Tertiary lymphoid tissues (TLTs) are ectopic lymphoid structures induced by multiple stimuli, including infection and tissue injuries; however, their clinical relevance in disease progression has remained unclear. We demonstrated previously that TLTs develop in mouse and human kidneys with aging and can be a potential marker of kidney injury and prognosis, and therapeutic targets. In addition, we found that two types of unique lymphocytes that emerge with aging, senescence-associated T cells and age-associated B cells, are essential for TLT formation in the kidney. Although TLTs develop with aging in other organs as well, their cellular and molecular components, and clinical significance remain unclear. In the present study, we found that TLTs developed in the liver with aging, and that their cellular and molecular components were similar to those in the kidneys. Notably, senescence-associated T cells and age-associated B cells were also present in hepatic TLTs. Furthermore, analysis of publicly available data on human liver biopsy transcriptomes revealed that the expression of TLT-related genes was elevated in the liver biopsy samples from hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected patients compared with those without HCV infection and was associated with liver injury and fibrosis. Therefore, we analyzed liver biopsy samples from 47 HCV patients and found that TLTs were present in 87.2% of cases and that the numbers and stages of TLTs were higher in aged patients and cellular and molecular components of TLTs in humans were similar to those in mice. Our findings suggesting that age-dependent TLT formation is a systemic phenomenon across the tissues and aging is also a predisposing factor for TLT formation across organs.
Copyright: © 2025 Toriu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Product Citations: 296
In PLoS ONE on 27 February 2025 by Toriu, N., Sato, Y., et al.
-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In Communications Biology on 17 January 2025 by Fuma, K., Iitani, Y., et al.
Histological chorioamnionitis (HCA) is a form of maternal immune activation (MIA) linked to an increased risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in offspring. Our previous study identified neurodevelopmental impairments in an MIA mouse model mimicking HCA. Thus, this study investigated the role of CD11c+ microglia, key contributors to myelination through IGF-1 production, in this pathology. In the mouse model, the CD11c+ microglial population was significantly lower in the MIA group than in the control group on postnatal day 3 (PN3d). Furthermore, myelination-related protein levels significantly decreased in the MIA group at PN8d. In humans, preterm infants with HCA exhibited higher IL-6 and IL-17A cord-serum levels and lower IGF-1 levels than those without HCA, followed by a higher incidence of delayed myelination on magnetic resonance imaging at the term-equivalent age. In silico analysis revealed that the transient induction of CD11c+ microglia during early development occurred similarly in mice and humans. Notably, a lack of high CD11c+ microglial population has been observed in children with neurodevelopmental disorders. This study reports impaired induction of CD11c+ microglia during postnatal development in a mouse model of MIA associated with delayed myelination. Our findings may inform strategies for improving outcomes in infants with HCA.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
In Frontiers in Immunology on 28 November 2024 by Kato, R., Yamamoto, T., et al.
It has recently become clear that the gut microbiota influence intestinal motility, intestinal barrier function, and mucosal immune function; therefore, the gut microbiota are deeply involved in the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis. The effects of the gut microbiota on the enteric nervous system (ENS) in the adult intestine, however, remain poorly understood. In the current study, we investigated the effects of the gut microbiota on the ENS. Male C57BL/6 SPF mice at 12 weeks of age were given a cocktail of four antibiotics (ABX) orally to induce dysbiosis (ABX mice). As early as six hours after ABX administration, the weight of the cecum of ABX mice increased to be significantly greater than that of vehicle-treated animals; moreover, ABX-induced dysbiosis reduced the density of enteric nerve fibers (marked by tubulin-β3 immunoreactivity) in the lamina propria of the proximal colon to approximately 60% that of control. TAK242, a TLR4 antagonist, significantly lowered the nerve fiber density in the lamina propria of the proximal colonic mucosa to approximately 60% that of vehicle-treated SPF mice. We thus developed and tested the hypothesis that mucosal glia expressing TLR4 are activated by enteric bacteria and release neurotrophic factors that contribute to the maintenance of enteric neural circuits. Neurotrophic factors in the mucosa of the SPF mouse proximal colon were examined immunohistochemically. Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) was abundantly expressed in the lamina propria; most of the CNTF immunoreactivity was observed in mucosal glia (marked by S100β immunoreactivity). Administration of CNTF (subcutaneously, 0.3 mg/kg, 3 doses, 2 hours apart) to ABX mice significantly increased mucosal nerve fiber density in the ABX mouse proximal colon to nearly control levels. The effect of CNTF on enteric mucosal nerve fibers was examined in isolated preparations of proximal colon of ABX mice. As it did in vivo, exposure to CNTF in vitro significantly increased enteric mucosal nerve fiber density in the ABX-treated colon. In conclusion, our evidence suggests that gut microbiota constitutively activate TLR4 signaling in enteric mucosal glia, which secrete CNTF in response. The resulting bacterial-driven glial release of CNTF helps to maintain the integrity of enteric mucosal nerve fibers.
Copyright © 2024 Kato, Yamamoto, Ogata, Miyata, Hayashi, Gershon and Kadowaki.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
In Gut on 7 December 2023 by Zevallos, V. F., Yogev, N., et al.
Wheat has become a main staple globally. We studied the effect of defined pro-inflammatory dietary proteins, wheat amylase trypsin inhibitors (ATI), activating intestinal myeloid cells via toll-like receptor 4, in experimental autoimmune encephalitis (EAE), a model of multiple sclerosis (MS).
EAE was induced in C57BL/6J mice on standardised dietary regimes with defined content of gluten/ATI. Mice received a gluten and ATI-free diet with defined carbohydrate and protein (casein/zein) content, supplemented with: (a) 25% of gluten and 0.75% ATI; (b) 25% gluten and 0.19% ATI or (c) 1.5% purified ATI. The effect of dietary ATI on clinical EAE severity, on intestinal, mesenteric lymph node, splenic and central nervous system (CNS) subsets of myeloid cells and lymphocytes was analysed. Activation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with MS and healthy controls was compared.
Dietary ATI dose-dependently caused significantly higher EAE clinical scores compared with mice on other dietary regimes, including on gluten alone. This was mediated by increased numbers and activation of pro-inflammatory intestinal, lymph node, splenic and CNS myeloid cells and of CNS-infiltrating encephalitogenic T-lymphocytes. Expectedly, ATI activated peripheral blood monocytes from both patients with MS and healthy controls.
Dietary wheat ATI activate murine and human myeloid cells. The amount of ATI present in an average human wheat-based diet caused mild intestinal inflammation, which was propagated to extraintestinal sites, leading to exacerbation of CNS inflammation and worsening of clinical symptoms in EAE. These results support the importance of the gut-brain axis in inflammatory CNS disease.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Plant Science
Mechanisms and treatments of neuropathic itch in a mouse model of lymphoma.
In The Journal of Clinical Investigation on 15 February 2023 by Chen, O., He, Q., et al.
Our understanding of neuropathic itch is limited due to a lack of relevant animal models. Patients with cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) experience severe itching. Here, we characterize a mouse model of chronic itch with remarkable lymphoma growth, immune cell accumulation, and persistent pruritus. Intradermal CTCL inoculation produced time-dependent changes in nerve innervations in lymphoma-bearing skin. In the early phase (20 days), CTCL caused hyperinnervations in the epidermis. However, chronic itch was associated with loss of epidermal nerve fibers in the late phases (40 and 60 days). CTCL was also characterized by marked nerve innervations in mouse lymphoma. Blockade of C-fibers reduced pruritus at early and late phases, whereas blockade of A-fibers only suppressed late-phase itch. Intrathecal (i.t.) gabapentin injection reduced late-phase, but not early-phase, pruritus. IL-31 was upregulated in mouse lymphoma, whereas its receptor Il31ra was persistently upregulated in Trpv1-expressing sensory neurons in mice with CTCL. Intratumoral anti-IL-31 treatment effectively suppressed CTCL-induced scratching and alloknesis (mechanical itch). Finally, i.t. administration of a TLR4 antagonist attenuated pruritus in early and late phases and in both sexes. Collectively, we have established a mouse model of neuropathic and cancer itch with relevance to human disease. Our findings also suggest distinct mechanisms underlying acute, chronic, and neuropathic itch.
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
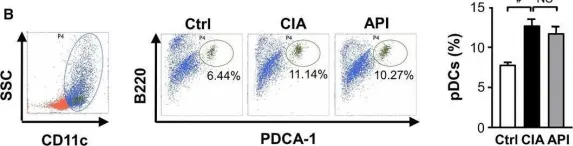
In J Cell Mol Med on 1 January 2016 by Li, X., Han, Y., et al.
Fig.7.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from J Cell Mol Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
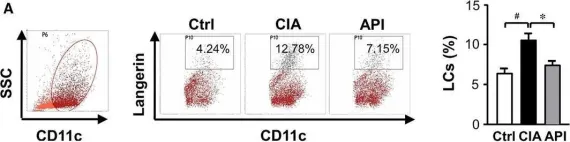
In J Cell Mol Med on 1 January 2016 by Li, X., Han, Y., et al.
Fig.7.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from J Cell Mol Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2