Age-related decline in the ability of bone marrow (BM) to recruit transplanted hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) limits the potential of HSPC-based medicine. Using in vivo imaging and manipulation combined with integrative metabolomic analyses, we show that, with aging, degradation of non-neurogenic acetylcholine disrupts the local Chrm5-eNOS-nitric oxide signaling, reducing arterial dilation and decreasing both BM blood flow and sinusoidal wall shear stress. Consequently, aging BM microenvironment impairs transendothelial migration of transplanted HSPCs, and their BM homing efficiency is reduced, mediated by decreased activation of Piezo1. Notably, pharmacological activation of Piezo1 improves HSPC homing efficiency and post-transplant survival of aged recipients. These findings suggest that age-related dysregulation of local arteries leads to impaired HSPC homing to BM by decreasing shear stress. Modulation of these mechanisms may improve the efficacy and safety of clinical transplantation in elderly patients.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 175
In Nature Communications on 1 July 2025 by Morikawa, T., Fujita, S., et al.
In Science Advances on 23 May 2025 by Adnani, L., Meehan, B., et al.
Aggressive brain tumors often exhibit immunologically 'cold' microenvironment, where the vascular barrier impedes effective immunotherapy in poorly understood ways. Tumor vasculature also plays a pivotal role in immunoregulation and antitumor immunity. Here, we show that small GTPase Rab27 controls the vascular morphogenesis and permeability for blood content and immune effectors. Thus, in Rab27a/b double knock out (Rab27-dKO) mice, the brain vasculature is abnormally scarce, while the blood vessels become dysmorphic and hyperpermeable in the context of brain tumors, including syngeneic glioblastoma. These defects are reflected in rearrangements of endothelial cell subpopulations with underlying diminution of venous endothelial subtype along with changes in gene and protein expression. Notably, Rab27-dKO brain endothelial cells exhibit deficient tight junctions, whereby they enable large-scale extravasation of cytotoxic T cells into the tumor mass. We show that Rab27-regulated vascular T cell infiltration can be exploited to enhance adoptive T cell therapy in syngeneic brain tumors.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Enhancing the potency of in vivo lentiviral vector mediated gene therapy to hepatocytes.
In Nature Communications on 23 May 2025 by Canepari, C., Milani, M., et al.
In vivo gene therapy to the liver using lentiviral vectors (LV) may represent a one-and-done therapeutic approach for monogenic diseases. Increasing LV gene therapy potency is crucial for reducing the effective doses, thus alleviating dose-dependent toxicities and facilitating manufacturing. LV-mediated liver transduction may be enhanced by positively selecting LV-transduced hepatocytes after treatment (a posteriori) or by augmenting the initial fraction of LV-targeted hepatocytes (a priori). We show here that the a posteriori enhancement increased transgene output without expansion of hepatocytes bearing LV genomic integrations near cancer genes, in mouse models of hemophilia, an inherited coagulation disorder. Furthermore, we enhanced hepatocyte transduction a priori in mice by transiently inhibiting antiviral pathways and/or through a fasting regimen. The most promising transduction-enhancer combination synergized with phagocytosis-shielded LV, resulting in a remarkable 40-fold increase in transgene output. Overall, our work highlights the potential of minimally invasive, cost-effective treatments capable of improving the potency of in vivo LV gene therapy to hepatocytes, in order to expand its applicability and ease clinical translation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
The impact of a high fat diet and platelet activation on pre-metastatic niche formation.
In Nature Communications on 2 April 2025 by Hergueta-Redondo, M., Sánchez-Redondo, S., et al.
There is active crosstalk between tumor cells and the tumor microenvironment during metastatic progression, a process that is significantly affected by obesity, particularly in breast cancer. Here we analyze the impact of a high fat diet (HFD) on metastasis, focusing on the role of platelets in the formation of premetastatic niches (PMNs). We find that a HFD provokes pre-activation of platelets and endothelial cells, promoting the formation of PMNs in the lung. These niches are characterized by increased vascular leakiness, platelet activation and overexpression of fibronectin in both platelets and endothelial cells. A HFD promotes interactions between platelets, tumor cells and endothelial cells within PMNs, enhancing tumor cell homing and metastasis. Importantly, therapeutic interventions like anti-platelet antibody administration or a dietary switch reduce metastatic cell homing and outgrowth. Moreover, blocking fibronectin reduces the interaction of tumor cells with endothelial cells. Importantly, when coagulation parameters prior to neoadjuvant treatment are considered, triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) female patients with reduced Partial Thromboplastin time (aPTT) had a significantly shorter time to relapse. These findings highlight how diet and platelet activation in pre-metastatic niches affect tumor cell homing and metastasis, suggesting potential therapeutic interventions and prognostic markers for TNBC patients.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Lymphatic collection and cell isolation from mouse models for multiomic profiling.
In Nature Protocols on 1 April 2025 by Sabatier, M., Solanki, A., et al.
Premetastatic cancer cells often spread from the primary lesion through the lymphatic vasculature and, clinically, the presence or absence of lymph node metastases impacts treatment decisions. However, little is known about cancer progression via the lymphatic system or of the effect that the lymphatic environment has on cancer progression. This is due, in part, to the technical challenge of studying lymphatic vessels and collecting lymph fluid. Here we provide a step-by-step procedure to collect both lymph and tumor-draining lymph in mouse models of cancer metastasis. This protocol has been adapted from established methods of lymph collection and was developed specifically for the collection of lymph from tumors. The approach involves the use of mice bearing melanoma or breast cancer orthotopic tumors. After euthanasia, the cisterna chyli and the tumor are exposed and viewed using a stereo microscope. Then, a glass cannula connected to a 1 mL syringe is inserted directly into the cisterna chyli or the tumor-draining lymphatics for collection of pure lymph. These lymph samples can be used to analyze the lymph-derived cancer cells using highly sensitive multiomics approaches to investigate the impact of the lymph environment during cancer metastasis. The procedure requires 2 h per mouse to complete and is suitable for users with minimal expertise in small animal handling and use of microsurgical tools under a stereo microscope.
© 2025. Springer Nature Limited.
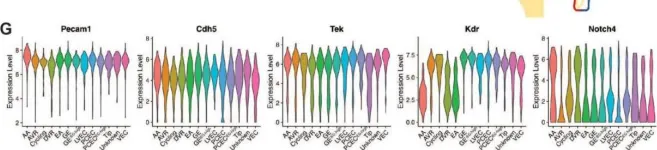
In Int J Mol Sci on 13 April 2024 by Zhou, A. X., Jeansson, M., et al.
Fig.1.G

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
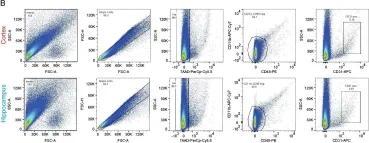
In Fluids Barriers CNS on 28 July 2021 by Schaffenrath, J., Huang, S. F., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Fluids Barriers CNS by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2