Atherosclerotic lesions mainly form in arterial areas exposed to low shear stress (LSS), where endothelial cells express a senescent and inflammatory phenotype. Conversely, areas exposed to high shear stress (HSS) are protected from plaque development. Endothelial extracellular vesicles (EVs) have been shown to regulate inflammation and senescence, and therefore play a crucial role in vascular homeostasis. Whilst previous studies have shown links between hemodynamic forces and EV release, the effects of shear stress on the release and uptake of endothelial EVs remains elusive. We aim to decipher the interplay between these processes in endothelial cells exposed to atheroprone or atheroprotective shear stress. Confluent HUVECs were exposed to LSS or HSS for 24 h. Large and small EVs were isolated from conditioned medium by centrifugation and size exclusion chromatography. They were characterised by TEM, Western blot, tunable resistive pulse sensing, flow cytometry and proteomics. Uptake experiments were performed using fluorescently-labelled EVs and differences between groups were assessed by flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. We found that levels of large and small EVs in conditioned media were fifty and five times higher in HSS than in LSS conditions, respectively. In vivo and in vitro uptake experiments revealed greater EV incorporation by cells exposed to LSS conditions. Additionally, endothelial LSS-EVs have a greater affinity for HUVECs than HSS-EVs or EVs derived from platelets, erythrocytes and leukocytes. Proteomic analysis revealed that LSS-EVs were enriched in adhesion proteins (PECAM1, MCAM), participating in EV uptake by endothelial cells. LSS-EVs also carried mitochondrial material, which may be implicated in elevating ROS levels in recipient cells. These findings suggest that shear stress influences EV biogenesis and uptake. Given the major role of EVs and shear stress in vascular health, deciphering the relation between these processes may yield innovative strategies for the early detection and treatment of endothelial dysfunction.
© 2024 The Authors. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Product Citations: 5
In Journal of Extracellular Vesicles on 1 October 2024 by Coly, P. M., Chatterjee, S., et al.
-
FC/FACS
In Cells on 13 September 2023 by Sekenova, A., Li, Y., et al.
Atherosclerosis (AS) is an inflammatory disease involving multiple factors in its initiation and development. In recent years, the potential application of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) for treating AS has been investigated. This study examined the effect of TNF-α preconditioning on MSCs' therapeutic efficacy in treating AS in ApoE KO mice. TNF-α-treated MSCs were administered to high-fat diet-treated ApoE KO mice. Cytokine and serum lipid levels were measured before and after treatment. Cryosections of the atherosclerotic aorta were stained with Oil-Red-O, and the relative areas of atherosclerotic lesions were measured. The level of Tregs were increased in TNF-α-MSC-treated animals compared to the MSCs group. In addition, the systemic administration of TNF-α-MSCs to ApoE KO mice reduced the level of proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IFN-γ and increased the level of the immunosuppressive IL-10 in the blood serum. Total cholesterol and LDL levels were decreased, and HDL levels were increased in the TNF-α-MSCs group of ApoE KO mice. A histological analysis showed that TNF-α-MSCs decreased the size of the atherosclerotic lesion in the aorta of ApoE KO mice by 38%, although there was no significant difference when compared with untreated MSCs. Thus, our data demonstrate that TNF-α-MSCs are more effective at treating AS than untreated MSCs.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cell Biology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Involucrin Modulates Vitamin D Receptor Activity in the Epidermis.
In The Journal of Investigative Dermatology on 1 June 2023 by Schmidt, A. D., Miciano, C., et al.
Terminally differentiated keratinocytes are critical for epidermal function and are surrounded by involucrin (IVL). Increased IVL expression is associated with a near-selective sweep in European populations compared with those in Africa. This positive selection for increased IVL in the epidermis identifies human adaptation outside of Africa. The functional significance is unclear. We hypothesize that IVL modulates the environmentally sensitive vitamin D receptor (VDR) in the epidermis. We investigated VDR activity in Ivl‒/‒ and wild-type mice using vitamin D agonist (MC903) treatment and comprehensively determined the inflammatory response using single-cell RNA sequencing and associated skin microbiome changes using 16S bacterial phylotyping. VDR activity and target gene expression were reduced in Ivl‒/‒ mouse skin, with decreased MC903-mediated skin inflammation and significant reductions in CD4+ T cells, basophils, macrophages, monocytes, and type II basal keratinocytes and an increase in suprabasal keratinocytes. Coinciding with the dampened MC903-mediated inflammation, the skin microbiota of Ivl‒/‒ mice was more stable than that of the wild-type mice, which exhibited an MC903-responsive increase in Bacteroidetes and a decrease in Firmicutes. Together, our studies in Ivl‒/‒ mice identify a functional role for IVL to positively impact VDR activity and suggest an emerging IVL/VDR paradigm for adaptation in the human epidermis.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 2 January 2023 by Coly, P. M., Chatterjee, S., et al.
Atherosclerotic lesions mainly form in arterial areas exposed to low shear stress (LSS), where endothelial cells express a senescent and inflammatory phenotype. Conversely, high shear stress (HSS) has atheroprotective effects on the endothelium. Endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles have been shown to regulate inflammation, senescence and angiogenesis and therefore play a crucial role in vascular homeostasis and disease. While previous studies have shown links between hemodynamic forces and extracellular vesicle release, the exact consequences of shear stress on the release and uptake of endothelial EVs remains elusive. Our aim is therefore to decipher the interplay between these processes in endothelial cells exposed to atheroprone or atheroprotective shear stress. Confluent human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were exposed to either LSS or HSS for 24 hours. Large and small EVs were isolated from conditioned medium by sequential centrifugation and size exclusion chromatography. They were characterized by TEM, Western blot analysis of EV markers, tunable resistive pulse sensing, flow cytometry and proteomics. Uptake experiments were performed using fluorescently-labeled EVs and differences between groups were assessed by flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. We found that levels of large and small EVs in HUVEC conditioned media were fifty and five times higher in HSS than in LSS conditions, respectively. In vivo and in vitro uptake experiments revealed greater EV incorporation by cells exposed to LSS conditions compared to HSS. Additionally, endothelial LSS-EVs appeared to have a greater affinity for HUVECs than HSS-EVs or EVs derived from platelets, red blood cells, granulocytes and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Proteomic analysis revealed that LSS-EVs were enriched in adhesion proteins such as PECAM1, MCAM, which were involved in EV uptake by endothelial cells. LSS-EVs also carried mitochondrial material, which may be involved in elevating reactive oxygen species levels in recipient cells. These findings suggest that endothelial shear stress has a significant impact during EV biogenesis and uptake. Given the major role of EVs and shear stress in vascular health, deciphering the relation between these processes may yield innovative strategies for the early detection and treatment of endothelial dysfunction.
In PLoS ONE on 23 May 2013 by Bohr, S., Patel, S. J., et al.
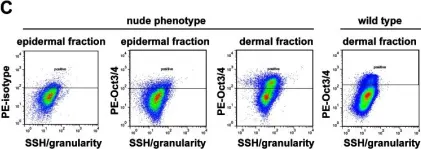
Hair cycling is a prime example of stem cell dependent tissue regeneration and replenishment, and its regulatory mechanisms remain poorly understood. In the present study, we evaluated the effect of a blockage in terminal keratinocytic lineage differentiation in the Foxn1(-/-) nude phenotype on the epithelial progeny. Most notably we found a constitutive upregulation of LIM homeobox protein 2 (Lhx2), a marker gene of epithelial stem cellness indispensible for hair cycle progression. However, histological evidence along with an erratic, acyclic rise of otherwise suppressed CyclinD1 levels along with several key markers of keratinocyte lineage differentiation indicate a frustrated expansion of epithelial stem cell niches in skin. In addition, CD49f/CD34/CD200-based profiling demonstrated highly significant shifts in subpopulations of epithelial progeny. Intriguingly this appeared to include the expansion of Oct4+ stem cells in dermal fractions of skin isolates in the Foxn1 knock-out opposed to wild type. Overall our findings indicate that the Foxn1(-/-) phenotype has a strong impact on epithelial progeny and thus offers a promising model to study maintenance and regulation of stem cell niches within skin not feasible in other in vitro or in vivo models.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In PLoS One on 23 May 2013 by Bohr, S., Patel, S. J., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1