Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are promising carriers for the delivery of a variety of chemical and biological drugs. However, their efficacy is limited by the lack of cellular specificity. Available methods to improve the tissue specificity of EVs predominantly rely on surface display of proteins and peptides, largely overlooking the dense glycocalyx that constitutes the outermost layer of EVs. In the present study, we report a reconfigurable glycoengineering strategy that can endogenously display glycans of interest on EV surface. Briefly, EV producer cells are genetically engineered to co-express a glycosylation domain (GD) inserted into the large extracellular loop of CD63 (a well-studied EV scaffold protein) and fucosyltransferase VII (FUT7) or IX (FUT9), so that the engineered EVs display the glycan of interest. Through this strategy, we showcase surface display of two types of glycan ligands, sialyl Lewis X (sLeX) and Lewis X, on EVs and achieve high specificity towards activated endothelial cells and dendritic cells, respectively. Moreover, the endothelial cell-targeting properties of sLeX-EVs were combined with the intrinsic therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), leading to enhanced attenuation of endothelial damage. In summary, this study presents a reconfigurable glycoengineering strategy to produce EVs with strong cellular specificity and highlights the glycocalyx as an exploitable trait for engineering EVs.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Product Citations: 12
Cell-specific targeting of extracellular vesicles through engineering the glycocalyx.
In Journal of Extracellular Vesicles on 1 December 2022 by Zheng, W., He, R., et al.
In STAR Protocols on 18 June 2021 by Nishihara, H., Gastfriend, B. D., et al.
We describe the extended endothelial cell culture method (EECM) for the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) into brain microvascular endothelial cell (BMEC)-like cells. EECM-BMEC-like cells resemble primary human BMECs in morphology, molecular junctional architecture, and diffusion barrier characteristics. A mature immune phenotype with proper endothelial adhesion molecule expression makes this model distinct from any other hPSC-derived in vitro blood-brain barrier (BBB) model and suitable to study immune cell migration across the BBB in a disease relevant and personalized fashion. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Lian et al. (2014), Nishihara et al. (2020a).
© 2021 The Author(s).
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In Frontiers in Immunology on 8 June 2021 by Chen, Y., Li, R., et al.
Severe cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) strongly hampered the broad clinical applicability of chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) therapy. Vascular endothelial activation has been suggested to contribute to the development of CRS and ICANS after CAR-T therapy. However, therapeutic strategies targeting endothelial dysfunction during CAR-T therapy have not been well studied yet. Here, we found that tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) produced by CAR-T cells upon tumor recognition and interleukin 1β (IL1β) secreted by activated myeloid cells were the main cytokines in inducing endothelial activation. Therefore, we investigated the potential effectiveness of TNFα and IL1β signaling blockade on endothelial activation in CAR-T therapy. The blockade of TNFα and IL1β with adalimumab and anti-IL1β antibody respectively, as well as the application of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) inhibitor, effectively ameliorated endothelial activation induced by CAR-T, tumor cells, and myeloid cells. Moreover, adalimumab and anti-IL1β antibody exerted synergistic effect on the prevention of endothelial activation induced by CAR-T, tumor cells, and myeloid cells. Our results indicate that TNFα and IL1β blockade might have therapeutic potential for the treatment of CAR-T therapy-associated CRS and neurotoxicity.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Li, Shang, Yang, Li, Wang and Wang.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Physiological Reports on 1 February 2021 by Beddek, K., Raffin, F., et al.
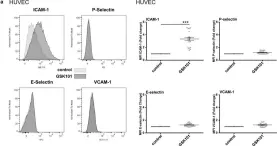
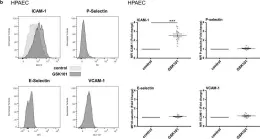
The Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) of endothelial cells contributes to many important functions including the regulation of Ca2+ homeostasis, cell volume, endothelial barrier permeability, and smooth muscle tone. However, its role in the transition of endothelial cells toward a pro-inflammatory phenotype has not been studied so far. Using both arterial and venous endothelial cells, we first show that the pharmacological activation of TRPV4 channels with GSK1016790A, a potent TRPV4 agonist, triggers robust and sustained Ca2+ increases, which are blocked by both TRPV4 antagonists HC067047 and RN9893. TRPV4 activation also triggers the actin cytoskeleton and adherens junction (VE-Cadherin) rearrangement in both arterial and venous endothelial cells and leads to rapid decreases of trans-endothelial electrical resistance. In addition to its effect on endothelial barrier integrity, TRPV4 activation selectively increases ICAM-1 surface expression in arterial and venous endothelial cells, due to the stimulation of ICAM-1 gene expression through the NF-κB transcription factor. TRPV4 channel activation also induced apoptosis of venous and arterial endothelial cells, while TRPV4 blockade reduced apoptosis, even in the absence of TRPV4 activation. As altered barrier integrity, increased adhesion molecule expression and apoptosis are hallmarks of the pro-inflammatory state of endothelial cells, our results indicate that TRPV4 channel activity can induce the transition of both venous and arterial endothelial cells toward a pro-inflammatory phenotype.
© 2021 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Fluids and Barriers of the CNS on 3 February 2020 by Nishihara, H., Soldati, S., et al.
The brain barriers establish compartments in the central nervous system (CNS) that significantly differ in their communication with the peripheral immune system. In this function they strictly control T-cell entry into the CNS. T cells can reach the CNS by either crossing the endothelial blood-brain barrier (BBB) or the epithelial blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier (BCSFB) of the choroid plexus (ChP).
Analysis of the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the migration of different human CD4+ T-cell subsets across the BBB versus the BCSFB.
Human in vitro models of the BBB and BCSFB were employed to study the migration of circulating and CNS-entry experienced CD4+ T helper cell subsets (Th1, Th1*, Th2, Th17) across the BBB and BCSFB under inflammatory and non-inflammatory conditions in vitro.
While under non-inflammatory conditions Th1* and Th1 cells preferentially crossed the BBB, under inflammatory conditions the migration rate of all Th subsets across the BBB was comparable. The migration of all Th subsets across the BCSFB from the same donor was 10- to 20-fold lower when compared to their migration across the BBB. Interestingly, Th17 cells preferentially crossed the BCSFB under both, non-inflamed and inflamed conditions. Barrier-crossing experienced Th cells sorted from CSF of MS patients showed migratory characteristics indistinguishable from those of circulating Th cells of healthy donors. All Th cell subsets could additionally cross the BCSFB from the CSF to ChP stroma side. T-cell migration across the BCSFB involved epithelial ICAM-1 irrespective of the direction of migration.
Our observations underscore that different Th subsets may use different anatomical routes to enter the CNS during immune surveillance versus neuroinflammation with the BCSFB establishing a tighter barrier for T-cell entry into the CNS compared to the BBB. In addition, CNS-entry experienced Th cell subsets isolated from the CSF of MS patients do not show an increased ability to cross the brain barriers when compared to circulating Th cell subsets from healthy donors underscoring the active role of the brain barriers in controlling T-cell entry into the CNS. Also we identify ICAM-1 to mediate T cell migration across the BCSFB.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Physiol Rep on 1 February 2021 by Beddek, K., Raffin, F., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Physiol Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
In Physiol Rep on 1 February 2021 by Beddek, K., Raffin, F., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Physiol Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2