Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors are a widely recognized and valued treatment option for patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T cell lymphomas (PTCL). Romidepsin is a relatively selective Class I HDAC inhibitor originally approved for patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) and subsequently R/R PTCL. Unfortunately, the FDA approval of romidepsin for R/R PTCL was withdrawn due to a negative Phase 4 post-marketing requirement (PMR), diminishing further the treatment options for patients with PTCL. Herein we describe the development of a first-in-class polymer nanoparticle of romidepsin (Nanoromidepsin) using an innovative amphiphilic di-block copolymer-based nanochemistry platform. Nanoromidepsin exhibited superior pharmacologic disposition, with improved tolerability and safety in murine models of T-cell lymphoma. Nanoromidepsin also exhibited superior anti-tumor efficacy in multiple models including in vitro T cell lymphoma (TCL) cell lines, ex vivo LGL leukemia primary patient samples, and murine TCL xenografts. Nanoromidepsin demonstrated greater accumulation in tumors and a statistically significant improvement in overall survival (OS) compared to romidepsin in murine xenograft models. These findings collectively justify the clinical development of Nanoromidepsin in patients with T-cell malignancies.
Product Citations: 12
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 19 July 2024 by Pal, I., Illendula, A., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) on 30 May 2023 by Cartwright, B. M., Fox, S. J., et al.
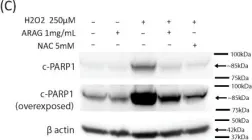
Current treatments for deep tissue burns are limited, and most serve only to enhance hydration or prevent bacterial growth. This leaves burn healing dependent on slow natural processes to debride the wound and reestablish the epidermal and dermal layers of the skin. Infections are well known to destabilize this process through a variety of mechanisms, most notably through increased inflammation and the resulting oxidative stress. In this study, we show that ARAG (an antioxidant-rich antimicrobial gel) can suppress the growth of multiple bacteria commonly found to infect burns (Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus vulgaris, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus aureus). This inhibition is comparable to that conferred by silver ion release from burn dressings such as Mepilex-Ag. We further show, using a porcine model for deep partial-thickness burns, that ARAG allows for enhanced wound healing over Mepilex-Ag, the current standard of care. Histological findings indicate this is likely due to increased wound debridement and dampening of late inflammatory processes, leading to more balanced physiologic healing. Taken together, these findings show promise for ARAG as a superior alternative to the current standard of care.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Obesity-induced galectin-9 is a therapeutic target in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
In Nature Communications on 3 March 2022 by Lee, M., Hamilton, J. A. G., et al.
The incidence of obesity is rising with greater than 40% of the world's population expected to be overweight or suffering from obesity by 2030. This is alarming because obesity increases mortality rates in patients with various cancer subtypes including leukemia. The survival differences between lean patients and patients with obesity are largely attributed to altered drug pharmacokinetics in patients receiving chemotherapy; whereas, the direct impact of an adipocyte-enriched microenvironment on cancer cells is rarely considered. Here we show that the adipocyte secretome upregulates the surface expression of Galectin-9 (GAL-9) on human B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells (B-ALL) which promotes chemoresistance. Antibody-mediated targeting of GAL-9 on B-ALL cells induces DNA damage, alters cell cycle progression, and promotes apoptosis in vitro and significantly extends the survival of obese but not lean mice with aggressive B-ALL. Our studies reveal that adipocyte-mediated upregulation of GAL-9 on B-ALL cells can be targeted with antibody-based therapies to overcome obesity-induced chemoresistance.
© 2022. The Author(s).
-
WB
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Viruses on 20 October 2021 by Mendonça-Vieira, L. R., Aníbal-Silva, C. E., et al.
ZIKV is a highly neurotropic virus that can cause the death of infected neuroprogenitor cells through mitochondrial damage and intrinsic apoptotic signaling. In this context, the role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in neuronal cell death caused by ZIKV still remains elusive.
We aimed at evaluating the role of these cellular components in the death of human undifferentiated neuroblastoma cell line infected with ZIKV.
ZIKV infection resulted in the extensive death of SH-SY5Y cells with the upregulation of several genes involved in survival and apoptotic responses as well as the colocalization of mitochondrial staining with ZIKV Envelope (E) protein. Notably, levels of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) were not altered during ZIKV infection in undifferentiated SH-SY5Y cells, and consistent with these results, the treatment of infected cells with the widely studied ROS scavenger N-acetylcysteine (NAC) did not prevent cell death in these cells.
Altogether, our results suggest that excessive ROS production is not the main trigger of SH-SY5Y cells death in ZIKV infection.
-
FC/FACS
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Degradation of CCNK/CDK12 is a druggable vulnerability of colorectal cancer.
In Cell Reports on 20 July 2021 by Dieter, S. M., Siegl, C., et al.
Novel treatment options for metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) are urgently needed to improve patient outcome. Here, we screen a library of non-characterized small molecules against a heterogeneous collection of patient-derived CRC spheroids. By prioritizing compounds with inhibitory activity in a subset of-but not all-spheroid cultures, NCT02 is identified as a candidate with minimal risk of non-specific toxicity. Mechanistically, we show that NCT02 acts as molecular glue that induces ubiquitination of cyclin K (CCNK) and proteasomal degradation of CCNK and its complex partner CDK12. Knockout of CCNK or CDK12 decreases proliferation of CRC cells in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. Interestingly, sensitivity to pharmacological CCNK/CDK12 degradation is associated with TP53 deficiency and consensus molecular subtype 4 in vitro and in patient-derived xenografts. We thus demonstrate the efficacy of targeted CCNK/CDK12 degradation for a CRC subset, highlighting the potential of drug-induced proteolysis for difficult-to-treat types of cancer.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
FC/FACS
-
Cancer Research
In Antioxidants (Basel) on 30 May 2023 by Cartwright, B. M., Fox, S. J., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Antioxidants (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1