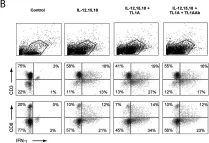
This study explored the combination of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) IL2 variant (FAP-IL2v), a novel immune-cytokine, with pembrolizumab in patients with advanced and/or metastatic melanoma.
This open-label, multicenter, phase Ib clinical study (NCT03875079) evaluated the safety, tolerability, pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and antitumor activity of FAP-IL2v (simlukafusp alfa, RO6874281) in combination with pembrolizumab. Patients with advanced and/or metastatic melanoma were either checkpoint inhibitor (CPI)-naïve or CPI-experienced. Patients received 10 mg FAP-IL2v either continuously once every 3 weeks (Q3W) or in an induction/maintenance setting consisting of a 3-week induction phase with weekly (QW) dosing followed by continuous Q3W dosing. Pembrolizumab was dosed Q3W at 200 mg.
Eighty-three patients were treated: 16 patients in two safety run-in cohorts and 67 patients in two extension cohorts; 75 (90.4%) patients were CPI-experienced. The pharmacokinetics of FAP-IL2v in combination with pembrolizumab was similar to that after administration as monotherapy. Consistent with the proposed mode of action, FAP-IL2v preferentially expanded NK and CD8 T cells. The most common FAP-IL2v-related grade 3/4 adverse events were lymphopenia (23%), elevated γ-glutamyltransferase (8%), elevated alanine aminotransferase (6%), and infusion-related reaction (6%). A response was observed in 5 of 75 (6.7%) CPI-experienced patients (all partial responses) and 2 of 8 CPI-naïve patients (one complete response and one partial response). The median progression-free survival was 3.1 months.
The safety profile of FAP-IL2v in combination with pembrolizumab was manageable and consistent with the known safety profile. However, further exploration of FAP-IL2v and pembrolizumab was precluded in patients with melanoma with prior CPI due to the lack of clinical activity.
In this phase Ib study, the combination of FAP-IL2v, an immune-cytokine developed to overcome the limitations of wild-type IL2, with the CPI pembrolizumab did not show meaningful antitumor activity in patients who had progressed on prior CPI therapy, suggesting that FAP-IL2v alone cannot overcome CPI resistance or unresponsiveness.
©2025 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Product Citations: 48
In Cancer Res Commun on 1 February 2025 by Muñoz-Couselo, E., Rivas, A. S., et al.
-
Cancer Research
In Cancer Res Commun on 1 December 2024 by Tasis, A., Papaioannou, N. E., et al.
CD8+ T cells are crucial for antitumor immunity. However, their functionality is often altered in higher-risk myelodysplastic neoplasms (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). To understand their role in disease progression, we conducted a comprehensive immunophenotypic analysis of 104 pretreatment bone marrow (BM) samples using mass and flow cytometry. Our findings revealed an increased frequency of CD57+CXCR3+ subset of CD8+ T cells in patients who did not respond to azacitidine (AZA) therapy. Furthermore, an increased baseline frequency (>29%) of the CD57+CXCR3+CD8+ T-cell subset was correlated with poor overall survival. We performed single-cell RNA sequencing to assess the transcriptional profile of BM CD8+ T cells from treatment-naïve patients. The response to AZA was linked to an enrichment of IFN-mediated pathways, whereas nonresponders exhibited a heightened TGF-β signaling signature. These findings suggest that combining AZA with TGF-β signaling inhibitors targeting CD8+ T cells could be a promising therapeutic strategy for patients with higher-risk MDS and AML.
Immunophenotypic analysis identified a BM CD57+CXCR3+ subset of CD8+ T cells associated with response to AZA in patients with MDS and AML. Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis revealed that IFN signaling is linked to the response to treatment, whereas TGF-β signaling is associated with treatment failure, providing insights into new therapeutic approaches.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 23 November 2024 by Zornikova, K., Dianov, D. V., et al.
CD8+ T-cell immunity, mediated through interactions between human leukocyte antigen (HLA) and the T-cell receptor (TCR), plays a pivotal role in conferring immune memory and protection against viral infections. The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants presents a significant challenge to the existing population immunity. While numerous SARS-CoV-2 mutations have been associated with immune evasion from CD8+ T cells, the molecular effects of most mutations on epitope-specific TCR recognition remain largely unexplored, particularly for epitope-specific repertoires characterized by common TCRs. In this study, we investigated an HLA-A*24-restricted NYN epitope (Spike448-456) that elicits broad and highly homologous CD8+ T cell responses in COVID-19 patients. Eleven naturally occurring mutations in the NYN epitope, all of which retained cell surface presentation by HLA, were tested against four transgenic Jurkat reporter cell lines. Our findings demonstrate that, with the exception of L452R and the combined mutation L452Q + Y453F, these mutations have minimal impact on the avidity of recognition by NYN peptide-specific TCRs. Additionally, we observed that a similar TCR responded differently to mutant epitopes and demonstrated cross-reactivity to the unrelated VYF epitope (ORF3a112-120). The results contradict the idea that immune responses with limited receptor diversity are insufficient to provide protection against emerging variants.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Clonal structure and the specificity of vaccine-induced T cell response to SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein.
In Frontiers in Immunology on 17 April 2024 by Sheetikov, S. A., Khmelevskaya, A. A., et al.
Adenovirus vaccines, particularly the COVID-19 Ad5-nCoV adenovirus vaccine, have emerged as promising tools in the fight against infectious diseases. In this study, we investigated the structure of the T cell response to the Spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus used in the COVID-19 Ad5-nCoV adenoviral vaccine in a phase 3 clinical trial (NCT04540419). In 69 participants, we collected peripheral blood samples at four time points after vaccination or placebo injection. Sequencing of T cell receptor repertoires from Spike-stimulated T cell cultures at day 14 from 17 vaccinated revealed a more diverse CD4+ T cell repertoire compared to CD8+. Nevertheless, CD8+ clonotypes accounted for more than half of the Spike-specific repertoire. Our longitudinal analysis showed a peak T cell response at day 14, followed by a decline until month 6. Remarkably, multiple T cell clonotypes persisted for at least 6 months after vaccination, as demonstrated by ex vivo stimulation. Examination of CDR3 regions revealed homologous sequences in both CD4+ and CD8+ clonotypes, with major CD8+ clonotypes sharing high similarity with annotated sequences specific for the NYNYLYRLF peptide, suggesting potential immunodominance. In conclusion, our study demonstrates the immunogenicity of the Ad5-nCoV adenoviral vaccine and highlights its ability to induce robust and durable T cell responses. These findings provide valuable insight into the efficacy of the vaccine against COVID-19 and provide critical information for ongoing efforts to control infectious diseases.
Copyright © 2024 Sheetikov, Khmelevskaya, Zornikova, Zvyagin, Shomuradova, Serdyuk, Shakirova, Peshkova, Titov, Romaniuk, Shagina, Chudakov, Kiryukhin, Shcherbakova, Khamaganova, Dzutseva, Afanasiev, Bogolyubova and Efimov.
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 1 March 2024 by Cottignies-Calamarte, A., Marteau, F., et al.
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) plays a central role in regulating cell energy balance. When activated, AMPK supresses energy-consuming pathways such as lipid and protein synthesis while increasing nutrient availability through the activation of autophagy. These pathways downstream AMPK activation contribute to SARS-CoV-2 infection, which hijacks autophagy and accumulates lipid droplets in viral factories to support viral replication. Here, we assessed the antiviral activity of the direct pan-AMPK allosteric activator MK-8722 in vitro. MK-8722 efficiently inhibited infection of Alpha and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variants in Vero76 and human bronchial epithelial Calu-3 cells at micromolar concentration. This inhibition relied on restoring the autophagic flux, which redirected newly synthesized viral proteins for degradation, and on a reduction in lipid metabolism, which affected the viral factories. Furthermore, MK-8722 treatment increased the type I interferon (IFN-I) response. Post-infection treatment with MK-8722 was enough to inhibit efficiently viral replication and restore the IFN-I response. Finally, MK-8722 treatment did not alter the SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8 + T cell response mounted upon Spike vaccination. Overall, by activating AMPK, MK-8722 acts as an effective antiviral against SARS-CoV-2 infection, even when applied post-exposure, paving the way for preclinical tests aimed at inhibiting viral replication and improving patients’ symptoms.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In PLoS One on 15 January 2014 by Reichwald, K., Jørgensen, T. Z., et al.
Fig.8.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In PLoS One on 15 January 2014 by Reichwald, K., Jørgensen, T. Z., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In PLoS One on 15 January 2014 by Reichwald, K., Jørgensen, T. Z., et al.
Fig.9.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3