The recruitment of the actin-regulatory proteins cortactin and profilin-1 (Pfn-1) to the membrane is important for the regulation of actin cytoskeletal reorganization and smooth muscle contraction. Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) and the type III intermediate filament protein vimentin are involved in smooth muscle contraction. Regulation of complex cytoskeletal signaling is not entirely elucidated. The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of nestin (a type VI intermediate filament protein) in cytoskeletal signaling in airway smooth muscle.
Nestin expression in human airway smooth muscle (HASM) was knocked down by specific shRNA or siRNA. The effects of nestin knockdown (KD) on the recruitment of cortactin and Pfn-1, actin polymerization, myosin light chain (MLC) phosphorylation, and contraction were evaluated by cellular and physiological approaches. Moreover, we assessed the effects of non-phosphorylatable nestin mutant on these biological processes.
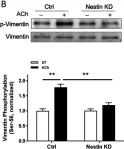
Nestin KD reduced the recruitment of cortactin and Pfn-1, actin polymerization, and HASM contraction without affecting MLC phosphorylation. Moreover, contractile stimulation enhanced nestin phosphorylation at Thr-315 and the interaction of nestin with Plk1. Nestin KD also diminished phosphorylation of Plk1 and vimentin. The expression of T315A nestin mutant (alanine substitution at Thr-315) reduced the recruitment of cortactin and Pfn-1, actin polymerization, and HASM contraction without affecting MLC phosphorylation. Furthermore, Plk1 KD diminished nestin phosphorylation at this residue.
Nestin is an essential macromolecule that regulates actin cytoskeletal signaling via Plk1 in smooth muscle. Plk1 and nestin form an activation loop during contractile stimulation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 14
In Respiratory Research on 14 June 2023 by Wang, Y., Liao, G., et al.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cell Biology
In Cells on 29 September 2022 by Wang, R., Khan, S., et al.
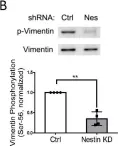
Airway smooth muscle cell migration plays a role in the progression of airway remodeling, a hallmark of allergic asthma. However, the mechanisms that regulate cell migration are not yet entirely understood. Nestin is a class VI intermediate filament protein that is involved in the proliferation/regeneration of neurons, cancer cells, and skeletal muscle. Its role in cell migration is not fully understood. Here, nestin knockdown (KD) inhibited the migration of human airway smooth muscle cells. Using confocal microscopy and the Imaris software, we found that nestin KD attenuated focal adhesion sizes during cell spreading. Moreover, polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) and vimentin phosphorylation at Ser-56 have been previously shown to affect focal adhesion assembly. Here, nestin KD reduced Plk1 phosphorylation at Thr-210 (an indication of Plk1 activation), vimentin phosphorylation at Ser-56, the contacts of vimentin filaments to paxillin, and the morphology of focal adhesions. Moreover, the expression of vimentin phosphorylation-mimic mutant S56D (aspartic acid substitution at Ser-56) rescued the migration, vimentin reorganization, and focal adhesion size of nestin KD cells. Together, our results suggest that nestin promotes smooth muscle cell migration. Mechanistically, nestin regulates Plk1 phosphorylation, which mediates vimenitn phosphorylation, the connection of vimentin filaments with paxillin, and focal adhesion assembly.
-
ICC-IF
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cell Biology
In Frontiers in Immunology on 9 April 2022 by Janjic, B. M., Kulkarni, A., et al.
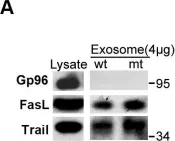
The essential innate immunity effector cells, natural killer and dendritic cells, express multiple plasma membrane-associated tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily (TNFSF) ligands that, through simultaneous and synergistic engagement, mediate anti-cancer cytotoxicity. Here, we report that circulating B cells, mediators of adaptive humoral immunity, also mediate this innate anti-cancer immune mechanism. We show that resting human B cells isolated from peripheral blood induce apoptosis of, and efficiently kill a large variety of leukemia and solid tumor cell types. Single-cell RNA sequencing analyses indicate, and flow cytometry data confirm that B cells from circulation express transmembrane TNF, Fas ligand (FasL), lymphotoxin (LT) α1β2 and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). The cytotoxic activity can be inhibited by individual and, especially, combined blockade of the four transmembrane TNFSF ligands. B cells from tumor-bearing head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients express lower levels of TNFSF ligands and are less cytotoxic than those isolated from healthy individuals. In conclusion, we demonstrate that B cells have the innate capacity to mediate anti-cancer cytotoxicity through concurrent activity of multiple plasma membrane-associated TNFSF ligands, that this mechanism is deficient in cancer patients and that it may be part of a general cancer immunosurveillance mechanism.
Copyright © 2022 Janjic, Kulkarni, Ferris, Vujanovic and Vujanovic.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In The FASEB Journal on 1 September 2021 by Wang, Y., Liao, G., et al.
Actin cytoskeletal reorganization plays an important role in regulating smooth muscle contraction, which is essential for the modulation of various physiological functions including airway tone. The adapter protein Abi1 (Abelson interactor 1) participates in the control of smooth muscle contraction. The mechanisms by which Abi1 coordinates smooth muscle function are not fully understood. Here, we found that contractile stimulation elicited Abi1 acetylation in human airway smooth muscle (HASM) cells. Mutagenesis analysis identified lysine-416 (K416) as a major acetylation site. Replacement of K416 with Q (glutamine) enhanced the interaction of Abi1 with neuronal Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP), an important actin-regulatory protein. Moreover, the expression of K416Q Abi1 promoted actin polymerization and smooth muscle contraction without affecting myosin light chain phosphorylation at Ser-19 and vimentin phosphorylation at Ser-56. Furthermore, p300 is a lysine acetyltransferase that catalyzes acetylation of histone and non-histone proteins in various cell types. Here, we discovered that a portion of p300 was localized in the cytoplasm of HASM cells. Knockdown of p300 reduced the agonist-induced Abi1 acetylation in HASM cells and in mouse airway smooth muscle tissues. Smooth muscle conditional knockout of p300 inhibited actin polymerization and the contraction of airway smooth muscle tissues without affecting myosin light chain phosphorylation and vimentin phosphorylation. Together, our results suggest that contractile stimulation induces Abi1 acetylation via p300 in smooth muscle. Acetylation at K416 promotes the coupling of Abi1 with N-WASP, which facilitates actin polymerization and smooth muscle contraction. This is a novel acetylation-dependent regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in smooth muscle.
© 2021 The Authors. The FASEB Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cell Biology
In Frontiers in Immunology on 19 June 2018 by Wang, Z., Wang, Z., et al.
γδ T cell-based immunotherapy for osteosarcoma (OS) has shown limited success thus far. DNA-demethylating agents not only induce tumor cell death but also have an immunomodulatory function. In this study, we have assessed the potential benefit of combining decitabine (DAC, a DNA demethylation drug) and γδ T cells for OS immunotherapy. DAC increased the expression of natural killer group 2D (NKG2D) ligands (NKG2DLs), including major histocompatibility complex class I-related chains B (MICB) and UL16-binding protein 1 (ULBP1), on the OS cell surface, making the cells more sensitive to recognition and destruction by cytotoxic γδ T cells. The upregulation of MICB and ULBP1 was due to promoter DNA demethylation. Importantly, the killing of OS cells by γδ T cells was partially reversed by blocking the NKG2D receptor, suggesting that the γδ T cell-mediated cytolysis of DAC-pretreated OS cells was mainly dependent on the NKG2D-NKG2DL axis. The in vivo results were consistent with the in vitro results. In summary, DAC could upregulate MICB and ULBP1 expression in OS cells, and combination treatment involving γδ T cell immunotherapy and DAC could be used to enhance the cytotoxic killing of OS cells by γδ T cells.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Respir Res on 14 June 2023 by Wang, Y., Liao, G., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Respir Res by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In Cells on 29 September 2022 by Wang, R., Khan, S., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In PLoS One on 25 May 2012 by Wan, C., Fu, J., et al.
Fig.7.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3