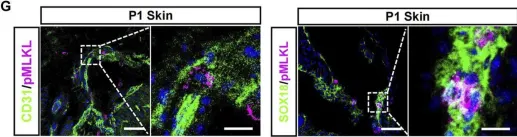
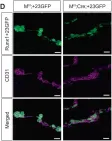
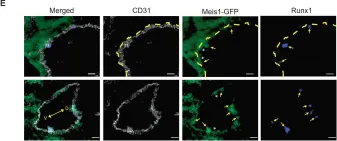
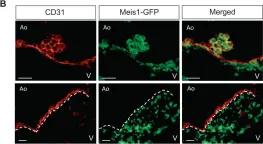
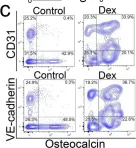
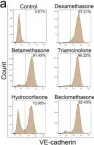
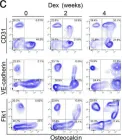
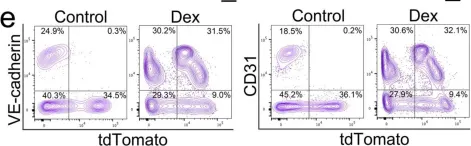
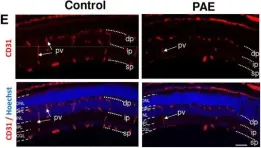
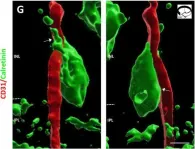
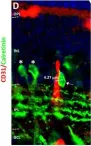
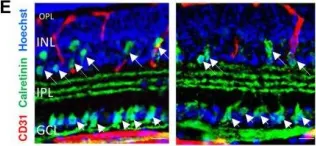
We characterized the timeline of molecular dysfunction in diabetic retinopathy (DR) and diabetic retinal disease (DRD) by studying the streptozotocin (STZ)-induced mouse retina over the course of 6 mo of diabetes. We performed bulk RNA-Seq on endothelial and retinal cells, separately, at 1, 3, and 6 mo of diabetes and single-cell RNA-Seq (scRNA-Seq) at 3 months. Transcriptomics changes were validated by in vitro and ex vivo assays and immunohistochemistry of mouse and human tissue. Bulk RNA-Seq revealed inflammation in endothelial cells at 1 mo. At 3 mo, scRNA-Seq identified glutamine-driven anaplerotic dysfunction in Müller cells, confirmed by retinal culture. We posited this glutamine deficiency would impact the photoreceptors and endothelial cells. We validated this hypothesis using endothelial cells in vitro, and immunohistochemistry of disrupted photoreceptor ribbon synapses in mouse and human diabetic retinas. In addition, glutamine deprivation increased the expression of apoptotic genes in endothelial cells. At 6 mo, we observed significant down-regulation of angiogenic pathways and elevated profibrotic markers. Our results suggest that dysfunction of the metabolic ecosystem linking the Müller-photoreceptor-endothelial cells is central to the early stages of DRD pathogenesis, impacting photoreceptor synapses and endothelial cells, before the appearance of the classic microvascular features of DR.
© 2025 Corano Scheri et al.
Product Citations: 1,762
Müller cell glutamine metabolism links photoreceptor and endothelial injury in diabetic retinopathy.
In Life Science Alliance on 1 February 2026 by Corano Scheri, K., Hsieh, Y. W., et al.
-
IF
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
The fibroblast epigenome underlies SS18::SSX-mediated transformation in synovial sarcoma.
In Nature Communications on 2 December 2025 by Hill, L. A., Scott, R. W., et al.
Synovial sarcoma (SyS) is an aggressive soft-tissue malignancy that is characterised by a pathognomonic t(X;18)(p11.2;q11.2) translocation, which produces the fusion oncogene named SS18::SSX. Despite recent advancements in our understanding of synovial sarcoma biology, the cell-of-origin remains undefined. A mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) specific CreERT2 line was employed to express SS18::SSX in fibroblasts and related cell types, resulting in 100% penetrant synovial sarcoma development in mice, with a median latency period of 16.2 ± 2.8 weeks. Murine tumours exhibited high concordance with human synovial sarcoma subtypes at the histological and molecular levels. Genetic refinement of the cell-of-origin revealed that synovial sarcomas derive from a rare Hic1+ Pdgfra+ Lgr5+ fibroblastic population. Furthermore, comparative transcriptomic analysis revealed the acquisition of a transformed phenotype initiated by the loss of a mature fibroblastic profile and subsequent unmasking of an epigenetically embedded embryonic MSC program. Adult and embryonic MSCs exhibited overlapping H2AK119ub and H3K4me3/H3K27me3 (bivalent) histone marks, while SS18::SSX-mediated transformation culminated in the widespread loss of H3K27me3 at these genes and their consequent transcription. Collectively, these studies define a rare MSC context, conducive for SS18::SSX-mediated transformation, and demonstrate that SyS tumorigenesis involves the induction and maintenance of an embryonic-like MSC phenotype.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Glial cells missing 1 triggers gliosis and angiogenesis after neonatal brain injury.
In IScience on 21 November 2025 by Hayashi, Y., Abdullah, A., et al.
The glial cells missing (Gcm) protein in Drosophila plays a crucial role in the cell fate switch in the nervous system and in induction of glial cell differentiation. However, the functions of the mammalian homolog Gcm1 in normal neural development and pathological conditions remain elusive. Here, we report that Gcm1 was upregulated in Nestin+ cells immediately after neonatal brain injury, followed by accumulation of GFAP+ and Olig2+ cells in the penumbra region. Injury-induced upregulation of Lif gene was mediated, at least in part, by the demethylation activity of Gcm1. In addition, Gcm1 strongly induced angiogenesis in the injury lesion as well as in the developing brain via vascular endothelial growth factor A and C activity. Lack of Gcm1-mediated angiogenesis could be a major cause of the dysplasia in placental labyrinths found in Gcm1 -/- embryos, leading to embryonic lethality. Our data suggest that Gcm1 triggers both gliosis and angiogenesis after brain injury and could be a target for therapeutic intervention.
© 2025 The Authors.
-
Neuroscience
DKK3-LRP1 complex and a chemical inhibitor regulate Aβ clearance in models of Alzheimer's disease.
In Science Advances on 7 November 2025 by Yang, R., Wang, L., et al.
Impaired clearance of amyloid-β (Aβ) contributes to Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis, but its upstream modulators remain poorly defined. We report secreted Dickkopf (DKK) proteins-DKK1 through DKK4-as previously unrecognized ligands of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1), a principal Aβ clearance receptor. Analyses of cells derived from a patient with AD, postmortem tissue, and 5×FAD mice reveal that DKK1 and DKK3 are elevated in AD and reduce Aβ uptake and degradation in neurons and astrocytes. Mechanistically, DKKs inhibit Aβ clearance by competitively binding LRP1 and promoting its internalization. In 5×FAD mice, DKK3 overexpression worsens, while knockout improves, Aβ pathology and cognitive outcomes. A targeted high-throughput screen of ~3000 compounds identified SJ-300 as a potent and selective inhibitor of the DKK3-LRP1 interaction. SJ-300 restores Aβ clearance and rescues cognitive function and neuropathology in 5×FAD mice. These findings uncover DKK3-LRP1 axis as a contributor for Aβ metabolism and nominate SJ-300 as a promising therapeutic candidate for AD intervention.
-
Neuroscience
Molecular profiling of brain endothelial cell to astrocyte endfoot communication in mouse and human.
In Nature Communications on 6 November 2025 by Hill, S. A., Bravo-Ferrer, I., et al.
Our understanding of how the body communicates with the brain to coordinate their functions is remarkably limited. At the blood-brain barrier (BBB), brain endothelial cells (BECs) are ideally positioned to mediate signaling between blood and brain parenchyma via direct communication with astrocyte perivascular processes (endfeet). We develop a method to define the mouse in vivo astrocyte endfoot proteome, which in combination with BEC-specific RNA-seq, reveal BEC to astrocyte endfoot ligand-receptor pairs that are modulated when mice are exposed to a peripheral inflammatory insult with lipopolysaccharide. We show that over 80% of these mouse BEC-endfoot ligand-receptor pairs are also found in the human BBB, with a subset of them differentially expressed in human multiple sclerosis or Alzheimer's disease compared to healthy individuals. Our findings reveal dynamic BEC-endfoot communication pathways that are relevant to human physiology and provide methodology and datasets for the translational study of BEC-astrocyte crosstalk in health and disease.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Neuroscience
In Cells on 11 October 2023 by Qiao, X., Yang, Y., et al.
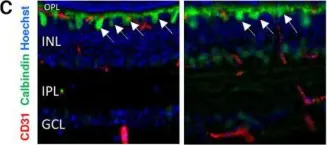
Fig.5.B
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Nat Commun on 15 August 2023 by Cai, Q., Li, X., et al.
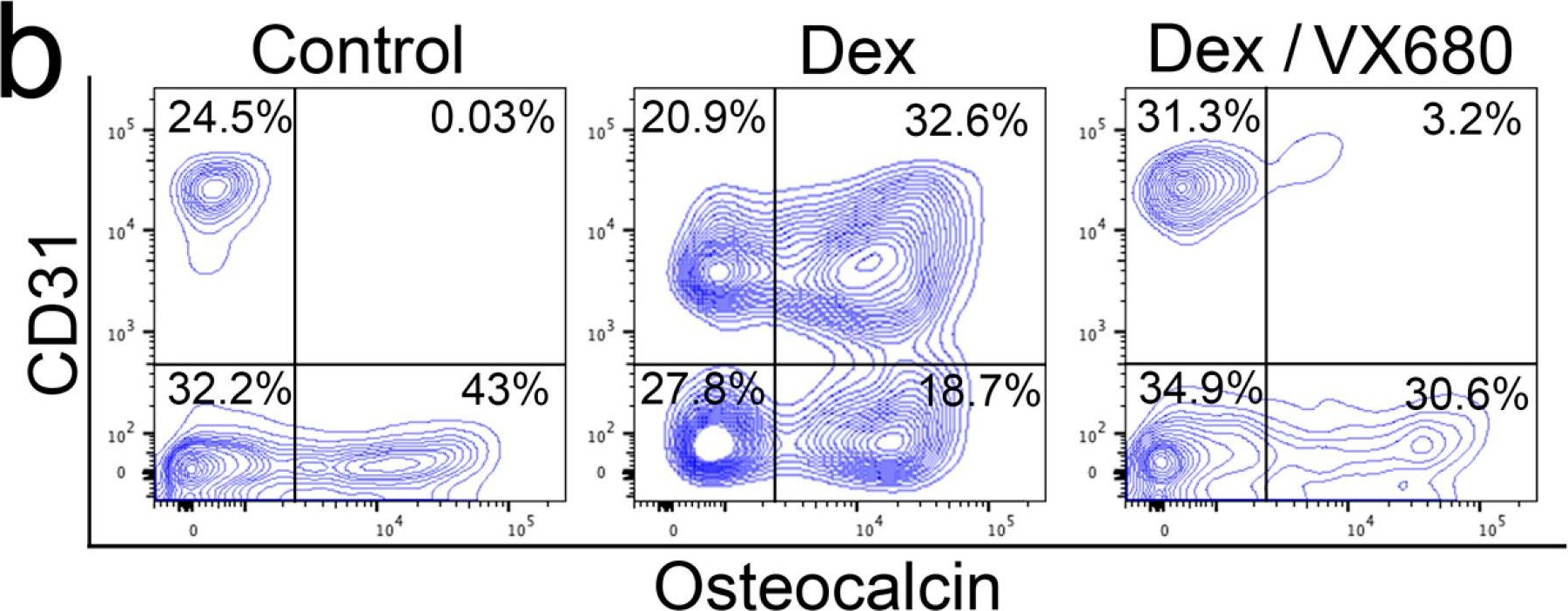
Fig.2.D
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nature Communications by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Nat Commun on 15 August 2023 by Cai, Q., Li, X., et al.
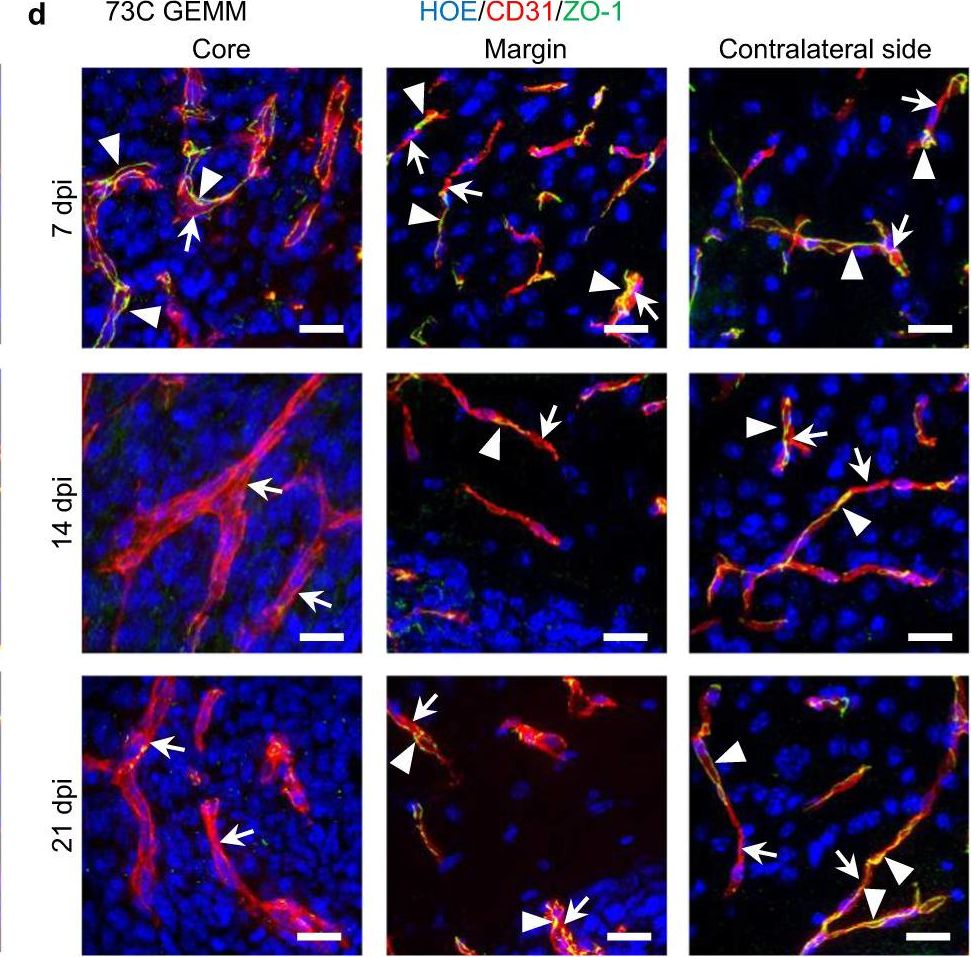
Fig.2.B
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nature Communications by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
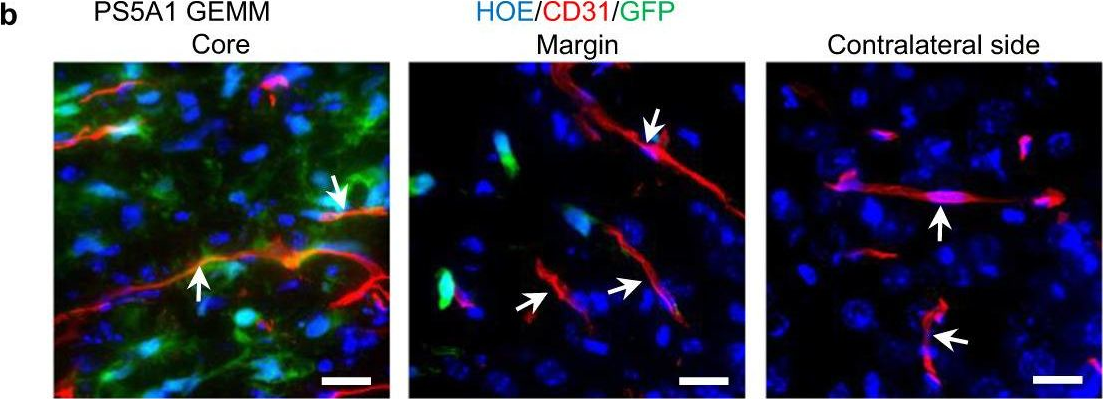
In Nat Commun on 15 August 2023 by Cai, Q., Li, X., et al.
Fig.2.C
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nature Communications by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Front Cell Dev Biol on 14 August 2023 by Meng, H., Zhao, Y., et al.
Fig.2.A
-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Front Cell Dev Biol on 14 August 2023 by Meng, H., Zhao, Y., et al.
Fig.4.C
-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Front Cell Dev Biol on 14 August 2023 by Meng, H., Zhao, Y., et al.
Fig.4.A
-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Front Cell Dev Biol on 14 August 2023 by Meng, H., Zhao, Y., et al.
Fig.4.M
-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Front Cell Dev Biol on 14 August 2023 by Meng, H., Zhao, Y., et al.
Fig.1.G
-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Nat Commun on 27 July 2023 by Coulombe, P., Cole, G., et al.
Fig.6.D
-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nature Communications by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Nat Commun on 27 July 2023 by Coulombe, P., Cole, G., et al.
Fig.4.E
-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nature Communications by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Nat Commun on 27 July 2023 by Coulombe, P., Cole, G., et al.
Fig.3.B
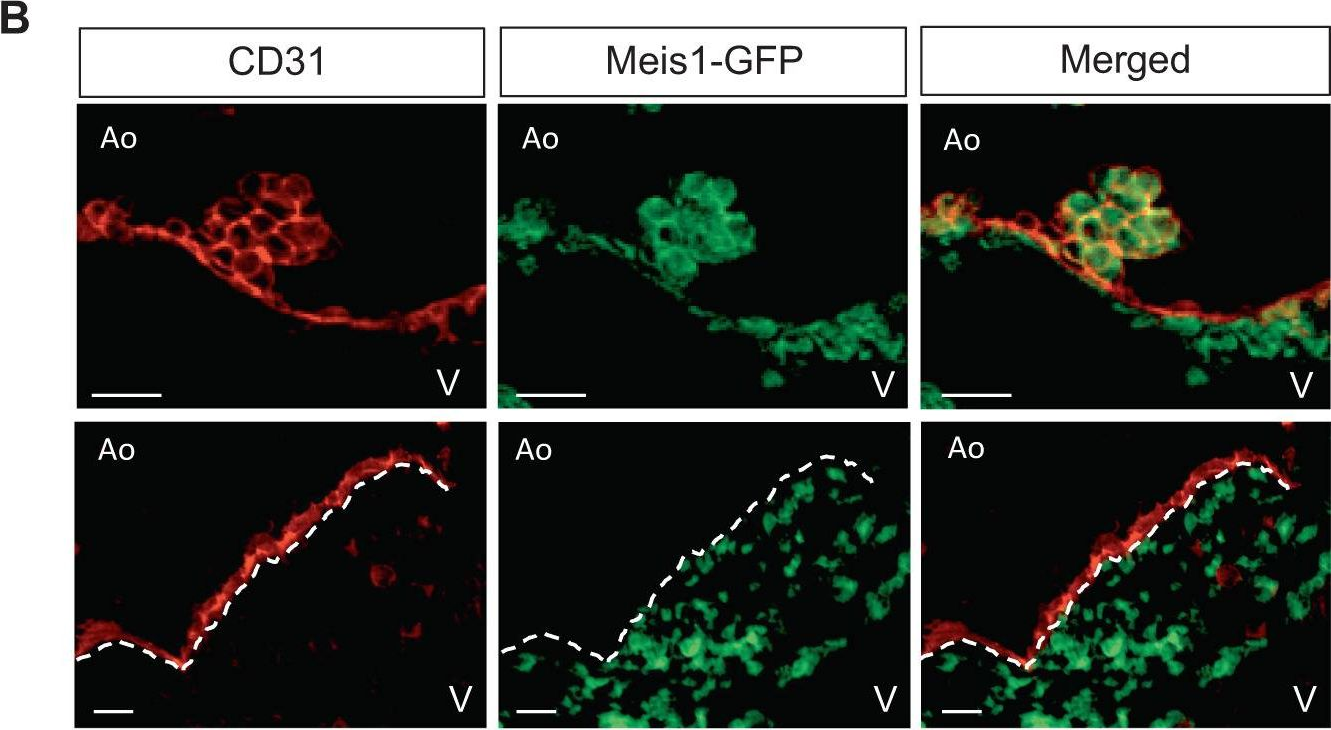
-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nature Communications by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Cells on 8 July 2023 by Qiao, X., Wu, X., et al.
Fig.1.C
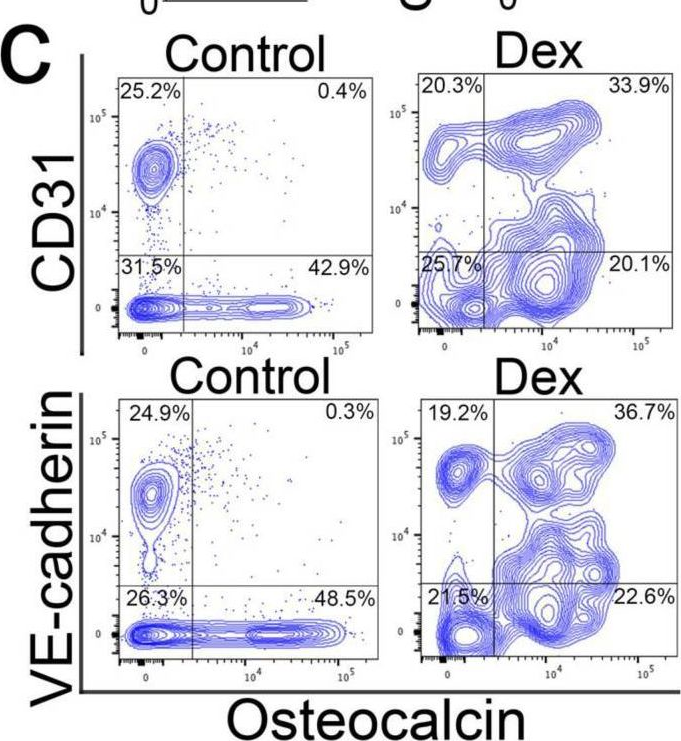
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Cells on 8 July 2023 by Qiao, X., Wu, X., et al.
Fig.7.A
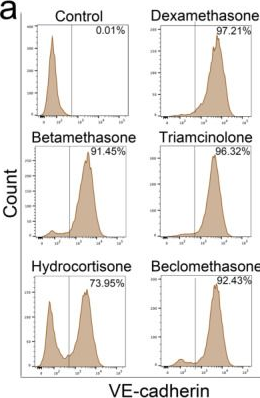
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Cells on 8 July 2023 by Qiao, X., Wu, X., et al.
Fig.2.C
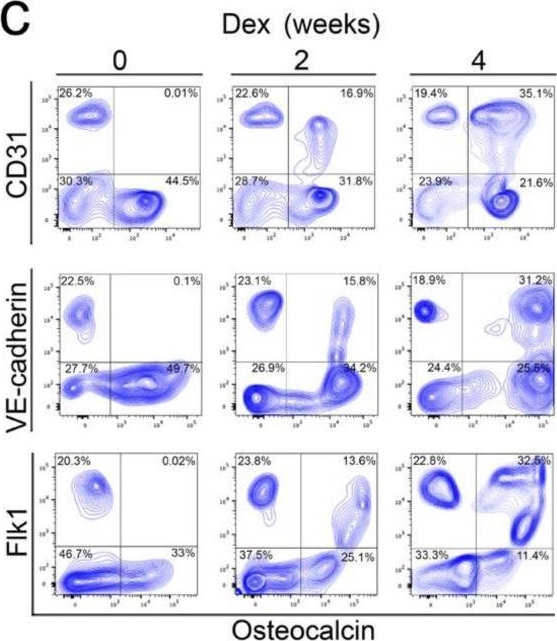
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Cells on 8 July 2023 by Qiao, X., Wu, X., et al.
Fig.3.E
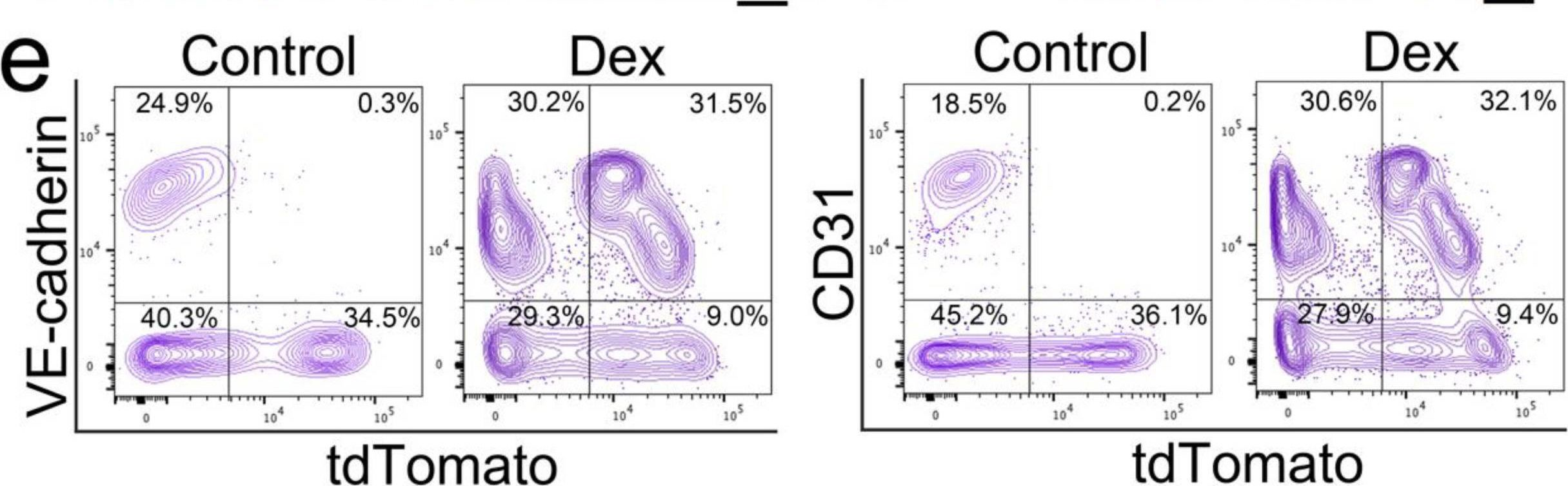
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Cancer Gene Ther on 1 July 2023 by Deguchi, A., Watanabe-Takahashi, M., et al.
Fig.5.B
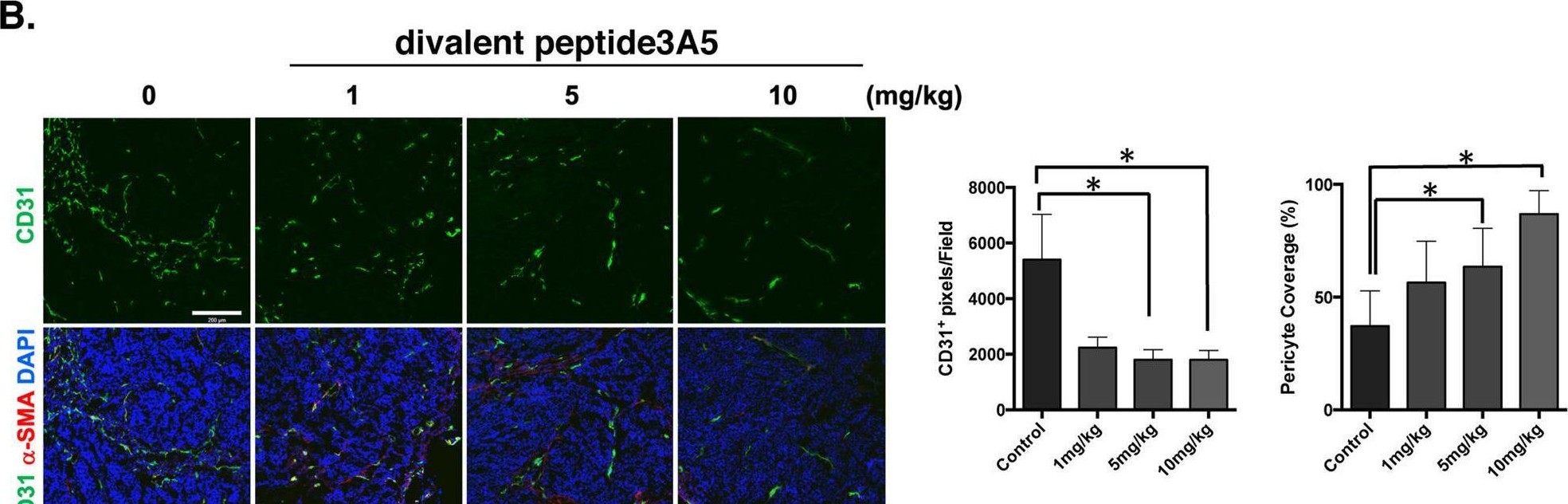
-
IHC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Cancer Gene Therapy by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Fluids Barriers CNS on 16 June 2023 by Gurler, G., Belder, N., et al.
Fig.1.E
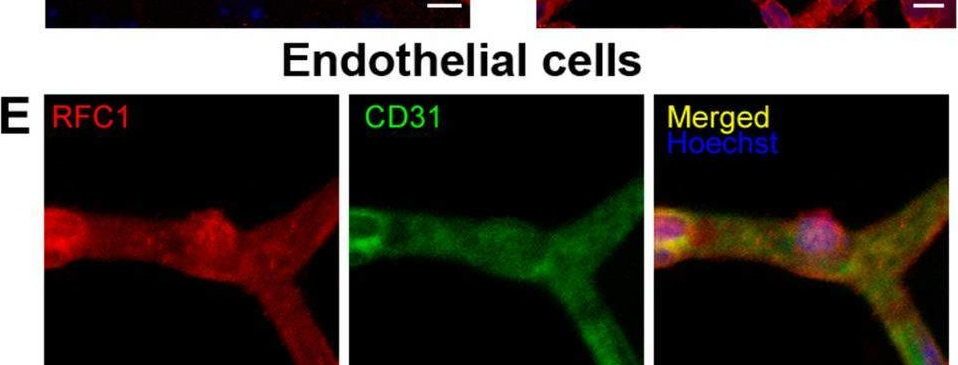
-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Fluids and Barriers of the CNS by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Elife on 18 April 2023 by Zhang, C., Guo, Z. F., et al.
Fig.6.C
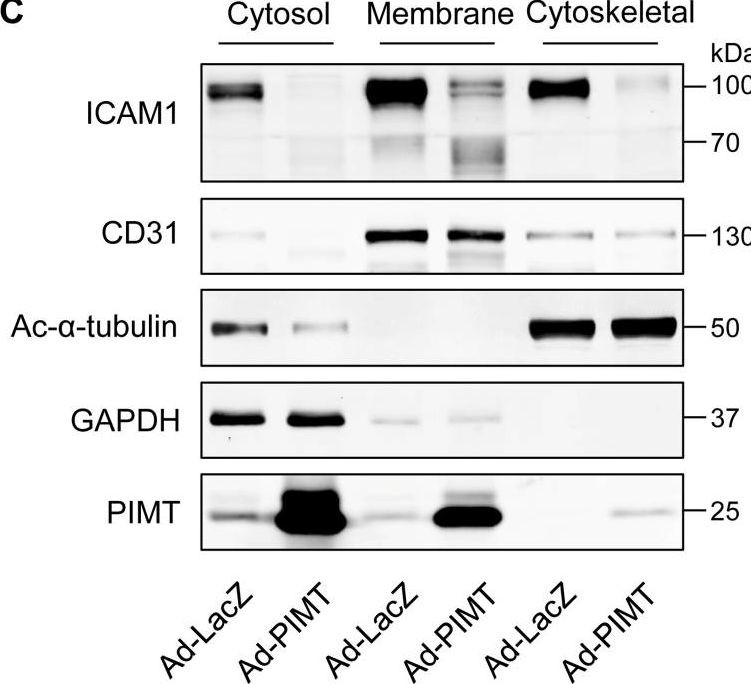
-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from eLife by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Eneuro on 1 April 2023 by Dumanoir, M., Leroy, A., et al.
Fig.3.E
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from ENeuro by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Eneuro on 1 April 2023 by Dumanoir, M., Leroy, A., et al.
Fig.2.E
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from ENeuro by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Eneuro on 1 April 2023 by Dumanoir, M., Leroy, A., et al.
Fig.5.G
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from ENeuro by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Eneuro on 1 April 2023 by Dumanoir, M., Leroy, A., et al.
Fig.5.D
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from ENeuro by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Eneuro on 1 April 2023 by Dumanoir, M., Leroy, A., et al.
Fig.4.E
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from ENeuro by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78
In Eneuro on 1 April 2023 by Dumanoir, M., Leroy, A., et al.
Fig.4.C
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from ENeuro by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 78