Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT) is a prevalent autoimmune disease lacking a specific cure. This study endeavours to explore the role of PD-1 in modulating glycolysis during CD4+ T cell differentiation in HT. The lactate and glucose content in different groups was assessed using lactate and glucose assay kits. The tissue and cellular expression of HK2 and LDHA proteins was examined through Western blot analysis, while Glut1 expression and the ratio of Treg/Th17 cells were analysed using flow cytometry. The glycolysis levels in the HT group were higher than those in the control group. Additionally, the HTE group exhibited a decreased proportion of CD4+ CD25+ Tregs and an increased proportion of CD4+ TH17 cells compared to the healthy control group. Following the addition of PD-1 inhibitors to the activated group, both the glycolysis levels and CD4+ T cell differentiation showed improvement. PD-1 can regulate aberrant CD4+ T cell differentiation by modulating the glycolytic pathway.
© 2025 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Product Citations: 96
In Immunology on 1 September 2025 by Jiang, X., Luo, T., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Veterinary Research on 21 July 2025 by Bian, L. J., Tang, Y., et al.
Classical swine fever virus (CSFV) spreads in domestic and wild pig populations, causing significant economic losses in the swine industry. Despite the global implementation of live attenuated vaccines, CSFV remains a persistent threat, with sporadic outbreaks reported annually. A major limitation of the current vaccines is safety concerns and the inability to differentiate infected from vaccinated animals (DIVA). The development of DIVA-compliant vaccines is desirable for effectively controlling or eradicating classical swine fever (CSF). Here, we developed two lipid nanoparticle (LNP)-encapsulated mRNA vaccines encoding either the extracellular domain of the CSFV envelope protein E2 (E2-ECD) or its N-terminal 172-amino acid fragment (E2-ECD-N). Immunological assays in mice revealed high antigenicity and long-lasting protective antibody responses from a single dose of either the E2-ECD or E2-ECD-N mRNA vaccine. Notably, both the E2-ECD and E2-ECD-N mRNA vaccines induced robust T cell responses in mice. Furthermore, a single dose (100 μg) of the E2-ECD mRNA vaccine was sufficient to induce long-term (up to 4 months) protective immunity against CSFV infection in rabbits. Our findings highlight the potential of CSFV-E2-based mRNA vaccines as promising strategies for effective CSF prevention and control while enabling DIVA.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Veterinary Research
In Nature Communications on 1 July 2025 by Perrotta, M., Perrotta, S., et al.
Activated immune cells infiltrate the vasculature during the pathophysiology of hypertension by establishing a vascular-immune interface that contributes to blood pressure dysregulation and organ failure. Many observations indicate a key role of CD8+ T cells in hypertension but mechanisms regulating their activation and interplay with the cardiovascular system are still unknown. In murine model, here we show that a specific member of the phosphoinositide-3-kinases (PI3K) family of lipid kinases, PI3Kγ, is a key intracellular signaling of CD8+ T cells activation and RANTES/CCL5 secretion in hypertension: CCL5-CCR5 signaling is crucial for the establishment of the vascular-immune interface in peripheral organs, lastly contributing to CD8+ tissue infiltration, organ dysfunction and blood pressure elevation. Our studies identify PI3Kγ as a booster of effector CD8+ T cell function, even in the absence of external stimuli. Lastly, an enhanced PI3Kγ signaling mediates the bystander activation of CD8+ T cells and proves effective in transferring the hypertensive phenotype between mice.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Journal of Natural Medicines on 1 July 2025 by Zhu, X., Yin, G., et al.
Dendrobium huoshanense has received special attention for its advantages in the treatment of lung cancer, but the underlying molecular mechanisms are not yet well understood. First, we obtained 8 active ingredients and 159 effective action targets of Dendrobium huoshanense using network pharmacology, and searching target interactions through STRING, constructing the PPI network and KEGG, GO and Hallmark enrichment analysis. Then, we combined target's enrichment analysis and GSEA enrichment analysis of IL-35, indicating the mechanism of cDHPs for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) may be related to tight junction and NSCLC pathway. Further, FXR1 and ACTR3 were identified as core therapeutic targets, and high expression of FXR1 or ACTR3 was significantly associated with poor prognosis of patients. The analysis of single-cell data also indicated that the percentage of CD4-CTLA4-Treg cells may be increased by the expression of IL-35, resulting in a suppressive immune microenvironment. Next, In vivo experiment, we detected iTr35 by flow cytometry, detected IL-35 level by RT-PCR, Western blotting and ELISA, and detected NK cell activity to explore the immunomodulatory effects and anti-tumor mechanism of cDHPs. After cDHPs administration, the conversion of CD4+ T cells to iTr35 is inhibited, p35 and EBI3 in both protein and mRNA levels, the levels of IL-35 and IL-4 in serum decreased. The levels of IFN-γ, while the activity of NK cells in mice increased, enhancing the anti-tumor immune effect of the organism. Finally, analysis of sequencing data from the immunotherapy cohort of tumor-bearing mice obtained from the TISMO database shows that the combination of cDHPs and PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies improves effector and thus PD-1/PD-L1 antibody efficacy. These findings suggest that cDHPs inhibit NSCLC proliferation and immune escape via the FXR1-IL-35 axis signaling pathway.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology on 15 June 2025 by Feng, C. Z., Zhong, S. Q., et al.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a leading cause of cancer-related morbidity and mortality globally. Exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) are known to modulate tumor progression by influencing immune responses and vascular dynamics. However, the roles of specific exosomal miRNAs, such as miR-425-5p and miR-135b-3p, in CRC remain unclear.
To explore the specific roles and underlying mechanisms of exosomal miR-425-5p and miR-135b-3p in CRC progression.
Differentially expressed miRNAs were identified through microarray analysis of exosomes isolated from CRC tissues and adjacent normal mucosa. Functional roles of miR-425-5p and miR-135b-3p were evaluated in vitro using macrophage polarization, T cell differentiation, and vascular permeability assays, as well as in vivo tumor formation and metastasis experiments in nude mice. Validation experiments were performed using CRC cell lines (HCT116 and SW620).
Exosomal miR-425-5p and miR-135b-3p were significantly upregulated in CRC compared to normal tissues. Functional studies revealed that miR-425-5p promotes macrophage M2-like polarization and suppresses T cell proinflammatory responses, while miR-135b-3p enhances vascular permeability and angiogenesis. Inhibition of these miRNAs in CRC cell-derived exosomes significantly suppressed tumor growth and metastasis in nude mice, reprogramming the tumor microenvironment toward reduced angiogenesis and enhanced immune activation. Combined inhibition of both miRNAs resulted in the most pronounced effects.
Exosomal miR-425-5p and miR-135b-3p drive CRC progression by promoting immune suppression and vascular permeability. Their inhibition offers a promising strategy for modulating the tumor microenvironment and limiting CRC metastasis.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Front Behav Neurosci on 1 November 2022 by Escudero-Lara, A., Cabañero, D., et al.
Fig.2.B
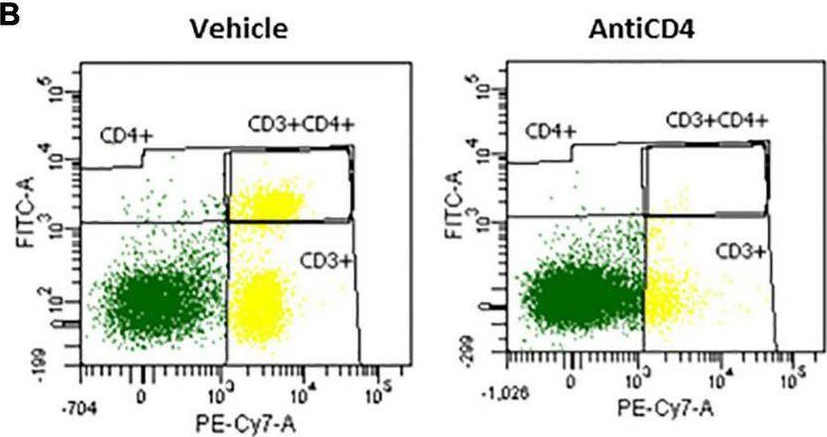
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Behav Neurosci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1