Obesity, a growing pandemic in Western societies, significantly impacts metabolic health and contributes to visual disorders. While the systemic consequences of obesity, such as chronic inflammation and insulin resistance, are well-studied in adults, its early-life effects on retinal health remain underexplored. Using a maternal Western Diet (WD) exposure model, we investigated the developmental impact of early-life metabolic disturbances on retinal and cognitive function. Our findings reveal that WD exposure from gestation to early adulthood accelerates the onset of features resembling diabetic retinopathy, including increased retinal vascularization, inflammation, and compromised blood-retina barrier integrity, observed within just four months. Females exhibited heightened vulnerability, showing pronounced ocular defects such as anophthalmia, microphthalmia, and congenital cataracts. These results underscore a critical developmental window during which metabolic disruptions predispose to sex-specific retinal and neurovascular pathologies. This work bridges the link between pediatric and adult obesity, highlighting the urgent need for early interventions to mitigate long-term visual impairments that could further impair recognition memory.
Product Citations: 111
Early exposure to Western Diet exacerbates visual outcomes in female mice
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 3 December 2024 by Meseguer, D., Furtado, J., et al.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology on 1 December 2024 by Khan, S. T., Ahuja, N., et al.
The pancreatic vasculature displays tissue-specific physiological and functional adaptations that support rapid insulin response by β-cells. However, the digestive enzymes have made it difficult to characterize pancreatic endothelial cells (ECs), resulting in the poor understanding of pancreatic EC specialization.
Available single-nuclei/single-cell RNA-sequencing data sets were mined to identify pancreatic EC-enriched signature genes and to develop an integrated atlas of human pancreatic ECs. We validated the findings using independent single-nuclei/single-cell RNA-sequencing data, bulk RNA-sequencing data of isolated ECs, spatial transcriptomics data, immunofluorescence, and RNAScope of selected markers. The NK2 homeobox 3 (NKX2-3) TF (transcription factor) was expressed in HUVECs via gene transfection, and the expression of pancreatic EC-enriched signature genes was assessed via RT-qPCR.
We defined a pancreatic EC-enriched gene signature conserved across species and developmental stages that included genes involved in ECM (extracellular matrix) composition (COL15A1 and COL4A1), permeability and barrier function (PLVAP, EHD4, CAVIN3, HSPG2, ROBO4, HEG1, and CLEC14A), and key signaling pathways (S1P [sphingosine-1-phosphate], TGF-β [transforming growth factor-β], RHO/RAC GTPase [guanosine triphosphatase], PI3K/AKT [phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B], and PDGF [platelet-derived growth factor]). The integrated atlas revealed the vascular hierarchy within the pancreas. We identified and validated a specialized islet capillary subpopulation characterized by genes involved in permeability (PLVAP and EHD4), immune-modulation (FABP5, HLA-C, and B2M), ECM composition (SPARC and SPARCL1), IGF (insulin-like growth factor) signaling (IGFBP7), and membrane transport (SLCO2A1, SLC2A3, and CD320). Importantly, we identified NKX2-3 as a key TF enriched in pancreatic ECs. DNA-binding motif analysis found NKX2-3 motifs in ≈40% of the signature genes. Induction of NKX2-3 in HUVECs promoted the expression of the islet capillary EC-enriched genes PLVAP and SPARCL1.
We defined a validated transcriptomic signature of pancreatic ECs and uncovered their intratissue transcriptomic heterogeneity. We showed that NKX2-3 acts upstream of PLVAP and provided a single-cell online resource that can be further explored by the community: https://vasconcelos.shinyapps.io/pancreatic_endothelial/.
-
Cardiovascular biology
In Cancer Immunology Research on 3 September 2024 by Franzolin, G., Brundu, S., et al.
Semaphorin-plexin signaling plays a major role in the tumor microenvironment (TME). In particular, Semaphorin 4D (SEMA4D) has been shown to promote tumor growth and metastasis; however, the role of its high-affinity receptor Plexin-B1 (PLXNB1), which is expressed in the TME, is poorly understood. In this study, we directly targeted PLXNB1 in the TME of triple-negative murine breast carcinoma to elucidate its relevance in cancer progression. We found that primary tumor growth and metastatic dissemination were strongly reduced in PLXNB1-deficient mice, which showed longer survival. PLXNB1 loss in the TME induced a switch in the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) toward a pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype and enhanced the infiltration of CD8+ T lymphocytes both in primary tumors and in distant metastases. Moreover, PLXNB1 deficiency promoted a shift in the Th1/Th2 balance of the T-cell population and an antitumor gene signature, with the upregulation of Icos, Perforin-1, Stat3, and Ccl5 in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). We thus tested the translational relevance of TME reprogramming driven by PLXNB1 inactivation for responsiveness to immunotherapy. Indeed, in the absence of PLXNB1, the efficacy of anti-PD-1 blockade was strongly enhanced, efficiently reducing tumor growth and distant metastasis. Consistent with this, pharmacological PLXNB1 blockade by systemic treatment with a specific inhibitor significantly hampered breast cancer growth and enhanced the antitumor activity of the anti-PD-1 treatment in a preclinical model. Altogether, these data indicate that PLXNB1 signaling controls the antitumor immune response in the TME and highlight this receptor as a promising immune therapeutic target for metastatic breast cancers.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Molecular Metabolism on 1 September 2024 by Duquenne, M., Deligia, E., et al.
In Western society, high-caloric diets rich in fats and sugars have fueled the obesity epidemic and its related disorders. Disruption of the body-brain communication, crucial for maintaining glucose and energy homeostasis, arises from both obesogenic and genetic factors, leading to metabolic disorders. Here, we investigate the role of hypothalamic tanycyte shuttles between the pituitary portal blood and the third ventricle cerebrospinal fluid in regulating energy balance.
We inhibited vesicle-associated membrane proteins (VAMP1-3)-mediated release in tanycytes by expressing the botulinum neurotoxin type B light chain (BoNT/B) in a Cre-dependent manner in tanycytes. This was achieved by injecting either TAT-Cre in the third ventricle or an AAV1/2 expressing Cre under the control of the tanycyte-specific promoter iodothyronine deiodinase 2 into the lateral ventricle of adult male mice.
In male mice fed a standard diet, targeted expression of BoNT/B in adult tanycytes blocks leptin transport into the mediobasal hypothalamus and results in normal-weight central obesity, including increased food intake, abdominal fat deposition, and elevated leptin levels but no marked change in body weight. Furthermore, BoNT/B expression in adult tanycytes promotes fatty acid storage, leading to glucose intolerance and insulin resistance. Notably, these metabolic disturbances occur despite a compensatory increase in insulin secretion, observed both in response to exogenous glucose boluses in vivo and in isolated pancreatic islets. Intriguingly, these metabolic alterations are associated with impaired spatial memory in BoNT/B-expressing mice.
These findings underscore the central role of tanycytes in brain-periphery communication and highlight their potential implication in the age-related development of type 2 diabetes and cognitive decline. Our tanycytic BoNT/B mouse model provides a robust platform for studying how these conditions progress over time, from prediabetic states to full-blown metabolic and cognitive disorders, and the mechanistic contribution of tanycytes to their development. The recognition of the impact of tanycytic transcytosis on hormone transport opens new avenues for developing targeted therapies that could address both metabolic disorders and their associated cognitive comorbidities, which often emerge or worsen with advancing age.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Neuroscience
In Advanced Healthcare Materials on 1 July 2024 by Mahmoudi, N., Roque, M., et al.
Despite progress in bone tissue engineering, reconstruction of large bone defects remains an important clinical challenge. Here, a biomaterial designed to recruit bone cells, endothelial cells, and neuronal fibers within the same matrix is developed, enabling bone tissue regeneration. The bioactive matrix is based on modified elastin-like polypeptides (ELPs) grafted with laminin-derived adhesion peptides IKVAV and YIGSR, and the SNA15 peptide for retention of hydroxyapatite (HA) particles. The composite matrix shows suitable porosity, interconnectivity, biocompatibility for endothelial cells, and the ability to support neurites outgrowth by sensory neurons. Subcutaneous implantation leads to the formation of osteoid tissue, characterized by the presence of bone cells, vascular networks, and neuronal structures, while minimizing inflammation. Using a rat femoral condyle defect model, longitudinal micro-CT analysis is performed, which demonstrates a significant increase in the volume of mineralized tissue when using the ELP-based matrix compared to empty defects and a commercially available control (Collapat). Furthermore, visible blood vessel networks and nerve fibers are observed within the lesions after a period of two weeks. By incorporating multiple key components that support cell growth, mineralization, and tissue integration, this ELP-based composite matrix provides a holistic and versatile solution to enhance bone tissue regeneration.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Healthcare Materials published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
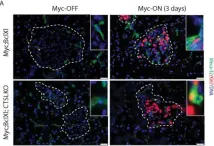
In PLoS One on 1 May 2015 by Brindle, N. R., Joyce, J. A., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
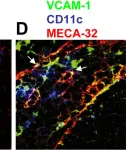
In PLoS Pathog on 19 September 2008 by Stanley, A. C., Dalton, J. E., et al.
Fig.5.D

-
ICC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2