The human brain harbors virus-specific, tissue-resident memory (TRM) CD8+ T cells. However, the impact of repeated peripheral viral infection on the generation, phenotype, localization, and recall responses of brain TRM remains elusive. Here, utilizing two murine models of peripheral viral infection, we demonstrate that circulating memory CD8+ T cells with previous antigen exposure exhibit a markedly reduced capacity to form brain TRM compared to naive CD8+ T cells. Repetitively stimulated brain TRM also demonstrate differential inhibitory receptor expression, preserved functionality, and divergent localization patterns compared to primary memory counterparts. Despite these differences, repetitively stimulated brain TRM provide similar protection against intracranial infection as primary populations with superior recall-based recruitment of peripheral lymphocytes. As CD8+ T cells may distinctly seed the brain with each repeated infection of the same host, these findings point to heterogeneity in the brain TRM pool that is dictated by prior peripheral antigen stimulation history.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 197
In Cell Reports on 25 February 2025 by Mix, M. R., van de Wall, S., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Ebola virus-induced eye sequelae: a murine model for evaluating glycoprotein-targeting therapeutics.
In EBioMedicine on 1 June 2024 by Lee, H. N., Xu, B., et al.
Ebola virus disease (EVD) survivors experience ocular sequelae including retinal lesions, cataracts, and vision loss. While monoclonal antibodies targeting the Ebola virus glycoprotein (EBOV-GP) have shown promise in improving prognosis, their effectiveness in mitigating ocular sequelae remains uncertain.
We developed and characterized a BSL-2-compatible immunocompetent mouse model to evaluate therapeutics targeting EBOV-GP by inoculating neonatal mice with vesicular stomatitis virus expressing EBOV-GP (VSV-EBOV). To examine the impact of anti-EBOV-GP antibody treatment on acute retinitis and ocular sequelae, VSV-EBOV-infected mice were treated with polyclonal antibodies or monoclonal antibody preparations with antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC-mAb) or neutralizing activity (NEUT-mAb).
Treatment with all anti-EBOV-GP antibodies tested dramatically reduced viremia and improved survival. Further, all treatments reduced the incidence of cataracts. However, NEUT-mAb alone or in combination with ADCC-mAb reduced viral load in the eyes, downregulated the ocular immune and inflammatory responses, and minimized retinal damage more effectively.
Anti-EBOV-GP antibodies can improve survival among EVD patients, but improved therapeutics are needed to reduce life altering sequelae. This animal model offers a new platform to examine the acute and long-term effect of the virus in the eye and the relative impact of therapeutic candidates targeting EBOV-GP. Results indicate that even antibodies that improve systemic viral clearance and survival can differ in their capacity to reduce acute ocular inflammation, and long-term retinal pathology and corneal degeneration.
This study was partly supported by Postgraduate Research Fellowship Awards from ORISE through an interagency agreement between the US DOE and the US FDA.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In STAR Protocols on 15 March 2024 by Ma, B., Zhou, Y., et al.
Here, we present a protocol for the examination of immune cells in the murine conjunctiva and lacrimal gland using flow cytometry. We describe steps for dissection, preparation of high-quality single-cell suspensions, utilization of comprehensive staining panels, and optimization of flow cytometry voltage. We then detail procedures for compensation adjustments and the implementation of effective gating strategies. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Ma et al.1.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cells on 4 December 2023 by Yalcin, B. H., Macas, J., et al.
The bone marrow (BM) hematopoietic system (HS) gives rise to blood cells originating from hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), including megakaryocytes (MKs) and red blood cells (erythrocytes; RBCs). Many steps of the cell-fate decision remain to be elucidated, being important for cancer treatment. To explore the role of Wnt/β-catenin for MK and RBC differentiation, we activated β-catenin signaling in platelet-derived growth factor b (Pdgfb)-expressing cells of the HS using a Cre-lox approach (Ctnnb1BM-GOF). FACS analysis revealed that Pdgfb is mainly expressed by megakaryocytic progenitors (MKPs), MKs and platelets. Recombination resulted in a lethal phenotype in mutants (Ctnnb1BM-GOFwt/fl, Ctnnb1BM-GOFfl/fl) 3 weeks after tamoxifen injection, showing an increase in MKs in the BM and spleen, but no pronounced anemia despite reduced erythrocyte counts. BM transplantation (BMT) of Ctnnb1BM-GOF BM into lethally irradiated wildtype recipients (BMT-Ctnnb1BM-GOF) confirmed the megakaryocytic, but not the lethal phenotype. CFU-MK assays in vitro with BM cells of Ctnnb1BM-GOF mice supported MK skewing at the expense of erythroid colonies. Molecularly, the runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) mRNA, known to suppress erythropoiesis, was upregulated in Ctnnb1BM-GOF BM cells. In conclusion, β-catenin activation plays a key role in cell-fate decision favoring MK development at the expense of erythroid production.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cell Biology
Blocking CD40 Alleviates Th1 and Th17 Cell Responses in Elastin Peptide-Induced Murine Emphysema.
In International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease on 29 November 2023 by Ma, T., Zhang, H., et al.
To investigate the role of the CD40-CD40 ligand (CD40L) pathway in the regulation of Th1, Th17, and regulatory T (Treg)-cell responses in an elastin peptide (EP)-induced autoimmune emphysema mouse model.
BALB/c mice were transnasally treated with EP on day 0, injected intravenously with anti-CD40 antibody via the tail vein on day 33, and sacrificed on day 40. The severity of emphysema was evaluated by determining the mean linear intercept (MLI) and destructive index (DI) from lung sections. The proportions of myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) and Th1, Th17, and Treg cells in the blood, spleen, and lungs were determined via flow cytometry. The levels of the cytokines interleukin (IL)-6, IL-17, interferon (IFN)-γ, and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β were detected via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Ifnγ, IL17a, Rorγt and Foxp3 transcription levels were detected via polymerase chain reaction.
CD40+ mDCs accumulated in the lungs of EP-stimulated mice. Blocking the CD40-CD40L pathway with an anti-CD40 antibody alleviated Th1 and Th17 responses; increased the proportion of Treg cells; decreased MLI and DI; reduced the levels of cytokines IL-6, IL-17, and IFN-γ as well as the transcription levels of Ifnγ, IL17a, and Rorγt; and upregulated the expression of TGF-β and Foxp3.
The CD40-CD40L pathway could play a critical role in Th1, Th17 and Treg cell dysregulation in EP-mediated emphysema and could be a potential therapeutic target.
© 2023 Ma et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
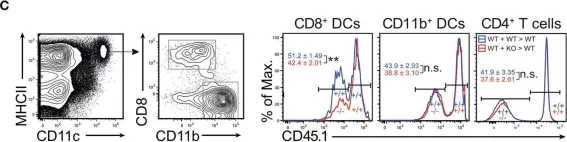
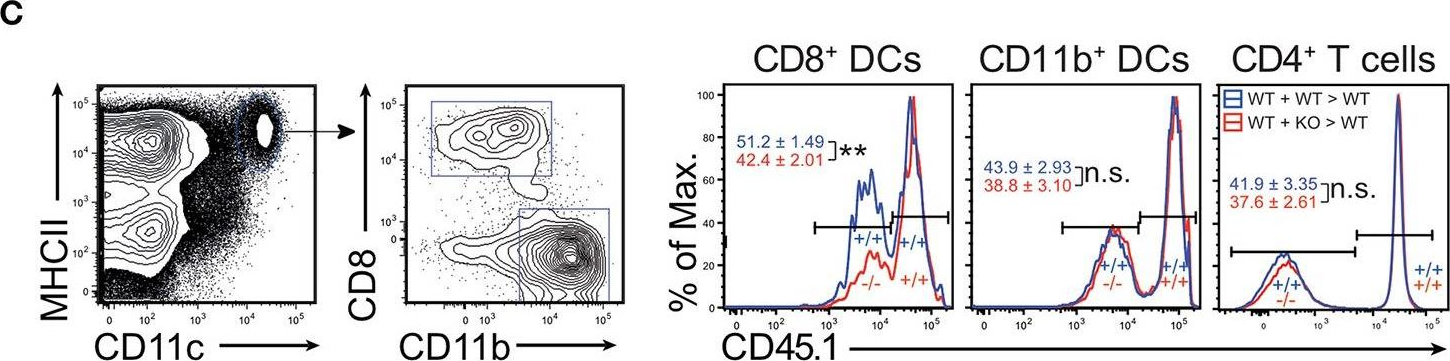
In Front Immunol on 28 February 2019 by Zwick, M., Ulas, T., et al.
Fig.4.C
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
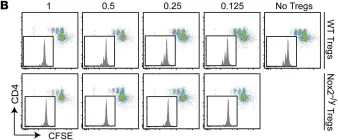
In J Clin Invest on 2 July 2018 by Emmerson, A., Trevelin, S. C., et al.
Fig.6.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from J Clin Invest by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
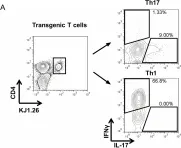
In PLoS One on 21 November 2012 by Patakas, A., Benson, R. A., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3