Chronic demyelination and oligodendrocyte loss deprive neurons of crucial support. It is the degeneration of neurons and their connections that drives progressive disability in demyelinating disease. However, whether chronic demyelination triggers neurodegeneration and how it may do so remain unclear. We characterize two genetic mouse models of inducible demyelination, one distinguished by effective remyelination and the other by remyelination failure and chronic demyelination. While both demyelinating lines feature axonal damage, mice with blocked remyelination have elevated neuronal apoptosis and altered microglial inflammation, whereas mice with efficient remyelination do not feature neuronal apoptosis and have improved functional recovery. Remyelination incapable mice show increased activation of kinases downstream of dual leucine zipper kinase (DLK) and phosphorylation of c-Jun in neuronal nuclei. Pharmacological inhibition or genetic disruption of DLK block c-Jun phosphorylation and the apoptosis of demyelinated neurons. Together, we demonstrate that remyelination is associated with neuroprotection and identify DLK inhibition as protective strategy for chronically demyelinated neurons.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 92
Remyelination protects neurons from DLK-mediated neurodegeneration.
In Nature Communications on 23 October 2024 by Duncan, G. J., Ingram, S. D., et al.
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Neuroscience
In Scientific Reports on 3 June 2024 by Wu, S. Y., Wang, C. H., et al.
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) poses challenges due to late-stage diagnosis and limited treatment response, often attributed to the hypoxic tumor microenvironment (TME). Sonoporation, combining ultrasound and microbubbles, holds promise for enhancing therapy. However, additional preclinical research utilizing commercially available ultrasound equipment for PDAC treatment while delving into the TME's intricacies is necessary. This study investigated the potential of using a clinically available ultrasound system and phase 2-proven microbubbles to relieve tumor hypoxia and enhance the efficacy of chemotherapy and immunotherapy in a murine PDAC model. This approach enables early PDAC detection and blood-flow-sensitive Power-Doppler sonoporation in combination with chemotherapy. It significantly extended treated mice's median survival compared to chemotherapy alone. Mechanistically, this combination therapy enhanced tumor perfusion and substantially reduced tumor hypoxia (77% and 67%, 1- and 3-days post-treatment). Additionally, cluster of differentiation 8 (CD8) T-cell infiltration increased four-fold afterward. The combined treatment demonstrated a strengthening of the anti-programmed death-ligand 1(αPDL1) therapy against PDAC. Our study illustrates the feasibility of using a clinically available ultrasound system with NH-002 microbubbles for early tumor detection, alleviating hypoxic TME, and improving chemotherapy and immunotherapy. It suggests the development of an adjuvant theragnostic protocol incorporating Power-Doppler sonoporation for pancreatic tumor treatment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In JCI Insight on 5 March 2024 by Silva-Rojas, R., Pérez-Guàrdia, L., et al.
Tubular aggregate myopathy (TAM) and Stormorken syndrome (STRMK) are clinically overlapping disorders characterized by childhood-onset muscle weakness and a variable occurrence of multisystemic signs, including short stature, thrombocytopenia, and hyposplenism. TAM/STRMK is caused by gain-of-function mutations in the Ca2+ sensor STIM1 or the Ca2+ channel ORAI1, both of which regulate Ca2+ homeostasis through the ubiquitous store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) mechanism. Functional experiments in cells have demonstrated that the TAM/STRMK mutations induce SOCE overactivation, resulting in excessive influx of extracellular Ca2+. There is currently no treatment for TAM/STRMK, but SOCE is amenable to manipulation. Here, we crossed Stim1R304W/+ mice harboring the most common TAM/STRMK mutation with Orai1R93W/+ mice carrying an ORAI1 mutation partially obstructing Ca2+ influx. Compared with Stim1R304W/+ littermates, Stim1R304W/+Orai1R93W/+ offspring showed a normalization of bone architecture, spleen histology, and muscle morphology; an increase of thrombocytes; and improved muscle contraction and relaxation kinetics. Accordingly, comparative RNA-Seq detected more than 1,200 dysregulated genes in Stim1R304W/+ muscle and revealed a major restoration of gene expression in Stim1R304W/+Orai1R93W/+ mice. Altogether, we provide physiological, morphological, functional, and molecular data highlighting the therapeutic potential of ORAI1 inhibition to rescue the multisystemic TAM/STRMK signs, and we identified myostatin as a promising biomarker for TAM/STRMK in humans and mice.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Therapeutic potential of rWnt5A in curbing Leishmania donovani infection.
In Infection and Immunity on 17 October 2023 by Maity, S., Sengupta, S., et al.
In view of the antagonism of Wnt5A signaling toward microbial pathogens, we were interested in evaluating the therapeutic potential of recombinant Wnt5A (rWnt5A) in curbing Leishmania donovani infection. Initially, using L. donovani-infected RAW 264.7 and peritoneal macrophages, we demonstrated that application of rWnt5A as opposed to the vehicle control to the infected cells significantly dampens L. donovani infection. Inhibition of infection was associated with increase in cell-associated reactive oxygen species (ROS), and blocked by the ROS production inhibitor diphenylene iodonium chloride (DPI). rWnt5A, but not the vehicle control (PBS: phosphate-buffered saline) administration to L. donovani-infected mice appreciably reduced the infection load, and inhibited disease progression as evident from the preservation of splenic white pulp architecture. rWnt5A administration, moreover, led to elevation of both cell-associated ROS and the activation of splenic T cells. Substantial increase in T cell-associated Interleukin-2 (IL-2) and Granzyme B (GRB) upon exposure of splenic lymphocytes harvested from rWnt5A-treated mice to L. donovani-infected RAW 264.7 macrophages in vitro validated the occurrence of L. donovani-responsive T cell activation in vivo. In summary, this study unveils the therapeutic potential of rWnt5A in curbing L. donovani infection and the progression of experimental visceral leishmaniasis possibly through increase in cellular ROS and T cell activation. Accordingly, it opens up a new avenue of investigation into the use of rWnt5A as a therapeutic agent for restraining the progression of drug-resistant L. donovani infection.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Androgen receptor is a determinant of melanoma targeted drug resistance.
In Nature Communications on 14 October 2023 by Samarkina, A., Youssef, M. K., et al.
Melanoma provides a primary benchmark for targeted drug therapy. Most melanomas with BRAFV600 mutations regress in response to BRAF/MEK inhibitors (BRAFi/MEKi). However, nearly all relapse within the first two years, and there is a connection between BRAFi/MEKi-resistance and poor response to immune checkpoint therapy. We reported that androgen receptor (AR) activity is required for melanoma cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. We show here that AR expression is markedly increased in BRAFi-resistant melanoma cells, and in sensitive cells soon after BRAFi exposure. Increased AR expression is sufficient to render melanoma cells BRAFi-resistant, eliciting transcriptional changes of BRAFi-resistant subpopulations, including elevated EGFR and SERPINE1 expression, of likely clinical significance. Inhibition of AR expression or activity blunts changes in gene expression and suppresses proliferation and tumorigenesis of BRAFi-resistant melanoma cells, promoting clusters of CD8+ T cells infiltration and cancer cells killing. Our findings point to targeting AR as possible co-therapeutical approach in melanoma treatment.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
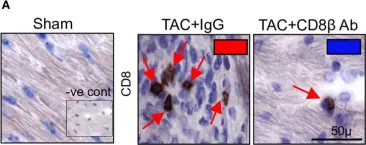
In Front Immunol on 10 December 2022 by Brassington, K., Kanellakis, P., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
IHC
-
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
In Front Immunol on 5 November 2019 by Zhang, F., Zhao, Q., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2