Influenza virus infection is a significant cause of global mortality. However, the development of influenza vaccines that induce robust immune responses at the site of respiratory mucosal exposure has proven challenging. Here, we assessed immune responses and protective efficacy of a rhesus adenovirus serotype 52 (RhAd52) vectored influenza vaccine encoding the hemagglutinin (HA) glycoprotein from A/California/07/2009 administrated by systemic or mucosal routes of immunization. We observed robust and durable systemic and mucosal immunity, including IgA and tissue resident memory T cells in the respiratory mucosa, in mice that received the vaccine intranasally or intratracheally. In contrast, only systemic immune responses were observed in mice that received the vaccine intramuscularly. Moreover, a single intranasal or intratracheal dose of RhAd52-HA provided near complete protection against a lethal challenge with a mouse-adapted influenza virus strain, whereas intramuscular immunization with RhAd52-HA and mRNA-HA provided less robust protection. Our data demonstrate the importance of mucosal immunity for enhancing vaccine protection against influenza.
© 2025 The Authors.
Product Citations: 364
Mucosal boosting increases protective efficacy of an influenza vaccine in mice.
In IScience on 20 June 2025 by Wang, L., Chan, C. N., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
PD-1 blockade employed at the time CD8+ T cells are activated enhances their antitumor efficacy.
In Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer on 7 May 2025 by Moseman, J. E., Rastogi, I., et al.
We have previously shown that immune checkpoint receptors, including PD-1, are upregulated on T cells at the time of their activation, and that blockade of these receptors can improve the efficacy of antitumor vaccines. In the present study, we sought to determine whether, and by what mechanisms, the timing of PD-1 blockade with respect to vaccination affects antitumor T cell function.
TRAMP-C1 or E.G7-OVA tumor-bearing mice received PD-1 blockade at different timing intervals with a tumor-associated antigen vaccine. Tumor growth, survival, and immune-infiltrating populations were assessed. In vitro models of T cell activation using OT-I T cells and PD-(L)1 axis disruption with a PD-1 blocking antibody or PD-L1KO dendritic cells were used.
Mice receiving PD-1 blockade at the time of T cell activation with vaccine had better antitumor outcomes in comparison to mice receiving PD-1 blockade before or after immunization. T cells activated in vitro in the presence of PD-(L)1 axis disruption had a more differentiated, functional phenotype with decreased CD28 and CCR7 expression and increased production of the Tc1 cytokines IL-2, TNFα, and IFNγ. Intriguingly, a small subset of undifferentiated cells (CD28+) was of a stem-like Tc17 phenotype (IL-17α+, TCF1+). Tumor-bearing mice receiving T cells activated in the presence of PD-(L)1-axis disruption had better antitumor outcomes and a greater number of complete responses.
These data indicate that PD-1 blockade, when used with antitumor vaccines, acts primarily at the time of T cell activation, not exclusively within the tumor microenvironment. Consequently, PD-1 blockade may be best used when delivered concurrently with T cell activating agents such as vaccines.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Dysfunctional β-cell autophagy induces β-cell stress and enhances islet immunogenicity.
In Frontiers in Immunology on 13 February 2025 by Austin, M. C., Muralidharan, C., et al.
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors that trigger autoimmune-mediated destruction of pancreatic β-cells. Defects in β-cell stress response pathways such as autophagy may play an important role in activating and/or exacerbating the immune response in disease development. Previously, we discovered that β-cell autophagy is impaired prior to the onset of T1D, implicating this pathway in T1D pathogenesis.
To assess the role of autophagy in β-cell health and survival, and whether defects in autophagy render islets more immunogenic.
We knocked out the critical autophagy enzyme, ATG7, in the β-cells of mice (ATG7Δβ-cell) then monitored blood glucose, performed glucose tolerance tests, and evaluated bulk islet mRNA and protein. We also assessed MHC-I expression and presence of CD45+ immune cells in ATG7Δβ-cell islets and evaluated how impaired autophagy affects EndoC-βH1 HLA-I expression under basal and IFNα stimulated conditions. Lastly, we co-cultured ATG7Δβ-cell islet cells with diabetogenic BDC2.5 helper T cells and evaluated T cell activation.
We found that all ATG7Δβ-cell mice developed diabetes between 11-15 weeks of age. Gene ontology analysis revealed a significant upregulation of pathways involved in inflammatory processes, response to ER stress, and the ER-associated degradation pathway. Interestingly, we also observed upregulation of proteins involved in MHC-I presentation, suggesting that defective β-cell autophagy may alter the immunopeptidome, or antigen repertoire, and enhance β-cell immune visibility. In support of this hypothesis, we observed increased MHC-I expression and CD45+ immune cells in ATG7Δβ-cell islets. We also demonstrate that HLA-I is upregulated in EndoC β-cells when autophagic degradation is inhibited. This effect was observed under both basal and IFNα stimulated conditions. Conversely, a stimulator of lysosome acidification/function, C381, decreased HLA-I expression. Lastly, we showed that in the presence of islet cells with defective autophagy, there is enhanced BDC2.5 T cell activation.
Our findings demonstrate that β-cell autophagy is critical to cell survival/function. Defective β-cell autophagy induces ER stress, alters pathways of antigen production, and enhances MHC-I/HLA-I presentation to surveilling immune cells. Overall, our results suggest that defects in autophagy make β-cells more susceptible to immune attack and destruction.
Copyright © 2025 Austin, Muralidharan, Roy, Crowder, Piganelli and Linnemann.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In IScience on 17 January 2025 by Matsushima, R., Wakamatsu, E., et al.
A co-signaling receptor, 2B4, has dual effects in immune cells, but its actual functions in T cells remain elusive. Here, using super-resolution imaging technology with an immunological synapse model, we showed that 2B4 forms "2B4 microclusters" immediately after 2B4-CD48 binding. A lipid phosphatase, SHIP-1, subsequently combined with 2B4 to form coinhibitory signalosomes, leading to the suppression of cytokine production. An activating adapter, SLAM-associated protein (SAP), attenuated the clustering of SHIP-1 and recruited a kinase, Fyn, enhancing the Vav1 signaling pathway as costimulatory signalosomes. Furthermore, we found that a chimeric antigen receptor with a 2B4 tail (2B4-CAR) retained the original signal transduction mechanism of 2B4. With endogenous levels of SAP expression, 2B4-CAR-T cells exposed sufficient antitumor efficacy in vivo without excess cytokine production. Our results may help explain the biphasic feature of 2B4 in T cell responses from the viewpoint of the signalosome and provide a new candidate for CAR development.
© 2024 The Authors.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nature Communications on 14 January 2025 by Hawman, D. W., Tipih, T., et al.
The ongoing circulation of influenza A H5N1 in the United States has raised concerns of a pandemic caused by highly pathogenic avian influenza. Although the United States has stockpiled and is prepared to produce millions of vaccine doses to address an H5N1 pandemic, currently circulating H5N1 viruses contain multiple mutations within the immunodominant head domain of hemagglutinin (HA) compared to the antigens used in stockpiled vaccines. It is unclear if these stockpiled vaccines will need to be updated to match the contemporary H5N1 strains. Here we show that a replicating RNA vaccine expressing the HA of an H5N1 isolated from a US dairy cow confers complete protection against homologous lethal challenge in mice. A repRNA encoding the HA of a clade 1 H5 from 2004 (A/Vietnam/1203/2004) as utilized by some stockpiled vaccines, confers only partial protection. Our data highlight the utility of nucleic acid vaccines to be rapidly updated to match emergent viruses of concern while demonstrating that contemporary bovine H5N1 viruses can evade immunity elicited by historical HA antigens.
© 2025. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Veterinary Research
In PLoS One on 16 October 2016 by Collinson-Pautz, M. R., Slawin, K. M., et al.
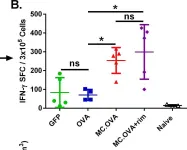
Fig.4.B

-
ELISpot
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In PLoS Negl Trop Dis on 7 January 2014 by Roupie, V., Pidot, S. J., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
ELISA
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Negl Trop Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In PLoS Negl Trop Dis on 7 January 2014 by Roupie, V., Pidot, S. J., et al.
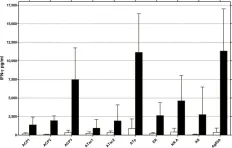
Fig.4.A

-
ELISA
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Negl Trop Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3