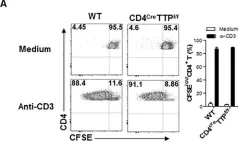
Detection of disseminated cancer cells (DCC) in the bone marrow (BM) of patients with breast cancer is a critical predictor of late recurrence and distant metastasis. Conventional therapies often fail to completely eradicate DCCs in patients. In this study, we demonstrate that intratumoral priming of antitumor CD4+ T helper 1 (Th1) cells was able to eliminate the DCC burden in distant organs and prevent overt metastasis, independent of CD8+ T cells. Intratumoral priming of tumor antigen-specific CD4+ Th1 cells enhanced their migration to the BM and distant metastatic site to selectively target DCC burden. The majority of these intratumorally activated CD4+ T cells were CD4+PD1- T cells, supporting their nonexhaustion stage. Phenotypic characterization revealed enhanced infiltration of memory CD4+ T cells and effector CD4+ T cells in the primary tumor, tumor-draining lymph node, and DCC-driven metastasis site. A robust migration of CD4+CCR7+CXCR3+ Th1 cells and CD4+CCR7-CXCR3+ Th1 cells into distant organs further revealed their potential role in eradicating DCC-driven metastasis. The intratumoral priming of antitumor CD4+ Th1 cells failed to eradicate DCC-driven metastasis in CD4- or IFN-γ knockout mice. Moreover, antitumor CD4+ Th1 cells, by increasing IFN-γ production, inhibited various molecular aspects and increased classical and nonclassical MHC molecule expression in DCCs. This reduced stemness and self-renewal while increasing immune recognition in DCCs of patients with breast cancer. These results unveil an immune basis for antitumor CD4+ Th1 cells that modulate DCC tumorigenesis to prevent recurrence and metastasis in patients.
©2025 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Product Citations: 206
Antitumor CD4+ T Helper 1 Cells Target and Control the Outgrowth of Disseminated Cancer Cells.
In Cancer Immunology Research on 2 May 2025 by Ganesan, R., Lee, M. C., et al.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In IScience on 21 March 2025 by Okoye, G. D., Kumar, A., et al.
Early immune dynamics during the initiation of fatal tularemia caused by Francisella tularensis infection remain unknown. Unto that end, we generated a transcriptomic map at single-cell resolution of the innate-like lymphocyte responses to F. tularensis live vaccine strain (LVS) infection of mice. We found that both interferon-γ (IFN-γ)-producing type 1 and interleukin-17 (IL-17)-producing type 3 innate-like lymphocytes expanded in the infected lungs. Natural killer (NK) and NKT cells drove the type 1 response, whereas mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) and γδ T cells drove the type 3 response. Furthermore, tularemia-like disease resistant NKT cell-deficient, Cd1d -/- mice accumulated more MAIT1 cells, MAIT17 cells, and cells with a hybrid phenotype between MAIT1 and MAIT17 cells than wild-type mice. Critically, adoptive transfer of LVS-activated MAIT cells from Cd1d -/- mice, which were enriched in MAIT17 cells, was sufficient to protect LVS-susceptible, immunodeficient RAG2 -/- mice from severe LVS infection-inflicted pathology. Collectively, our findings position MAIT cells as potential mediators of IL-17-dependent protection from pulmonary tularemia-like disease.
© 2025 The Author(s).
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nature Communications on 19 March 2025 by Huang, R., Shen, Z. Y., et al.
Anti-programmed death 1 (αPD1) immune checkpoint blockade is used in combination for cancer treatment but associated with cardiovascular toxicity. Leflunomide (Lef) can suppress the growth of several tumor and mitigate cardiac remodeling in mice. However, the role of Lef in αPD1-induced cardiotoxicity remains unclear. Here, we report that Lef treatment inhibits αPD1-related cardiotoxicity without compromising the efficacy of αPD1-mediated immunotherapy. Lef changes community structure of gut microbiota in αPD1-treated melanoma-bearing mice. Moreover, mice receiving microbiota transplants from Lef+αPD1-treated melanoma-bearing mice have better cardiac function compared to mice receiving transplants from αPD1-treated mice. Mechanistically, we analyze metabolomics and identify indole-3-propionic acid (IPA), which protects cardiac dysfunction in αPD1-treated mice. IPA can directly bind to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and promote phosphoinositide 3-kinase expression, thus curtailing the cardiomyocyte response to immune injury. Our findings reveal that Lef mitigates αPD1-induced cardiac toxicity in melanoma-bearing mice through modulation of the microbiota-IPA-heart axis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cardiovascular biology
In World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology on 15 March 2025 by Qian, W., Xu, C. Y., et al.
Activation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a pivotal process in tumor metastasis and evasion, as well as the NLRP3 inflammasome, both promote colorectal cancer (CRC) progression. Recent studies have shown that Transmembrane protein 176B (TMEM176B) regulates NLRP3 and promotes CRC malignant phenotypes.
To investigate the role of TMEM176B in modulating NLRP3 inflammasome and its implications on EMT and tumor progression in CRC.
CRC in situ mouse and co-cultured cell models were established using CT26 cells, BALB/c mice, and primary cultured mouse natural killer (NK) cells. Short hairpin RNA knocked down TMEM176B and NLRP3 expression in CT26 cells. Fluorescence imaging, Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling assays, immunohistochemistry staining, flow cytometry, and molecular assays were used to investigate the effects of TMEM176B knockdown on the NLRP3 inflammasome in NK cells to assess tumor metastasis, apoptosis, and EMT indicators.
Silencing TMEM176B in CRC mice significantly reduced tumor metastasis, proliferation, and EMT, while activating apoptosis, NLRP3 inflammasome, and NK cell activity. Furthermore, silencing TMEM176B in co-cultured cell models inhibited cell migration and invasion, and promoted apoptosis. The interference of NLRP3 reversed these effects by modulating key proteins such as phosphorylated nuclear factor kappa B subunit 1 p65, matrix metallopeptidase 9, and transforming growth factor-β.
This study highlights the critical role of TMEM176B/NLRP3 in CRC progression and provides a basis for targeting this axis as a novel therapeutic approach to manage CRC progression and metastasis.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Cancer Research
In Cancer Discovery on 13 January 2025 by Priego, N., de Pablos-Aragoneses, A., et al.
Immunotherapies against brain metastases have shown clinical benefits when applied to asymptomatic patients, but they are largely ineffective in symptomatic cases for unknown reasons. Here, we dissect the heterogeneity in metastasis-associated astrocytes using single-cell RNA sequencing and report a population that blocks the antitumoral activity of infiltrating T cells. This protumoral activity is mediated by the secretion of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP1) from a cluster of pSTAT3+ astrocytes that acts on CD63+ CD8+ T cells to modulate their function. Using genetic and pharmacologic approaches in mouse and human brain metastasis models, we demonstrate that combining immune checkpoint blockade antibodies with the inhibition of astrocyte-mediated local immunosuppression may benefit patients with symptomatic brain metastases. We further reveal that the presence of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in liquid biopsies provides a biomarker to select patients for this combined immunotherapy. Overall, our findings demonstrate an unexpected immunomodulatory role for astrocytes in brain metastases with clinical implications. Significance: This study presents a significant advancement in understanding immune modulation in brain tumors and offers new insights into the potential therapeutic interventions for brain metastases. See related commentary by Lorger and James, p. 11.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
In Cells on 2 January 2024 by Miles, M. A., Luong, R., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 6
In Cells on 2 January 2024 by Miles, M. A., Luong, R., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 6
In Front Immunol on 15 September 2020 by Peng, H., Ning, H., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 6
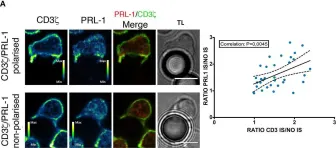
In Front Immunol on 6 December 2018 by Castro-Sánchez, P., Ramirez-Munoz, R., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 6
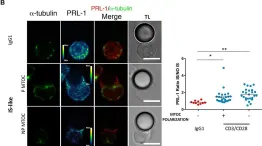
In Front Immunol on 6 December 2018 by Castro-Sánchez, P., Ramirez-Munoz, R., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 6
In Nat Commun on 17 October 2018 by Flores, C. T., Wildes, T. J., et al.
Fig.6.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 6