Antibodies against the spike protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) can drive adaptive evolution in immunocompromised patients with chronic infection. Here we longitudinally analyze SARS-CoV-2 sequences in a B cell-depleted, lymphoma patient with chronic, ultimately fatal infection, and identify three mutations in the spike protein that dampen convalescent plasma-mediated neutralization of SARS-CoV-2. Additionally, four mutations emerge in non-spike regions encoding three CD8 T cell epitopes, including one nucleoprotein epitope affected by two mutations. Recognition of each mutant peptide by CD8 T cells from convalescent donors is reduced compared to its ancestral peptide, with additive effects resulting from double mutations. Querying public SARS-CoV-2 sequences shows that these mutations have independently emerged as homoplasies in circulating lineages. Our data thus suggest that potential impacts of CD8 T cells on SARS-CoV-2 mutations, at least in those with humoral immunodeficiency, warrant further investigation to inform on vaccine design.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 114
In Nature Communications on 23 September 2022 by Khatamzas, E., Antwerpen, M. H., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology : the Official Journal of the Society On NeuroImmune Pharmacology on 1 June 2022 by Carlini, F., Ivaldi, F., et al.
Deoxycytidine kinase (dCK) and 5' deoxynucleotidase (NT5C2) are involved in metabolism of cladribine (2CdA), the immunomodulatory drug for multiple sclerosis; by mediating phosphorylation (activation) or phosphorolysis (deactivation) of 2CdA, respectively, these enzymes promote or prevent its accumulation in the cell, which leads to cell death. In particular, lymphocytes which present with a high intracellular dCK/NT5C2 ratio are more sensitive to 2CdA than other immune cells. We aim at determining if the expression of these enzymes and/or their activity differ in specific progenitor and mature immune cells and are influenced by cellular activation and/or exposure to 2CdA. Flow cytometry analysis showed no difference in dCK/NT5C2 ratio in progenitor and mature immune cells. 2CdA induced apoptosis in stimulated T and B cells and unstimulated B cells. dCK expression was enhanced by 2CdA at mRNA and protein levels in activated T cells and mRNA level in activated B cells. dCK activity, measured through an in-house luminescence release enzyme assay was higher in activated T and B cells, and such an increase was abrogated in activated B cells, but not T cells, upon exposure to 2CdA. These results reveal an important relationship between dCK activity and the effect of 2CdA on B and T cells, according to their activation status. Further study is warranted to evaluate whether dCK activity could, in the future, be a suitable predictive biomarker of lymphocyte response to 2CdA.
© 2021. The Author(s).
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Scientific Reports on 27 September 2021 by Valentin Hansen, S., Høy Hansen, M., et al.
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a malignancy arising from naive B lymphocytes with common bone marrow (BM) involvement. Although t(11;14) is a primary event in MCL development, the highly diverse molecular etiology and causal genomic events are still being explored. We investigated the transcriptome of CD19+ BM cells from eight MCL patients at single-cell level. The transcriptomes revealed marked heterogeneity across patients, while general homogeneity and clonal continuity was observed within the patients with no clear evidence of subclonal involvement. All patients were SOX11+CCND1+CD20+. Despite monotypic surface immunoglobulin (Ig) κ or λ protein expression in MCL, 10.9% of the SOX11 + malignant cells expressed both light chain transcripts. The early lymphocyte transcription factor SOX4 was expressed in a fraction of SOX11 + cells in two patients and co-expressed with the precursor lymphoblastic marker, FAT1, in a blastoid case, suggesting a potential prognostic role. Additionally, SOX4 was found to identify non-malignant SOX11- pro-/pre-B cell populations. Altogether, the observed expression of markers such as SOX4, CD27, IgA and IgG in the SOX11+ MCL cells, may suggest that the malignant cells are not fixed in the differentiation state of naïve mature B cells, but instead the patients carry B lymphocytes of different differentiation stages.
© 2021. The Author(s).
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Frontiers in Immunology on 11 September 2021 by Ferre, E. M. N., Schmitt, M. M., et al.
Patients with the monogenic immune dysregulatory syndrome autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (APECED), which is caused by loss-of-function mutations in the autoimmune regulator (AIRE) gene, uniformly carry neutralizing autoantibodies directed against type-I interferons (IFNs) and many develop autoimmune pneumonitis, both of which place them at high risk for life-threatening COVID-19 pneumonia. Bamlanivimab and etesevimab are monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that target the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and block entry of SARS-CoV-2 in host cells. The use of bamlanivimab and etesevimab early during infection was associated with reduced COVID-19-associated hospitalization and death in patients at high risk for progressing to severe disease, which led the US Food and Drug Administration to issue an emergency use authorization for their administration in non-hypoxemic, non-hospitalized high-risk patients. However, the safety and efficacy of these mAbs has not been evaluated in APECED patients. We enrolled two siblings with APECED on an IRB-approved protocol (NCT01386437) and admitted them prophylactically at the NIH Clinical Center for evaluation of mild-to-moderate COVID-19. We assessed the safety and clinical effects of early treatment with bamlanivimab and etesevimab. The administration of bamlanivimab and etesevimab was well tolerated and was associated with amelioration of COVID-19 symptoms and prevention of invasive ventilatory support, admission to the intensive care, and death in both patients without affecting the production of antibodies to the nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2. If given early in the course of COVID-19 infection, bamlanivimab and etesevimab may be beneficial in APECED and other high-risk patients with neutralizing autoantibodies directed against type-I IFNs.
Copyright © 2021 Ferré, Schmitt, Ochoa, Rosen, Shaw, Burbelo, Stoddard, Rampertaap, DiMaggio, Bergerson, Rosenzweig, Notarangelo, Holland and Lionakis.
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies on 9 April 2021 by Olwenyi, O. A., Asingura, B., et al.
In Sub-Saharan Africa, herbal therapy continues to be utilized for HIV-1 disease management. However, the therapeutic benefits of these substances remain ambiguous. To date, little is known about the effects of these plant extracts on chronic CD4 + T-cell activation and exhaustion which is partly driven by HIV-1 associated microbial translocation.
Effects of Azadirachta indica, Momordica foetida and Moringa oleifera ethanol: water mixtures on cell viability were evaluated using the Guava PCA system. Then, an in-vitro cell culture model was developed to mimic CD4+ T cell exposures to antigens following HIV-1 microbial translocation. In this, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) isolated from HIV negative (n = 13), viral load < 1000 copies per mL (n = 10) and viral load > 1000 copies per mL (n = 6) study participants from rural Uganda were treated with Staphylococcus enterotoxin B (SEB). Then, the candidate plant extract (A. indica) was added to test the potential to inhibit corresponding CD4+ T cell activation. Following BD Facs Canto II event acquisition, variations in %CD38, %CD69, Human Leukocyte Antigen -DR (HLA-DR), Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 3 (Tim-3), interferon gamma (IFN γ) and interleukin 2 (IL-2) CD4 + T cell expression were evaluated.
Following exposure to SEB, only A. indica demonstrated a concentration-dependent ability to downregulate the levels of CD4 + T cell activation. At the final concentration of 0.500 μg/mL of A. indica, a significant downregulation of CD4 + CD38 + HLA-DR+ expression was observed in HIV negative (p < 0.0001) and both HIV infected groups (P = 0.0313). This plant extract also significantly lowered SEB induced % CD4+ T cell HLADR, PD-1 and Tim-3 levels. PD-1 and CD69 markers were only significantly downmodulated in only the HIV negative ((p = 0.0001 and p = 0.0078 respectively) and viral load< 1000 copies per ml (p = 0.0078) groups.
A. indica exhibited the in-vitro immunomodulatory potential to inhibit the continuum of SEB induced CD4+ T-cell activation/ exhaustion without impacting general T-cell specific functions such as cytokine secretion. Additional studies are needed to confirm A. indica as a source of natural products for targeting persistent immune activation and inflammation during ART.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Front Immunol on 18 July 2017 by Tilly, G., Doan-Ngoc, T. M., et al.
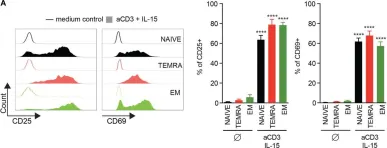
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
In Arthritis Res Ther on 4 December 2013 by Revu, S., Neregård, P., et al.
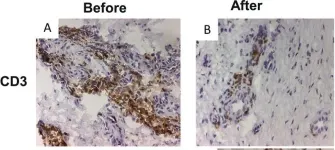
Fig.1.A,B

-
IHC
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Arthritis Res Ther by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
In PLoS One on 5 May 2011 by Wang, C. Q., Cruz-Inigo, A. E., et al.
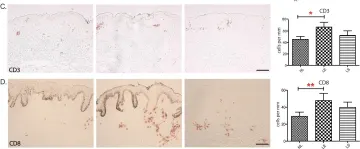
Fig.1.C

-
IHC
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
In Arthritis Res Ther on 25 May 2007 by Magnusson, S. E., Engström, M., et al.
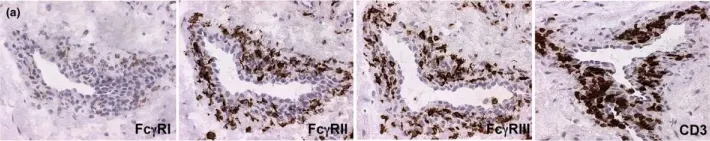
Fig.5.B

-
IHC
-
Collected and cropped from Arthritis Res Ther by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4