Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) contains inflammatory cues that enable peripheral immune surveillance of the central nervous system (CNS). While some cranial nerves allow for CSF efflux, the immune environment around CSF-interfacing cranial nerves during neuroinflammation is still poorly understood. Using a mouse model of multiple sclerosis [experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE)] and CNS Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection (CNS-Mtb), we examined immune responses around olfactory nerve bundles near the cribriform plate, a key CSF efflux route. During neuroinflammation, we found increased perineural immune cells that had access to intracranial injected beads, dye, and bacteria. Additionally, we identified osseous channels connecting the environment surrounding olfactory nerves to bone marrow in the cribriform plate (cpBM). Notably, the cpBM undergoes myelopoiesis during EAE, has access to components of intracranial drainage, and is vulnerable to Mtb bacteria invasion during CNS-Mtb infection. Our findings improve the understanding of how the environments of CSF-interfacing cranial nerves and bone marrow are altered within the skull during neuroinflammatory disease.
Product Citations: 191
In Science Advances on 27 June 2025 by Laaker, C., Kovács, K. G., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America on 25 March 2025 by Dos S P Andrade, A. C., Lacasse, E., et al.
Platelets, known for maintaining blood balance, also participate in antimicrobial defense. Upon severeacute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, platelets become hyperactivated, releasing molecules such as cytokines, granule contents, and bioactive lipids. The key effector biolipids produced by platelets include 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12-HETE) and 12-hydroxyeicosatrienoic acid (12-HETrE), produced by 12-lipoxygenase (12-LOX), and prostaglandins and thromboxane, produced by cyclooxygenase-1. While prostaglandin E2 and thromboxane B2 were previously associated with lung inflammation in severe COVID-19, the role of platelet 12-LOX in SARS-CoV-2 infection remains unclear. Using mice deficient for platelets' 12-LOX, we report that SARS-CoV-2 infection resulted in higher lung inflammation characterized by histopathological tissue analysis, increased leukocyte infiltrates, and cytokine production relative to wild-type mice. In addition, distinct platelet and lung transcriptomic changes, including alterations in NOD-like receptor (NLR) family pyrin domain-containing 1 (NLRP1) inflammasome-related gene expression, were observed. Mass spectrometry lipidomic analysis in 12-LOX-deficient-infected mice revealed significant changes in bioactive lipid content, including reduced levels of 12-HETrE that inversely correlated with disease severity. Finally, platelet 12-LOX deficiency was associated with increased morbidity and lower survival rates relative to wild type (WT) mice. Overall, this study highlights the complex interplay between 12-LOX-related lipid metabolism and inflammatory responses during SARS-CoV-2 infection. The findings provide valuable insights into potential therapeutic targets aimed at mitigating severe outcomes, emphasizing the pivotal role of platelet enzymes in the host response to viral infections.
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Somatic mtDNA mutation burden shapes metabolic plasticity in leukemogenesis.
In Science Advances on 3 January 2025 by Li-Harms, X., Lu, J., et al.
The role of somatic mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations in leukemogenesis remains poorly characterized. To determine the impact of somatic mtDNA mutations on this process, we assessed the leukemogenic potential of hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) from mtDNA mutator mice (Polg D257A) with or without NMyc overexpression. We observed a higher incidence of spontaneous leukemogenesis in recipients transplanted with heterozygous Polg HPCs and a lower incidence of NMyc-driven leukemia in those with homozygous Polg HPCs compared to controls. Although mtDNA mutations in heterozygous and homozygous HPCs caused similar baseline impairments in mitochondrial function, only heterozygous HPCs responded to and supported altered metabolic demands associated with NMyc overexpression. Homozygous HPCs showed altered glucose utilization with pyruvate dehydrogenase inhibition due to increased phosphorylation, exacerbated by NMyc overexpression. The impaired growth of NMyc-expressing homozygous HPCs was partially rescued by inhibiting pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, highlighting a relationship between mtDNA mutation burden and metabolic plasticity in leukemogenesis.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
In Cancer Science on 1 December 2024 by Yumoto, S., Horiguchi, H., et al.
Use of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) as cancer immunotherapy has advanced rapidly in the clinic; however, mechanisms underlying resistance to ICI therapy, including impaired T cell infiltration, low immunogenicity, and tumor "immunophenotypes" governed by the host, remain unclear. We previously reported that in some cancer contexts, tumor cell-derived angiopoietin-like protein 2 (ANGPTL2) has tumor-promoting functions. Here, we asked whether ANGPTL2 deficiency could enhance antitumor ICI activity in two inflammatory contexts: a murine syngeneic model of colorectal cancer and a mouse model of high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity. Systemic ANGPTL2 deficiency potentiated ICI efficacy in the syngeneic model, supporting an immunosuppressive role for host ANGPTL2. Relevant to the mechanism, we found that ANGPTL2 induces pro-inflammatory cytokine production in adipose tissues, driving generation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in bone marrow and contributing to an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and resistance to ICI therapy. Moreover, HFD-induced obese mice showed impaired responsiveness to ICI treatment, suggesting that obesity-induced chronic inflammation facilitated by high ANGPTL2 expression blocks ICI antitumor effects. Our findings overall provide novel insight into protumor ANGPTL2 functions and illustrate the essential role of the host system in ICI responsiveness.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Somatic mtDNA Mutation Burden Shapes Metabolic Plasticity in Leukemogenesis
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 27 September 2024 by Li-Harms, X., Lu, J., et al.
ABSTRACT The role of somatic mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations in leukemogenesis remains poorly characterized. To determine the impact of somatic mtDNA mutations on the process, we assessed the leukemogenic potential of hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) from mtDNA mutator mice (Polg D257A) with or without NMyc overexpression. We observed a higher incidence of spontaneous leukemogenesis in recipients transplanted with heterozygous Polg HPCs and a lower incidence of NMyc-driven leukemia in those with homozygous Polg HPCs compared to controls. Although mtDNA mutations in heterozygous and homozygous HPCs caused similar baseline impairments in mitochondrial function, only heterozygous HPCs responded to and supported altered metabolic demands associated with NMyc overexpression. Homozygous HPCs showed altered glucose utilization with pyruvate dehydrogenase inhibition due to increased phosphorylation, exacerbated by NMyc overexpression. The impaired growth of NMyc-expressing homozygous HPCs was partially rescued by inhibiting pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, highlighting a relationship between mtDNA mutation burden and metabolic plasticity in leukemogenesis. TEASER Somatic mtDNA mutations as drivers of metabolic change in the development of leukemia.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
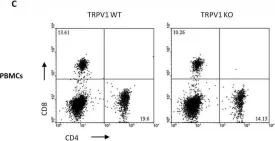
In Front Immunol on 30 November 2023 by Sandoval, S., Malany, K., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
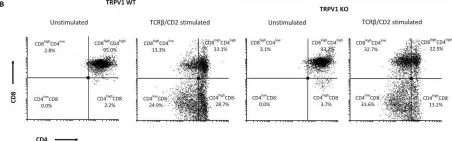
In Int J Mol Sci on 25 March 2023 by Cozzolino, M., Gyongyosi, A., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
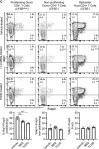
In Oncotarget on 31 October 2017 by Amantini, C., Farfariello, V., et al.
Fig.7.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
In Oncotarget on 31 October 2017 by Amantini, C., Farfariello, V., et al.
Fig.7.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4