h4>Summary/h4> Effective T cell responses against target cells require controlled production of the key pro-inflammatory cytokines IFN-γ, TNF and IL-2. Post-transcriptional events determine the magnitude and duration of cytokine production in T cells, a process that is largely regulated by RNA binding proteins (RBPs). Here we studied the identity and mode of action of RBPs interacting with cytokine mRNAs. With an RNA aptamer-based capture assay from human T cell lysates, we identified >130 RBPs interacting with the full length 3’untranslated regions of IFNG , TNF and IL2. The RBP landscape altered upon T cell activation. Furthermore, RBPs display temporal activity profiles to control cytokine production. Whereas HuR promotes early cytokine production, the peak production levels and response duration is controlled by ZFP36L1, ATXN2L and ZC3HAV1. Importantly, ZFP36L1 deletion boosts T cell responses against tumors in vivo, revealing the potential of the RBP map to identify critical modulators of T cell responses.
Product Citations: 123
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 3 November 2021 by Popovic, B., Guislain, A., et al.
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Mucosal Immunology on 1 September 2021 by Joosse, M. E., Charbit-Henrion, F., et al.
Single genetic mutations predispose to very early onset inflammatory bowel disease (VEO-IBD). Here, we identify a de novo duplication of the 10p15.1 chromosomal region, including the IL2RA locus, in a 2-year-old girl with treatment-resistant pancolitis that was brought into remission by colectomy. Strikingly, after colectomy while the patient was in clinical remission and without medication, the peripheral blood CD4:CD8 ratio was constitutively high and CD25 expression was increased on circulating effector memory, Foxp3+, and Foxp3neg CD4+ T cells compared to healthy controls. This high CD25 expression increased IL-2 signaling, potentiating CD4+ T-cell-derived IFNγ secretion after T-cell receptor (TCR) stimulation. Restoring CD25 expression using the JAK1/3-inhibitor tofacitinib controlled TCR-induced IFNγ secretion in vitro. As diseased colonic tissue, but not the unaffected duodenum, contained mainly CD4+ T cells with a prominent IFNγ-signature, we hypothesize that local microbial stimulation may have initiated colonic disease. Overall, we identify that duplication of the IL2RA locus can associate with VEO-IBD and suggest that increased IL-2 signaling predisposes to colonic intestinal inflammation.
© 2021. The Author(s).
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In The Journal of Clinical Investigation on 15 July 2021 by Sattler, A., Schrezenmeier, E., et al.
Novel mRNA-based vaccines have been proven to be powerful tools in combating the global pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2, with BNT162b2 (trade name: Comirnaty) efficiently protecting individuals from COVID-19 across a broad age range. Still, it remains largely unknown how renal insufficiency and immunosuppressive medication affect development of vaccine-induced immunity. We therefore comprehensively analyzed humoral and cellular responses in kidney transplant recipients after the standard second vaccination dose. As opposed to all healthy vaccinees and the majority of hemodialysis patients, only 4 of 39 and 1 of 39 transplanted individuals showed IgA and IgG seroconversion at day 8 ± 1 after booster immunization, with minor changes until day 23 ± 5, respectively. Although most transplanted patients mounted spike-specific T helper cell responses, frequencies were significantly reduced compared with those in controls and dialysis patients and this was accompanied by a broad impairment in effector cytokine production, memory differentiation, and activation-related signatures. Spike-specific CD8+ T cell responses were less abundant than their CD4+ counterparts in healthy controls and hemodialysis patients and almost undetectable in transplant patients. Promotion of anti-HLA antibodies or acute rejection was not detected after vaccination. In summary, our data strongly suggest revised vaccination approaches in immunosuppressed patients, including individual immune monitoring for protection of this vulnerable group at risk of developing severe COVID-19.
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In European Journal of Immunology on 1 June 2021 by Spoerl, S., Kremer, A. N., et al.
COVID-19 is a life-threatening disease leading to bilateral pneumonia and respiratory failure. The underlying reasons why a smaller percentage of patients present with severe pulmonary symptoms whereas the majority is only mildly affected are to date not well understood. Comparing the immunological phenotype in healthy donors and patients with mild versus severe COVID-19 shows that in COVID-19 patients, NK-/B-cell activation and proliferation are enhanced independent of severity. As an important precondition for effective antibody responses, T-follicular helper cells and antibody secreting cells are increased both in patients with mild and severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. Beyond this, T cells in COVID-19 patients exhibit a stronger activation profile with differentiation toward effector cell phenotypes. Importantly, when looking at the rates of pulmonary complications in COVID-19 patients, the chemokine receptor CCR4 is higher expressed by both CD4 and CD8 T cells of patients with severe COVID-19. This raises the hypothesis that CCR4 upregulation on T cells in the pathogenesis of COVID-19 promotes stronger T-cell attraction to the lungs leading to increased immune activation with presumably higher pulmonary toxicity. Our study contributes significantly to the understanding of the immunological changes during COVID-19, as new therapeutic agents, preferentially targeting the immune system, are highly warranted.
© 2021 The Authors. European Journal of Immunology published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports on 25 May 2021 by Mold, J. E., Modolo, L., et al.
The CD8+ T cell response to an antigen is composed of many T cell clones with unique T cell receptors, together forming a heterogeneous repertoire of effector and memory cells. How individual T cell clones contribute to this heterogeneity throughout immune responses remains largely unknown. In this study, we longitudinally track human CD8+ T cell clones expanding in response to yellow fever virus (YFV) vaccination at the single-cell level. We observed a drop in clonal diversity in blood from the acute to memory phase, suggesting that clonal selection shapes the circulating memory repertoire. Clones in the memory phase display biased differentiation trajectories along a gradient from stem cell to terminally differentiated effector memory fates. In secondary responses, YFV- and influenza-specific CD8+ T cell clones are poised to recapitulate skewed differentiation trajectories. Collectively, we show that the sum of distinct clonal phenotypes results in the multifaceted human T cell response to acute viral infections.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
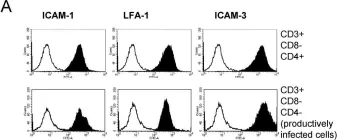
In Retrovirology on 31 March 2008 by Puigdomènech, I., Massanella, M., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Retrovirology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1