Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes lower respiratory tract infections with significant morbidity and mortality at the extremes of age. Vaccines based on the viral fusion protein are approved for adults over 60, but infant protection relies on passive immunity via antibody transfer or maternal vaccination. An infant vaccine that rapidly elicits protective antibodies would fulfill a critical unmet need. Antibodies arising from the VH3-21/VL1-40 gene pairing can neutralize RSV without the need for affinity maturation, making them attractive to target through vaccination. Here, we develop an anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibody (ai-mAb) immunogen that is specific for unmutated VH3-21/VL1-40 B cell receptors (BCRs). The ai-mAb efficiently engages B cells with bona fide target BCRs and does not activate off-target non-neutralizing B cells, unlike recombinant pre-fusion (preF) protein used in current RSV vaccines. These results establish proof of concept for using an ai-mAb-derived vaccine to target B cells hardwired to produce RSV-neutralizing antibodies.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 11
Targeting RSV-neutralizing B cell receptors with anti-idiotypic antibodies.
In Cell Reports on 22 October 2024 by Scharffenberger, S. C., Wan, Y. H., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Development of a VRC01-class germline targeting immunogen derived from anti-idiotypic antibodies.
In Cell Reports on 4 May 2021 by Seydoux, E., Wan, Y. H., et al.
An effective HIV-1 vaccine will likely need to elicit broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs). Broad and potent VRC01-class bNAbs have been isolated from multiple infected individuals, suggesting that they could be reproducibly elicited by vaccination. Several HIV-1 envelope-derived germline-targeting immunogens have been designed to engage naive VRC01-class precursor B cells. However, they also present off-target epitopes that could hinder development of VRC01-class bNAbs. We characterize a panel of anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibodies (ai-mAbs) raised against inferred-germline (iGL) VRC01-class antibodies. By leveraging binding, structural, and B cell sorting data, we engineered a bispecific molecule derived from two ai-mAbs; one specific for VRC01-class heavy chains and one specific for VRC01-class light chains. The bispecific molecule preferentially activates iGL-VRC01 B cells in vitro and induces specific antibody responses in a murine adoptive transfer model with a diverse polyclonal B cell repertoire. This molecule represents an alternative non-envelope-derived germline-targeting immunogen that can selectively activate VRC01-class precursors in vivo.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Anti-idiotypic antibodies elicit anti-HIV-1-specific B cell responses.
In The Journal of Experimental Medicine on 7 October 2019 by Dosenovic, P., Pettersson, A. K., et al.
Human anti-HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) protect against infection in animal models. However, bNAbs have not been elicited by vaccination in diverse wild-type animals or humans, in part because B cells expressing the precursors of these antibodies do not recognize most HIV-1 envelopes (Envs). Immunogens have been designed that activate these B cell precursors in vivo, but they also activate competing off-target responses. Here we report on a complementary approach to expand specific B cells using an anti-idiotypic antibody, iv8, that selects for naive human B cells expressing immunoglobulin light chains with 5-amino acid complementarity determining region 3s, a key feature of anti-CD4 binding site (CD4bs)-specific VRC01-class antibodies. In mice, iv8 induced target cells to expand and mature in the context of a polyclonal immune system and produced serologic responses targeting the CD4bs on Env. In summary, the results demonstrate that an anti-idiotypic antibody can specifically recognize and expand rare B cells that express VRC01-class antibodies against HIV-1.
© 2019 Dosenovic et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Coordinated balance of Rac1 and RhoA plays key roles in determining phagocytic appetite.
In PLoS ONE on 5 April 2017 by Kim, S. Y., Kim, S., et al.
The removal of unwanted or damaged cells by phagocytes is achieved via a finely regulated cleaning process called efferocytosis. To characterize the mechanisms through which phagocytes control the intake of apoptotic cells, we investigated how the phagocyte's appetite for engulfed cells may be coordinated by RhoA and Rac1 in the phagocytic cup. We used FRET biosensors to visualize the spatiotemporal dynamics of Rho-family GTPases, and found that RhoA, which is known to be downregulated during phagocytosis, was transiently upregulated at the phagocytic cup immediately prior to ingestion. Conversely, Rac1 was upregulated during the engulfment process and then downregulated prior to phagosomal maturation. Moreover, disturbance of the dynamic activities of RhoA led to uncontrolled engulfment, such as fast and undiscerning eating. Our results reveal that the temporal activity of RhoA GTPase alters the Rac1/RhoA balance at the phagocytic cup prior to ingestion, and that this plays a distinct role in orchestrating efferocytosis, with RhoA modulating the rate of engulfment to ensure that the phagocyte engulfs an appropriate amount of the correct material.
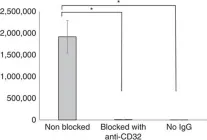
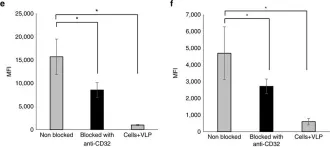
Extinct type of human parvovirus B19 persists in tonsillar B cells.
In Nature Communications on 4 April 2017 by Pyöriä, L., Toppinen, M., et al.
Parvovirus B19 (B19V) DNA persists lifelong in human tissues, but the cell type harbouring it remains unclear. We here explore B19V DNA distribution in B, T and monocyte cell lineages of recently excised tonsillar tissues from 77 individuals with an age range of 2-69 years. We show that B19V DNA is most frequent and abundant among B cells, and within them we find a B19V genotype that vanished from circulation >40 years ago. Since re-infection or re-activation are unlikely with this virus type, this finding supports the maintenance of pathogen-specific humoral immune responses as a consequence of B-cell long-term survival rather than continuous replenishment of the memory pool. Moreover, we demonstrate the mechanism of B19V internalization to be antibody dependent in two B-cell lines as well as in ex vivo isolated tonsillar B cells. This study provides direct evidence for a cell type accountable for B19V DNA tissue persistence.
-
IF
-
Block
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nat Commun on 4 April 2017 by Pyöriä, L., Toppinen, M., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
Block
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In Nat Commun on 4 April 2017 by Pyöriä, L., Toppinen, M., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
Block
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In Nat Commun on 4 April 2017 by Pyöriä, L., Toppinen, M., et al.
Fig.2.E

-
Block
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3