Crohn's disease (CD) is a persistent inflammatory disorder primarily affecting the terminal ileum. The TnfΔΑRE mice, which spontaneously develop CD-like ileitis due to TNF overexpression, represent a faithful model of the human disease. Here, via single-cell RNA sequencing in TnfΔΑRE mice, we show that murine TNF-dependent ileitis is characterized by cell expansion in tertiary lymphoid organs (TLO), T cell effector reprogramming, and accumulation of activated macrophages in the submucosal granulomas. Within the stromal cell compartment, fibroblast subsets (telocytes, trophocytes, PdgfraloCd81- cells) are less abundant while lymphatic endothelial cells (LEC) and fibroblastic reticular cells (FRC) show relative expansion compared to the wild type. All three fibroblast subsets show strong pro-inflammatory signature. TNFR1 loss or gain of function experiments in specific fibroblast subsets suggest that the TnfΔΑRE-induced ileitis is initiated in the lamina propria via TNF pathway activation in villus-associated fibroblasts (telocytes and PdgfraloCd81- cells), which are responsible for the organization of TLOs. Trophocytes drive disease progression in the submucosal layer, accompanied by the excessive formation of granulomas. These findings provide evidence for spatial regulation of inflammation by fibroblast subsets and underscore the pivotal role of fibroblasts in the inception and advancement of ileitis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 56
In Nature Communications on 28 March 2025 by Iliopoulou, L., Tzaferis, C., et al.
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nature Genetics on 1 March 2025 by Lim, B., Kamal, A., et al.
Cell fate plasticity enables development, yet unlocked plasticity is a cancer hallmark. While transcription master regulators induce lineage-specific genes to restrict plasticity, it remains unclear whether plasticity is actively suppressed by lineage-specific repressors. Here we computationally predict so-called safeguard repressors for 18 cell types that block phenotypic plasticity lifelong. We validated hepatocyte-specific candidates using reprogramming, revealing that prospero homeobox protein 1 (PROX1) enhanced hepatocyte identity by direct repression of alternative fate master regulators. In mice, Prox1 was required for efficient hepatocyte regeneration after injury and was sufficient to prevent liver tumorigenesis. In line with patient data, Prox1 depletion caused hepatocyte fate loss in vivo and enabled the transition of hepatocellular carcinoma to cholangiocarcinoma. Conversely, overexpression promoted cholangiocarcinoma to hepatocellular carcinoma transdifferentiation. Our findings provide evidence for PROX1 as a hepatocyte-specific safeguard and support a model where cell-type-specific repressors actively suppress plasticity throughout life to safeguard lineage identity and thus prevent disease.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Genetics
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Somatic mtDNA mutation burden shapes metabolic plasticity in leukemogenesis.
In Science Advances on 3 January 2025 by Li-Harms, X., Lu, J., et al.
The role of somatic mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations in leukemogenesis remains poorly characterized. To determine the impact of somatic mtDNA mutations on this process, we assessed the leukemogenic potential of hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) from mtDNA mutator mice (Polg D257A) with or without NMyc overexpression. We observed a higher incidence of spontaneous leukemogenesis in recipients transplanted with heterozygous Polg HPCs and a lower incidence of NMyc-driven leukemia in those with homozygous Polg HPCs compared to controls. Although mtDNA mutations in heterozygous and homozygous HPCs caused similar baseline impairments in mitochondrial function, only heterozygous HPCs responded to and supported altered metabolic demands associated with NMyc overexpression. Homozygous HPCs showed altered glucose utilization with pyruvate dehydrogenase inhibition due to increased phosphorylation, exacerbated by NMyc overexpression. The impaired growth of NMyc-expressing homozygous HPCs was partially rescued by inhibiting pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, highlighting a relationship between mtDNA mutation burden and metabolic plasticity in leukemogenesis.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
Ribosomal S6 kinase 1 regulates inflammaging via the senescence secretome.
In Nature Aging on 1 November 2024 by Gallage, S., Irvine, E. E., et al.
Inhibition of S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) extends lifespan and improves healthspan in mice, but the underlying mechanisms are unclear. Cellular senescence is a stable growth arrest accompanied by an inflammatory senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). Cellular senescence and SASP-mediated chronic inflammation contribute to age-related pathology, but the specific role of S6K1 has not been determined. Here we show that S6K1 deletion does not reduce senescence but ameliorates inflammation in aged mouse livers. Using human and mouse models of senescence, we demonstrate that reduced inflammation is a liver-intrinsic effect associated with S6K deletion. Specifically, we show that S6K1 deletion results in reduced IRF3 activation; impaired production of cytokines, such as IL1β; and reduced immune infiltration. Using either liver-specific or myeloid-specific S6K knockout mice, we also demonstrate that reduced immune infiltration and clearance of senescent cells is a hepatocyte-intrinsic phenomenon. Overall, deletion of S6K reduces inflammation in the liver, suggesting that suppression of the inflammatory SASP by loss of S6K could underlie the beneficial effects of inhibiting this pathway on healthspan and lifespan.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Somatic mtDNA Mutation Burden Shapes Metabolic Plasticity in Leukemogenesis
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 27 September 2024 by Li-Harms, X., Lu, J., et al.
ABSTRACT The role of somatic mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations in leukemogenesis remains poorly characterized. To determine the impact of somatic mtDNA mutations on the process, we assessed the leukemogenic potential of hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) from mtDNA mutator mice (Polg D257A) with or without NMyc overexpression. We observed a higher incidence of spontaneous leukemogenesis in recipients transplanted with heterozygous Polg HPCs and a lower incidence of NMyc-driven leukemia in those with homozygous Polg HPCs compared to controls. Although mtDNA mutations in heterozygous and homozygous HPCs caused similar baseline impairments in mitochondrial function, only heterozygous HPCs responded to and supported altered metabolic demands associated with NMyc overexpression. Homozygous HPCs showed altered glucose utilization with pyruvate dehydrogenase inhibition due to increased phosphorylation, exacerbated by NMyc overexpression. The impaired growth of NMyc-expressing homozygous HPCs was partially rescued by inhibiting pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, highlighting a relationship between mtDNA mutation burden and metabolic plasticity in leukemogenesis. TEASER Somatic mtDNA mutations as drivers of metabolic change in the development of leukemia.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
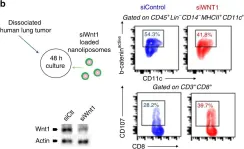
In Nat Commun on 29 March 2019 by Kerdidani, D., Chouvardas, P., et al.
Fig.7.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1