Foamy and inflammatory macrophages play pathogenic roles in metabolic disorders. However, the mechanisms that promote foamy and inflammatory macrophage phenotypes under acute-high-fat feeding (AHFF) remain elusive. Herein, we investigated the role of acyl-CoA synthetase-1 (ACSL1) in favoring the foamy/inflammatory phenotype of monocytes/macrophages upon short-term exposure to palmitate or AHFF. Palmitate exposure induced a foamy/inflammatory phenotype in macrophages which was associated with increased ACSL1 expression. Inhibition/knockdown of ACSL1 in macrophages suppressed the foamy/inflammatory phenotype through the inhibition of the CD36-FABP4-p38-PPARδ signaling axis. ACSL1 inhibition/knockdown suppressed macrophage foaming/inflammation after palmitate stimulation by downregulating the FABP4 expression. Similar results were obtained using primary human monocytes. As expected, oral administration of ACSL1 inhibitor triacsin-C in mice before AHFF normalized the inflammatory/foamy phenotype of the circulatory monocytes by suppressing FABP4 expression. Our results reveal that targeting ACSL1 leads to the attenuation of the CD36-FABP4-p38-PPARδ signaling axis, providing a therapeutic strategy to prevent the AHFF-induced macrophage foaming and inflammation.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Product Citations: 13
In IScience on 21 July 2023 by Al-Rashed, F., Haddad, D., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
HIV silencing and cell survival signatures in infected T cell reservoirs.
In Nature on 1 February 2023 by Clark, I. C., Mudvari, P., et al.
Rare CD4 T cells that contain HIV under antiretroviral therapy represent an important barrier to HIV cure1-3, but the infeasibility of isolating and characterizing these cells in their natural state has led to uncertainty about whether they possess distinctive attributes that HIV cure-directed therapies might exploit. Here we address this challenge using a microfluidic technology that isolates the transcriptomes of HIV-infected cells based solely on the detection of HIV DNA. HIV-DNA+ memory CD4 T cells in the blood from people receiving antiretroviral therapy showed inhibition of six transcriptomic pathways, including death receptor signalling, necroptosis signalling and antiproliferative Gα12/13 signalling. Moreover, two groups of genes identified by network co-expression analysis were significantly associated with HIV-DNA+ cells. These genes (n = 145) accounted for just 0.81% of the measured transcriptome and included negative regulators of HIV transcription that were higher in HIV-DNA+ cells, positive regulators of HIV transcription that were lower in HIV-DNA+ cells, and other genes involved in RNA processing, negative regulation of mRNA translation, and regulation of cell state and fate. These findings reveal that HIV-infected memory CD4 T cells under antiretroviral therapy are a distinctive population with host gene expression patterns that favour HIV silencing, cell survival and cell proliferation, with important implications for the development of HIV cure strategies.
© 2023. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cancer Cell on 13 December 2021 by Duraiswamy, J., Turrini, R., et al.
The mechanisms regulating exhaustion of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) and responsiveness to PD-1 blockade remain partly unknown. In human ovarian cancer, we show that tumor-specific CD8+ TIL accumulate in tumor islets, where they engage antigen and upregulate PD-1, which restrains their functions. Intraepithelial PD-1+CD8+ TIL can be, however, polyfunctional. PD-1+ TIL indeed exhibit a continuum of exhaustion states, with variable levels of CD28 costimulation, which is provided by antigen-presenting cells (APC) in intraepithelial tumor myeloid niches. CD28 costimulation is associated with improved effector fitness of exhausted CD8+ TIL and is required for their activation upon PD-1 blockade, which also requires tumor myeloid APC. Exhausted TIL lacking proper CD28 costimulation in situ fail to respond to PD-1 blockade, and their response may be rescued by local CTLA-4 blockade and tumor APC stimulation via CD40L.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Ceramide kinase regulates TNF-α-induced immune responses in human monocytic cells.
In Scientific Reports on 15 April 2021 by Al-Rashed, F., Ahmad, Z., et al.
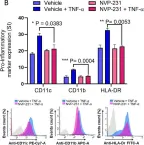
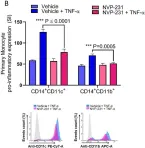
Ceramide kinase (CERK) phosphorylates ceramide to produce ceramide-1-phosphate (C1P), which is involved in the development of metabolic inflammation. TNF-α modulates inflammatory responses in monocytes associated with various inflammatory disorders; however, the underlying mechanisms remain not fully understood. Here, we investigated the role of CERK in TNF-α-induced inflammatory responses in monocytes. Our results show that disruption of CERK activity in monocytes, either by chemical inhibitor NVP-231 or by small interfering RNA (siRNA), results in the defective expression of inflammatory markers including CD11c, CD11b and HLA-DR in response to TNF-α. Our data show that TNF-α upregulates ceramide phosphorylation. Inhibition of CERK in monocytes significantly reduced the secretion of IL-1β and MCP-1. Similar results were observed in CERK-downregulated cells. TNF-α-induced phosphorylation of JNK, p38 and NF-κB was reduced by inhibition of CERK. Additionally, NF-κB/AP-1 activity was suppressed by the inhibition of CERK. Clinically, obese individuals had higher levels of CERK expression in PBMCs compared to lean individuals, which correlated with their TNF-α levels. Taken together, these results suggest that CERK plays a key role in regulating inflammatory responses in human monocytes during TNF-α stimulation. CERK may be a relevant target for developing novel therapies for chronic inflammatory diseases.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Scientific Reports on 8 October 2020 by Al-Rashed, F., Ahmad, Z., et al.
Obesity is associated with elevated levels of TNF-α and proinflammatory CD11c monocytes/macrophages. TNF-α mediated dysregulation in the plasticity of monocytes/macrophages is concomitant with pathogenesis of several inflammatory diseases, including metabolic syndrome, but the underlying mechanisms are incompletely understood. Since neutral sphingomyelinase-2 (nSMase2: SMPD3) is a key enzyme for ceramide production involved in inflammation, we investigated whether nSMase2 contributed to the inflammatory changes in the monocytes/macrophages induced by TNF-α. In this study, we demonstrate that the disruption of nSMase activity in monocytes/macrophages either by chemical inhibitor GW4869 or small interfering RNA (siRNA) against SMPD3 results in defects in the TNF-α mediated expression of CD11c. Furthermore, blockage of nSMase in monocytes/macrophages inhibited the secretion of inflammatory mediators IL-1β and MCP-1. In contrast, inhibition of acid SMase (aSMase) activity did not attenuate CD11c expression or secretion of IL-1β and MCP-1. TNF-α-induced phosphorylation of JNK, p38 and NF-κB was also attenuated by the inhibition of nSMase2. Moreover, NF-kB/AP-1 activity was blocked by the inhibition of nSMase2. SMPD3 was elevated in PBMCs from obese individuals and positively corelated with TNF-α gene expression. These findings indicate that nSMase2 acts, at least in part, as a master switch in the TNF-α mediated inflammatory responses in monocytes/macrophages.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Sci Rep on 15 April 2021 by Al-Rashed, F., Ahmad, Z., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
In Sci Rep on 15 April 2021 by Al-Rashed, F., Ahmad, Z., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2