The ovary is the first organ to age in the human body, affecting both fertility and overall health. However, the biological mechanisms underlying human ovarian aging remain poorly understood. Here we present a comprehensive single-nuclei multi-omics atlas of four young (ages 23-29 years) and four reproductively aged (ages 49-54 years) human ovaries. Our analyses reveal coordinated changes in transcriptomes and chromatin accessibilities across cell types in the ovary during aging, notably mTOR signaling being a prominent ovary-specific aging pathway. Cell-type-specific regulatory networks reveal enhanced activity of the transcription factor CEBPD across cell types in the aged ovary. Integration of our multi-omics data with genetic variants associated with age at natural menopause demonstrates a global impact of functional variants on gene regulatory networks across ovarian cell types. We nominate functional non-coding regulatory variants, their target genes and ovarian cell types and regulatory mechanisms. This atlas provides a valuable resource for understanding the cellular, molecular and genetic basis of human ovarian aging.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 62
Molecular and genetic insights into human ovarian aging from single-nuclei multi-omics analyses.
In Nature Aging on 1 February 2025 by Jin, C., Wang, X., et al.
-
Genetics
CRISPR screening uncovers nucleolar RPL22 as a heterochromatin destabilizer and senescence driver.
In Nucleic Acids Research on 28 October 2024 by Li, H. Y., Wang, M., et al.
Dysfunction of the ribosome manifests during cellular senescence and contributes to tissue aging, functional decline, and development of aging-related disorders in ways that have remained enigmatic. Here, we conducted a comprehensive CRISPR-based loss-of-function (LOF) screen of ribosome-associated genes (RAGs) in human mesenchymal progenitor cells (hMPCs). Through this approach, we identified ribosomal protein L22 (RPL22) as the foremost RAG whose deficiency mitigates the effects of cellular senescence. Consequently, absence of RPL22 delays hMPCs from becoming senescent, while an excess of RPL22 accelerates the senescence process. Mechanistically, we found in senescent hMPCs, RPL22 accumulates within the nucleolus. This accumulation triggers a cascade of events, including heterochromatin decompaction with concomitant degradation of key heterochromatin proteins, specifically heterochromatin protein 1γ (HP1γ) and heterochromatin protein KRAB-associated protein 1 (KAP1). Subsequently, RPL22-dependent breakdown of heterochromatin stimulates the transcription of ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), triggering cellular senescence. In summary, our findings unveil a novel role for nucleolar RPL22 as a destabilizer of heterochromatin and a driver of cellular senescence, shedding new light on the intricate mechanisms underlying the aging process.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
Tumour necrosis factor α regulates the miR-27a-3p-Sfrp1 axis in a mouse model of osteoporosis.
In Experimental Physiology on 1 July 2024 by Zhang, D. F., Jin, X. N., et al.
Osteoporosis is a metabolic bone disease that involves gradual loss of bone density and mass, thus resulting in increased fragility and risk of fracture. Inflammatory cytokines, such as tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α), inhibit osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), and several microRNAs are implicated in osteoporosis development. This study aimed to explore the correlation between TNF-α treatment and miR-27a-3p expression in BMSC osteogenesis and further understand their roles in osteoporosis. An osteoporosis animal model was established using ovariectomized (OVX) mice. Compared with Sham mice, the OVX mice had a significantly elevated level of serum TNF-α and decreased level of bone miR-27a-3p, and in vitro TNF-α treatment inhibited miR-27a-3p expression in BMSCs. In addition, miR-27a-3p promoted osteogenic differentiation of mouse BMSCs in vitro, as evidenced by alkaline phosphatase staining and Alizarin Red-S staining, as well as enhanced expression of the osteogenic markers Runx2 and Osterix. Subsequent bioinformatics analysis combined with experimental validation identified secreted frizzled-related protein 1 (Sfrp1) as a downstream target of miR-27a-3p. Sfrp1 overexpression significantly inhibited the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in vitro and additional TNF-α treatment augmented this inhibition. Moreover, Sfrp1 overexpression abrogated the promotive effect of miR-27a-3p on the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. Furthermore, the miR-27a-3p-Sfrp1 axis was found to exert its regulatory function in BMSC osteogenic differentiation via regulating Wnt3a-β-catenin signalling. In summary, this study revealed that TNF-α regulated a novel miR-27a-3p-Sfrp1 axis in osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. The data provide new insights into the development of novel therapeutic strategies for osteoporosis.
© 2024 The Authors. Experimental Physiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Physiological Society.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
In Theranostics on 10 June 2024 by Fu, Y., Zhang, M., et al.
Rationale: It has been emergingly recognized that apoptosis generates plenty of heterogeneous apoptotic vesicles (apoVs), which play a pivotal role in the maintenance of organ and tissue homeostasis. However, it is unknown whether apoVs influence postnatal ovarian folliculogenesis. Methods: Apoptotic pathway deficient mice including Fas mutant (Fasmut ) and Fas ligand mutant (FasLmut ) mice were used with apoV replenishment to evaluate the biological function of apoVs during ovarian folliculogenesis. Ovarian function was characterized by morphological analysis, biochemical examination and cellular assays. Mechanistical studies were assessed by combinations of transcriptomic and proteomic analysis as well as molecular assays. CYP17A1-Cre; Axin1fl /fl mice was established to verify the role of WNT signaling during ovarian folliculogenesis. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) mice and 15-month-old mice were used with apoV replenishment to further validate the therapeutic effects of apoVs based on WNT signaling regulation. Results: We show that systemic administration of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived apoptotic vesicles (MSC-apoVs) can ameliorate impaired ovarian folliculogenesis, PCOS phenotype, and reduced birth rate in Fasmut and FasLmut mice. Mechanistically, transcriptome analysis results revealed that MSC-apoVs downregulated a number of aberrant gene expression in Fasmut mice, which were enriched by kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis in WNT signaling and sex hormone biosynthesis. Furthermore, we found that apoptotic deficiency resulted in aberrant WNT/β-catenin activation in theca and mural granulosa cells, leading to responsive action of dickkopf1 (DKK1) in the cumulus cell and oocyte zone, which downregulated WNT/β-catenin expression in oocytes and, therefore, impaired ovarian folliculogenesis via NPPC/cGMP/PDE3A/cAMP cascade. When WNT/β-catenin was specially activated in theca cells of CYP17A1-Cre; Axin1fl /fl mice, the same ovarian impairment phenotypes observed in apoptosis-deficient mice were established, confirming that aberrant activation of WNT/β-catenin in theca cells caused the impairment of ovarian folliculogenesis. We firstly revealed that apoVs delivered WNT membrane receptor inhibitor protein RNF43 to ovarian theca cells to balance follicle homeostasis through vesicle-cell membrane integration. Systemically infused RNF43-apoVs down-regulated aberrantly activated WNT/β-catenin signaling in theca cells, contributing to ovarian functional maintenance. Since aging mice have down-regulated expression of WNT/β-catenin in oocytes, we used MSC-apoVs to treat 15-month-old mice and found that MSC-apoVs effectively ameliorated the ovarian function and fertility capacity of these aging mice through rescuing WNT/β-catenin expression in oocytes. Conclusion: Our studies reveal a previously unknown association between apoVs and ovarian folliculogenesis and suggest an apoV-based therapeutic approach to improve oocyte function and birth rates in PCOS and aging.
© The author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Preprint on Research Square on 11 September 2023 by Shen, X., Fu, D., et al.
Backgroud: During various stages of fracture healing, macrophages control mesenchymal stem cells' (BMSCs') proliferative behavior and osteogenic differentiation through varying polarization states. BMSCs also regulate their own osteogenic differentiation through the polarization state of macrophages to meet the requirements of tissue repair and osteogenic environment. A crucial role in cell proliferation, differentiation, and death is played by the evolutionarily conserved Notch signaling system. It also plays an important role in the osteogenic differentiation and regulation of macrophage polarization of BMSCs. The NOTCH signaling pathway typically plays a role in information exchange through direct contact between cells. Therefore, the Notch signaling pathway is involved in information exchange during direct contact between macrophages and BMSCs. Methods: A co culture system of mouse monocytic megacytic leukemia cell line (RAW264.7) and BMSC was established. RAW264.7 cells in logarithmic growth phase were divided into M0 group (unpolarized) and M1 group (LPS+INF γ induction), M2 group (IL4+IL13 induction), polarization status was detected by flow cytometry, and then BMSC were added to detect the Notch signaling pathway and the expression levels of RUNX2 gene and protein at different time points in each group. To further validate the role of the NOTCH signaling pathway in osteogenesis, we chose to apply the NOTCH signaling blocker RO4929097 to the co culture system of M2 and BMSC.According to whether blockers were used or not, they were divided into control group, M2 group, M2+blocker group, and blocker group. The transmission of the NOTCH signaling pathway in the interaction between M2 and BMSC as well as the production of Hes1 linked to the osteogenic gene RUNX2 were observed by blocking the NOTCH signaling pathway's conduction. At the same time, we detected the polarization of RAW264.7 cells in Mo and M1 groups to determine whether there was a change in the polarization state of RAW264.7 cells after the addition of BMSC. Results: : PCR and WB results showed that the NOTCH signaling pathway and osteogenic specific RUNX2 related protein and gene expression were basically synchronized: the expression of Jagged1 and Notch1 in M2 group was higher than that in M0 and M1 groups (p<0.05), while the expression level of M0 group was higher than that in M1 group (p<0.05). Hes1, as an associated gene and protein of Notch signaling pathway and Runx2, had the highest expression level with RUNX2 in M2 group (p<0.05), followed by M0, and the lowest in M1 group.This revealed that the Notch signaling pathway is involved in the bone immune regulatory effect between RAW264.7 and BMSC. After administering the NOTCH signaling blocker RO4929097, the M2 group had the highest expression of Notch signaling pathway related protein genes (p<0.05), followed by the control group (<0.05), and the blocker group had the lowest expression level (p<0.05), indicating a higher expression of the NOTCH signaling pathway between M2 cells and BMSC. The M2+blocker group had a higher expression level than the blocker group, suggesting that there are other pathways between M2 and BMSC that affect the conduction of the NOTCH signaling pathway. BMSC and RAW264.7 were co cultured, and flow cytometry analysis showed that the proportion of M2 like cells in the M0 group was higher than that in the M1 group. Conclusion: In the co culture system of macrophages and BMSC,the Notch signaling pathway promotes macrophage polarization towards M2 type, thereby regulating the osteogenic differentiation of BMSC and participating in the bone immune regulation of macrophages and mesenchymal stem cells.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In PLoS One on 11 August 2015 by Eichin, D., Laurila, J. P., et al.
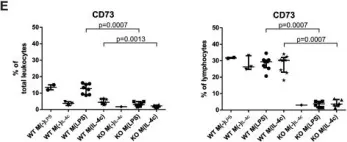
Fig.5.E

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In PLoS One on 11 August 2015 by Eichin, D., Laurila, J. P., et al.
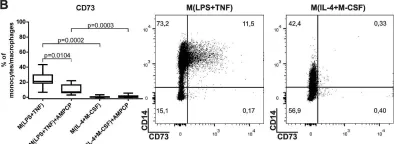
Fig.2.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In PLoS One on 11 August 2015 by Eichin, D., Laurila, J. P., et al.
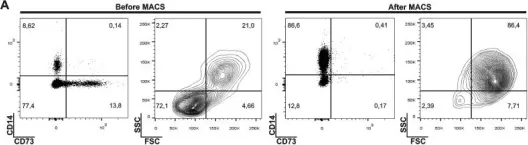
Fig.2.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3