Proteasome inhibitors (PIs) bortezomib, carfilzomib and ixazomib are approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma and have clinical activity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The predominant form of proteasome in these hematologic malignancies is the lymphoid tissue-specific immunoproteasome. FDA-approved PIs inhibit immunoproteasomes and ubiquitously expressed constitutive proteasomes causing on-target toxicities in non-hematological tissues. Replacing PIs with selective immunoproteasome inhibitors (IPIs) should reduce these toxicities. We have previously shown that IPI ONX-0914 causes apoptosis of ALL cells expressing the KMT2A::AFF1 (MLL-AF4) fusion protein but did not elucidate the mechanism. Here we show that a novel, highly specific IPI M3258 induces rapid apoptosis in ALL cells in vitro and is comparable to bortezomib in its ability to reduce tumor growth and to cause tumor regression when combined with chemotherapy in vivo. Treatment of KMT2A::AFF1 ALL cells with M3258, ONX-0914, and bortezomib induced proteotoxic stress that was prevented by the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide, which dramatically desensitized cells to PI-induced apoptosis. Thus, similar to multiple myeloma, ALL cells are sensitive to PIs and IPIs due to increased proteotoxic stress caused by elevated rates of protein synthesis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 49
In Scientific Reports on 19 May 2025 by Jenkins, T. W., Fitzgerald, J. E., et al.
-
Cancer Research
Simple Isolation of Human Bone Marrow Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells.
In Current Protocols on 1 January 2025 by Tonyalı, G., Kılıc, E., et al.
Bone marrow adipose tissue (BMAT) has garnered significant attention due to its critical roles in leukemia pathogenesis, cancer metastasis, and bone marrow failure. BMAT is a metabolically active, distinct tissue that differs from other fat depots. Marrow adipocytes, closely interacting with hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells and osteoblasts, play a pivotal role in regulating their functions. However, standardized methods for isolating and defining human BMAT (hBMAT) remain unclear. In animal models, BMAT is commonly isolated directly from the bone marrow through flushing, enzymatic digestion, or mechanical disruption. In humans, BMAT isolation often involves the adipogenic induction of bone marrow mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (BM-MSCs) derived from bone marrow aspirates. However, this approach reflects cellular responses to chemical stimuli and may not accurately represent in vivo differentiation potential. Similarly, BMAT obtained from hip or knee replacement surgeries might not reflect basal physiological conditions due to inflammatory influences. Here, we describe a direct method for culturing BMAT from the fatty layer of bone marrow aspirates obtained from healthy transplant donors. This protocol employs centrifugation and washing steps using basic laboratory equipment, offering simple and non-enzymatic approach. For validation, isolated cells are characterized according to the International Society for Cell & Gene Therapy (ISCT) criteria. © 2025 Wiley Periodicals LLC. Basic Protocol 1: Isolation of human BMAT-MSCs from the fatty layer of the bone marrow Basic Protocol 2: Culture expansion, trypsinization, and cryopreservation of BMAT-MSCs Support Protocol 1: Immunophenoypic characterization of human BMAT-MSCs by flow cytometry Support Protocol 2: In vitro characterization of multilineage differentiation potential of human BMAT-MSCs Support Protocol 3: Further characterization of gene expression in human BMAT-MSCs using qRT-PCR.
© 2025 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Isolation of Human Bone Marrow Non-hematopoietic Cells for Single-cell RNA Sequencing.
In Bio-protocol on 20 June 2024 by Li, H., Bräunig, S., et al.
The intricate composition, heterogeneity, and hierarchical organization of the human bone marrow hematopoietic microenvironment (HME) present challenges for experimentation, which is primarily due to the scarcity of HME-forming cells, notably bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs). The limited understanding of non-hematopoietic cell phenotypes complicates the unraveling of the HME's intricacies and necessitates a precise isolation protocol for systematic studies. The protocol presented herein puts special emphasis on the accuracy and high quality of BMSCs obtained for downstream sequencing analysis. Utilizing CD45 and CD235a as negative markers ensures sufficient enrichment of non-hematopoietic cells within the HME. By adding positive selection based on CD271 expression, this protocol allows for selectively isolating the rare and pivotal bona fide stromal cell population with high precision. The outlined step-by-step protocol provides a robust tool for isolating and characterizing non-hematopoietic cells, including stromal cells, from human bone marrow preparations. This approach thus contributes valuable information to promote research in a field that is marked by a scarcity of studies and helps to conduct important experimentation that will deepen our understanding of the intricate cellular interactions within the bone marrow niche. Key features • Isolation of high-quality human non-hematopoietic bone marrow cells for scRNAseq • Targeted strategy for enriching low-frequency stromal cells.
©Copyright : © 2024 The Authors; This is an open access article under the CC BY license.
-
Genetics
In Cell Journal on 1 August 2023 by Torabi, S., Zarrabi, M., et al.
Macrophages are multifunctional immune cells widely used in immunological research. While autologous macrophages have been widely used in several biomedical applications, allogeneic macrophages have also demonstrated similar or even superior therapeutic potential. The umbilical cord blood (UCB) is a well-described source of abundant allogenic monocytes and macrophages that is easy to collect and can be processed without invasive methods. Current monocyte isolation procedures frequently result in heterogenous cell products, with limited yields, activated cells, and high cost. This study outlines a simple isolation method that results in high yields and pure monocytes with the potential to differentiate into functional macrophages.
In the experimental study, we describe a simple and efficient protocol to isolate highpurity monocytes. After collection of human UCB samples, we used a gradient-based procedure composed of three consecutive gradient steps: i. Hydroxyethyl starch-based erythrocytes sedimentation, followed by ii. Mononuclear cells (MNCs) isolation by Ficoll-Hypaque gradient, and iii. Separation of monocytes from lymphocytes by a slight hyperosmolar Percoll gradient (0.573 g/ml). Then the differentiation potential of isolated monocytes to pro- and antiinflammatory macrophages were evaluated in the presence of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and macrophage CSF (M-CSF), respectively. The macrophages were functionally characterized as well.
A high yield of monocytes after isolation (25 to 50 million) with a high purity (>95%) could be obtained from every 100-150 ml UCB. Isolated monocytes were defined based on their phenotype and surface markers expression pattern. Moreover, they possess the ability to differentiate into pro- or anti-inflammatory macrophages with specific phenotypes, gene/surface protein markers, cytokine secretion patterns, T-cell interactions, and phagocytosis activity.
Here we describe a simple and reproducible procedure for isolation of pure monocytes from UCB, which could be utilized to provide functional macrophages as a reliable and feasible source of allogenic macrophages for biomedical research.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cardiovascular biology
In Journal of Extracellular Biology on 1 December 2022 by Lau, H. C., Han, D. W., et al.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) released by a variety of cell types have been shown to act as a natural delivery system for bioactive molecules such as RNAs and proteins. EV therapy holds great promise as a safe and cell-free therapy for many immunological and degenerative diseases. However, translation to clinical application is limited by several factors, including insufficient large-scale manufacturing technologies and low yield. We have developed a novel drug delivery platform technology, BioDrone™, based on cell-derived vesicles (CDVs) produced from diverse cell sources by using a proprietary extrusion process. This extrusion technology generates nanosized vesicles in far greater numbers than naturally obtained EVs. We demonstrate that the CDVs are surrounded by a lipid bilayer membrane with a correct membrane topology. Physical, biochemical and functional characterisation results demonstrate the potential of CDVs to act as effective therapeutics. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (UCMSC)-derived CDVs exhibit a biological activity that is similar to UCMSCs or UCMSC-derived EVs. Lastly, we present the establishment of a GMP-compliant process to allow the production of a large number of UCMSC-CDVs in a reproducible manner. GMP-compliant manufacturing of CDVs will facilitate the preclinical and clinical evaluation of these emerging therapeutics in anti-inflammatory or regenerative medicine. This study also represents a crucial step in the development of this novel drug delivery platform based on CDVs.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Extracellular Biology published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
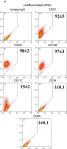
In PLoS One on 31 July 2012 by Ferro, F., Spelat, R., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
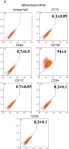
In PLoS One on 31 July 2012 by Ferro, F., Spelat, R., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2