and >90% pure hematopoietic progenitors within 10 days. hPSC-derived hematopoietic progenitors generate T, B, NK, erythroid, and myeloid cells in vitro and, critically, express hallmark HSC transcription factors HLF and HOXA5-HOXA10, which were previously challenging to upregulate. We differentiated hPSCs into highly enriched HLF+ HOXA+ hematopoietic progenitors with near-stoichiometric efficiency by blocking formation of unwanted lineages at each differentiation step. hPSC-derived HLF+ HOXA+ hematopoietic progenitors could avail both basic research and cellular therapies.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 28 February 2024 by Araki, D., Hong, S., et al.
The transplantation of gene-modified autologous hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) offers a promising therapeutic approach for hematological and immunological disorders. However, this strategy is often limited by the toxicities associated with traditional conditioning regimens. Antibody-based conditioning strategies targeting cKIT and CD45 antigens have shown potential in mitigating these toxicities, but their long-term safety and efficacy in clinical settings require further validation. In this study, we investigate the thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor, cMPL, as a novel target for conditioning protocols. We demonstrate that high surface expression of cMPL is a hallmark feature of long-term repopulating hematopoietic stem cells (LT-HSCs) within the adult human CD34+ HSPC subset. Targeting the cMPL receptor facilitates the separation of human LT-HSCs from mature progenitors, a delineation not achievable with cKIT. Leveraging this finding, we developed a cMPL-targeting immunotoxin, demonstrating its ability to selectively deplete host cMPL high LT-HSCs with a favorable safety profile and rapid clearance within 24 hours post-infusion in rhesus macaques. These findings present significant potential to advance our understanding of human hematopoiesis and enhance the therapeutic outcomes of ex vivo autologous HSPC gene therapies. Abstract Figure Graphical abstract
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In JCI Insight on 22 August 2023 by Schuetz, A., Corley, M. J., et al.
Transgender women (TGW) are disproportionally affected by HIV infection, with a global estimated prevalence of 19.9%, often attributed to behavioral risk factors, with less known about biological factors. We evaluated potential biological risk factors for HIV acquisition in TGW at the sites of viral entry by assessing immune parameters of the neovaginal surface and gut mucosa. The neovagina in TGW, compared with the vagina in cisgender women (CW), shows distinct cell composition and may pose a more inflammatory environment, evidenced by increased CD4+ T cell activation and higher levels of soluble markers of inflammation (C-reactive protein, soluble CD30). Increased inflammation may be driven by microbiome composition, as shown by a greater abundance of Prevotella and a higher Shannon Diversity Index. In addition, we have observed higher frequency of CD4+CCR5+ target cells and decreased DNA methylation of the CCR5 gene in the gut mucosa of TGW compared with CW and men who have sex with men, which was inversely correlated with testosterone levels. The rectal microbiome composition in TGW appears to favor a proinflammatory milieu as well as mucosal barrier disruption. Thus, it is possible that increased inflammation and higher frequencies of CCR5-expressing target cells at sites of mucosal viral entry may contribute to increased risk of HIV acquisition in TGW, with further validation in larger studies warranted.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Human T cells efficiently control RSV infection.
In JCI Insight on 8 June 2023 by De, C., Pickles, R. J., et al.
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection causes significant morbidity and mortality in infants, immunocompromised individuals, and older individuals. There is an urgent need for effective antivirals and vaccines for high-risk individuals. We used 2 complementary in vivo models to analyze RSV-associated human lung pathology and human immune correlates of protection. RSV infection resulted in widespread human lung epithelial damage, a proinflammatory innate immune response, and elicited a natural adaptive human immune response that conferred protective immunity. We demonstrated a key role for human T cells in controlling RSV infection. Specifically, primed human CD8+ T cells or CD4+ T cells effectively and independently control RSV replication in human lung tissue in the absence of an RSV-specific antibody response. These preclinical data support the development of RSV vaccines, which also elicit effective T cell responses to improve RSV vaccine efficacy.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In PLoS One on 27 January 2019 by Varkey, R., Du, Q., et al.
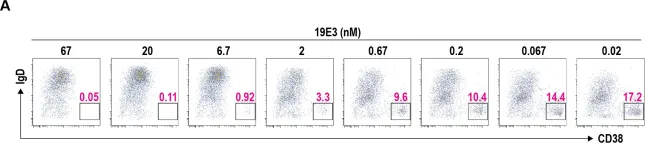
Fig.5.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
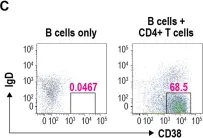
In PLoS One on 27 January 2019 by Varkey, R., Du, Q., et al.
Fig.5.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
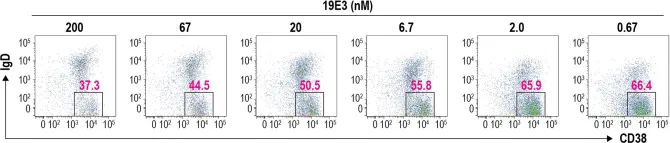
In PLoS One on 27 January 2019 by Varkey, R., Du, Q., et al.
Fig.5.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
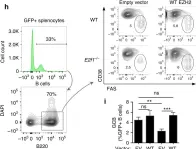
In Nat Commun on 12 October 2017 by Béguelin, W., Rivas, M. A., et al.
Fig.7.H

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4