In aging, skeletal muscle strength and regenerative capacity decline, due in part to functional impairment of muscle stem cells (MuSCs), yet the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Here, we capitalize on mass cytometry to identify high CD47 expression as a hallmark of dysfunctional MuSCs (CD47hi) with impaired regenerative capacity that predominate with aging. The prevalent CD47hi MuSC subset suppresses the residual functional CD47lo MuSC subset through a paracrine signaling loop, leading to impaired proliferation. We uncover that elevated CD47 levels on aged MuSCs result from increased U1 snRNA expression, which disrupts alternative polyadenylation. The deficit in aged MuSC function in regeneration can be overcome either by morpholino-mediated blockade of CD47 alternative polyadenylation or antibody blockade of thrombospondin-1/CD47 signaling, leading to improved regeneration in aged mice, with therapeutic implications. Our findings highlight a previously unrecognized age-dependent alteration in CD47 levels and function in MuSCs, which underlies reduced muscle repair in aging.Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 49
In Cell Stem Cell on 1 December 2022 by Porpiglia, E., Mai, T., et al.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
MARVEL domain containing CMTM4 affects CXCR4 trafficking.
In Molecular Biology of the Cell on 1 November 2022 by Bona, A., Seifert, M., et al.
The MARVEL proteins CMTM4 and CMTM6 control PD-L1, thereby influencing tumor immunity. We found that defective zebrafish cmtm4 slowed the development of the posterior lateral line (pLL) by altering the Cxcr4b gradient across the pLL primordium (pLLP). Analysis in mammalian cells uncovered that CMTM4 interacted with CXCR4, altering its glycosylation pattern, but did not affect internalization or degradation of CXCR4 in the absence of its ligand CXCL12. Synchronized release of CXCR4 from the endoplasmic reticulum revealed that CMTM4 slowed CXCR4 trafficking from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane without affecting overall cell surface expression. Altered CXCR4 trafficking reduced ligand-induced CXCR4 degradation and affected AKT but not ERK1/2 activation. CMTM4 expression, in contrast to that of CXCR4, correlated with the survival of patients with renal cell cancer in the TCGA cohort. Furthermore, we observed that cmtm4 depletion promotes the separation of cells from the pLLP cell cluster in zebrafish embryos. Collectively, our findings indicate that CMTM4 exerts general roles in the biosynthetic pathway of cell surface molecules and seems to affect CXCR4-dependent cell migration.
-
FC/FACS
-
Cell Biology
Role of the CXCR4-LASP1 Axis in the Stabilization of Snail1 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.
In Cancers on 21 August 2020 by Subramaniyan, B., Sridharan, S., et al.
The CXCL12-CXCR4 axis plays a vital role in many steps of breast cancer metastasis, but the molecular mechanisms have not been fully elucidated. We previously reported that activation of CXCR4 by CXCL12 promotes the nuclear localization of LASP1 (LIM and SH3 protein 1). The nuclear LASP1 then interacts with Snail1 in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell lines. In this study, we report that the nuclear accumulation and retention of Snail1 was dependent on an increase in nuclear LASP1 levels driven by active CXCR4. The CXCR4-LASP1 axis may directly regulate the stabilization of nuclear Snail1, by upregulating nuclear levels of pS473-Akt, pS9-GSK-3β, A20, and LSD1. Furthermore, the activation of CXCR4 induced association of LASP1 with Snail1, A20, GSK-3β, and LSD1 endogenously. Thus, nuclear LASP1 may also regulate protein-protein interactions that facilitate the stability of Snail1. Genetic ablation of LASP1 resulted in the mislocalization of nuclear Snail1, loss of the ability of TNBC cells to invade Matrigel and a dysregulated expression of both epithelial and mesenchymal markers, including an increased expression of ALDH1A1, a marker for epithelial breast cancer stem-like cells. Our findings reveal a novel role for the CXCR4-LASP1 axis in facilitating the stability of nuclear localized Snail1.
-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
In Molecular Therapy on 4 December 2019 by Melo, M., Porter, E., et al.
RNA replicons are a promising platform technology for vaccines. To evaluate the potential of lipid nanoparticle-formulated replicons for delivery of HIV immunogens, we designed and tested an alphavirus replicon expressing a self-assembling protein nanoparticle immunogen, the glycoprotein 120 (gp120) germline-targeting engineered outer domain (eOD-GT8) 60-mer. The eOD-GT8 immunogen is a germline-targeting antigen designed to prime human B cells capable of evolving toward VRC01-class broadly neutralizing antibodies. Replicon RNA was encapsulated with high efficiency in 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane (DOTAP)-based lipid nanoparticles, which provided effective delivery in the muscle and expression of luciferase lasting ∼30 days in normal mice, contrasting with very brief and low levels of expression obtained by delivery of equivalent modified mRNA (modRNA). eOD-GT8 60-mer-encoding replicons elicited high titers of gp120-specific antibodies following a single injection in mice, and increased levels of antigen-specific germinal center B cells compared with protein immunization. Immunization of transgenic mice expressing human inferred-germline VRC01 heavy chain B cell receptors that are the targets of the eOD antigen led to priming of B cells and somatic hypermutation consistent with VRC01-class antibody development. Altogether, these data suggest replicon delivery of Env immunogens may be a promising avenue for HIV vaccine development.
Copyright © 2019 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Protective role of B cells in sterile particulate-induced lung injury.
In JCI Insight on 16 May 2019 by Atif, S. M., Mack, D. G., et al.
Susceptibility to chronic beryllium (Be) disease is linked to HLA-DP molecules possessing a glutamic acid at the 69th position of the β-chain (βGlu69), with the most prevalent βGlu69-containing molecule being HLA-DP2. We have previously shown that HLA-DP2 transgenic (Tg) mice exposed to Be oxide (BeO) develop mononuclear infiltrates in a peribronchovascular distribution and a beryllium-specific, HLA-DP2-restricted CD4+ T cell response. In addition to T cells, B cells constituted a major portion of infiltrated leukocytes in the lung of BeO-exposed HLA-DP2 Tg mice and sequester BeO particles within ectopic lymphoid aggregates and granulomas. B cell depletion was associated with a loss of lymphoid aggregates and granulomas as well as a significant increase in lung injury in BeO-exposed mice. The protective role of B cells was innate in origin, and BeO-induced B cell recruitment to the lung was dependent on MyD88 signaling. Similar to BeO-exposed HLA-DP2 mice, B cells also accumulate in the lungs of CBD subjects, located at the periphery and surrounding the granuloma. Overall, our data suggest a novel modulatory role for B cells in the protection of the lung against sterile particulate exposure, with B cell recruitment to the inflamed lung occurring in an antigen-independent and MyD88-dependent manner.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
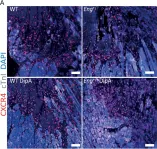
In PLoS One on 19 December 2017 by Dingenouts, C. K. E., Bakker, W., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1