The epigenetic modification of histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) by the embryonic ectoderm development (EED) protein is closely associated with the regulation of transcriptional programs and is implicated in autoimmune diseases. However, the efficacy of targeting H3K27me3 for the treatment of neuroinflammation remains unclear. In this study, we demonstrate that systemic administration of an EED inhibitor diminishes the inflammatory response mediated by dendritic cells (DCs), thereby alleviating experimental autoimmune encephalitis (EAE), a representative mouse model of autoimmune diseases in the central nervous system (CNS). Our findings indicate that EED inhibitors suppress DC migration by upregulating genes in the WNT signaling pathway that are epigenetically marked by H3K27me3. Conversely, inhibiting the WNT pathway partially reverses the impaired DC migration caused by EED inhibitors. Additionally, the genetic deletion of Eed inhibits DC migration and effectively mitigates autoimmune symptoms and inflammatory infiltration into the CNS in EAE. These results highlight EED as a critical regulator of DC migration and suggest its potential as a therapeutic target for autoimmune disorders.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 268
In Journal of Neuroinflammation on 1 April 2025 by Hong, W., Ma, H., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. B on 1 March 2025 by Hong, W., Ma, H., et al.
Dendritic cells (DCs) serve as the primary antigen-presenting cells in autoimmune diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and exhibit distinct signaling profiles due to antigenic diversity. Type II collagen (CII) has been recognized as an RA-specific antigen; however, little is known about CII-stimulated DCs, limiting the development of RA-specific therapeutic interventions. In this study, we show that CII-stimulated DCs display a preferential gene expression profile associated with migration, offering a new perspective for targeting DC migration in RA treatment. Then, saikosaponin D (SSD) was identified as a compound capable of blocking CII-induced DC migration and effectively ameliorating arthritis. Optineurin (OPTN) is further revealed as a potential SSD target, with Optn deletion impairing CII-pulsed DC migration without affecting maturation. Function analyses uncover that OPTN prevents the proteasomal transport and ubiquitin-dependent degradation of C-C chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7), a pivotal chemokine receptor in DC migration. Optn-deficient DCs exhibit reduced CCR7 expression, leading to slower migration in CII-surrounded environment, thus alleviating arthritis progression. Our findings underscore the significance of antigen-specific DC activation in RA and suggest OPTN is a crucial regulator of CII-specific DC migration. OPTN emerges as a promising drug target for RA, potentially offering significant value for the therapeutic management of RA.
© 2025 The Authors.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 22 January 2025 by Fusilier, Z., Simon, F., et al.
During tumorigenesis, the extracellular matrix (ECM), which constitutes the structural scaffold of tissues, is profoundly remodeled. While the impact of such remodeling on tumor growth and invasion has been extensively investigated, much less is known on the consequences of ECM remodeling on tumor infiltration by immune cells. By combining tissue imaging and machine-learning, we here show that the localization of T lymphocytes and neutrophils, which orchestrate antitumor immune responses, can be predicted by defined topographical features of fibrillar collagen networks. We further show that these collagen topographies result from the activation of a fibrotic pathway controlled by the transcription factor Tcf4 upon depletion of tumor-associated macrophages at late tumor stages. This pathway promotes the deposition of collagen 3 by both tumor and stromal cells, resulting in intermingled collagen networks that favor intra-tumoral T cell and neutrophil localization. Importantly, analysis of human colorectal cancer public bulk RNAseq databases showed a strong correlation between Tcf4 and collagen 3 , as well as between the expression of these genes and tumor infiltration by T lymphocytes and neutrophils, attesting the clinical relevance of our findings. This study highlights the key structural role of macrophages on the tumor extracellular matrix and identifies collagen network topographies as a major regulator of tumor infiltration by immune cells.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In eLife on 22 November 2024 by Garnica, J., Solé, P., et al.
Chronic antigenic stimulation can trigger the formation of interleukin 10 (IL-10)-producing T-regulatory type 1 (TR1) cells in vivo. We have recently shown that murine T-follicular helper (TFH) cells are precursors of TR1 cells and that the TFH-to-TR1 cell transdifferentiation process is characterized by the progressive loss and acquisition of opposing transcription factor gene expression programs that evolve through at least one transitional cell stage. Here, we use a broad range of bulk and single-cell transcriptional and epigenetic tools to investigate the epigenetic underpinnings of this process. At the single-cell level, the TFH-to-TR1 cell transition is accompanied by both, downregulation of TFH cell-specific gene expression due to loss of chromatin accessibility, and upregulation of TR1 cell-specific genes linked to chromatin regions that remain accessible throughout the transdifferentiation process, with minimal generation of new open chromatin regions. By interrogating the epigenetic status of accessible TR1 genes on purified TFH and conventional T-cells, we find that most of these genes, including Il10, are already poised for expression at the TFH cell stage. Whereas these genes are closed and hypermethylated in Tconv cells, they are accessible, hypomethylated, and enriched for H3K27ac-marked and hypomethylated active enhancers in TFH cells. These enhancers are enriched for binding sites for the TFH and TR1-associated transcription factors TOX-2, IRF4, and c-MAF. Together, these data suggest that the TR1 gene expression program is genetically imprinted at the TFH cell stage.
© 2024, Garnica et al.
In Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. B on 1 October 2024 by Wang, L., Yin, H., et al.
Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F (TWHF) is a traditional Chinese medicine widely used in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), with triptolide (TP) as its main active ingredient. However, its side effects also induced by TP, especially hepatotoxicity and reproductive toxicity, largely limit its application in a subset of patients. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) developed for the treatment of SLE that deplete B cells by targeting B cell-expressing antigens, such as CD19, have failed in clinical trials, partly due to their poor efficacy in consuming B cells. Here, we report the development of a rationally designed antibody‒drug conjugate (ADC), CD19 mAb-TP conjugate, to alleviate the side effects of TWHF and simultaneously improve the therapeutic efficacy of CD19 mAb. The CD19 mAb-TP conjugate, which was named ADC-TP, selectively depleted B cell subsets both in vitro and in vivo and effectively alleviated disease symptoms in mouse lupus models with enhanced therapeutic efficacy than CD19 mAb and fewer side effects than TP. Our present study proposes a CD19 mAb‒TP conjugate strategy to mitigate the toxicity of TWHF while also enhancing the therapeutical efficacy of CD19 mAbs for the treatment of SLE, providing a feasible method for improving the current agents used for treating SLE.© 2024 The Authors.
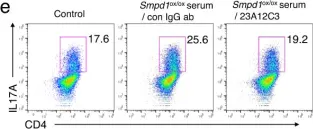
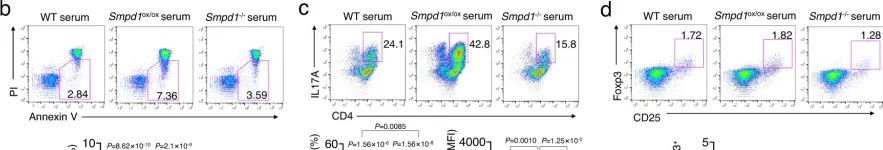
In Nat Commun on 24 March 2023 by Choi, B. J., Park, M. H., et al.
Fig.6.E

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
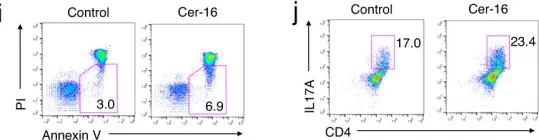
In Nat Commun on 24 March 2023 by Choi, B. J., Park, M. H., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Nat Commun on 24 March 2023 by Choi, B. J., Park, M. H., et al.
Fig.2.I

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
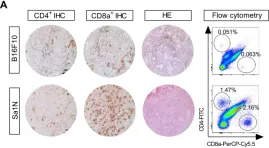
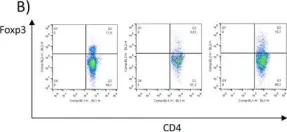
In Theranostics on 23 November 2019 by Kristensen, L. K., Fröhlich, C., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Theranostics by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
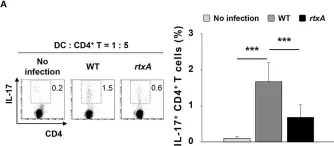
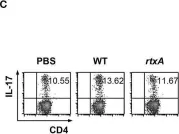
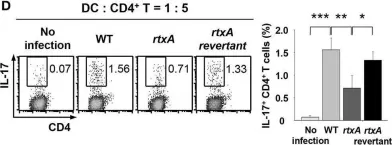
In Front Immunol on 5 October 2018 by Lee, A., Kim, M. S., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Front Immunol on 5 October 2018 by Lee, A., Kim, M. S., et al.
Fig.3.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Front Immunol on 5 October 2018 by Lee, A., Kim, M. S., et al.
Fig.4.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
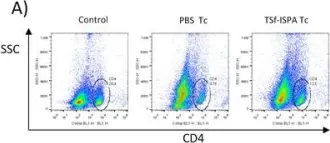
In Oncotarget on 29 August 2017 by Prochetto, E., Roldán, C., et al.
Fig.6.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Oncotarget on 29 August 2017 by Prochetto, E., Roldán, C., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9