Chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG) is a chronic disease of the gastric mucosa characterized by a reduction or an absolute disappearance of the original gastric glands, possibly replaced by pseudopyloric fibrosis, intestinal metaplasia, or fibrosis. CAG develops progressively into intestinal epithelial metaplasia, dysplasia, and ultimately, gastric cancer. Epidemiological statistics have revealed a positive correlation between the incidence of CAG and age. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a type of adult stem cells derived from mesoderm, with strong tissue repair capabilities. Therefore, the restoration of the gastric mucosa may serve as an efficacious strategy to ameliorate CAG and avert gastric cancer. However, the mechanisms by which MSCs inhibit the relentless progression of aging atrophic gastritis remain to be elucidated. This study endeavored to assess a novel approach utilizing MSCs to treat CAG and forestall carcinogenics.
In this study, we selected mice with atrophic gastritis from naturally aging mice and administered human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hUMSCs) via tail vein injection to evaluate the therapeutic effects of hUMSCs on age-related chronic atrophic gastritis. Initially, we employed methods such as ELISA, immunohistochemical analysis, and TUNEL assays to detect changes in the mice post-hUMSC injection. Proteomic and bioinformatics analyses were conducted to identify differentially expressed proteins, focusing on NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase core subunit S8 (Ndufs8). Co-culturing hUMSCs with Ndufs8 knockout gastric mucosal epithelial cells (GMECs), we utilized flow cytometry, Western blotting, real-time quantitative PCR, and immunofluorescence to investigate the mechanisms of action of hUMSCs.
We observed that hUMSCs are capable of migrating to and repairing damaged gastric mucosa. Initially, hUMSCs significantly enhanced the secretion of gastric proteins PG-1 and G17, while concurrently reducing inflammatory cytokines. Furthermore, hUMSCs mitigated gastric fibrosis and apoptosis in mucosal cells. Proteomic and bioinformatic analyses revealed alterations in the protein network involved in mitochondrial autophagy, with Ndufs8 playing a pivotal role. Upon knocking out Ndufs8 in GMECs, we noted mitochondrial damage and reduced autophagy, leading to an aged phenotype in GMECs. Co-culturing Ndufs8-knockout GMECs with hUMSCs demonstrated that hUMSCs could ameliorate mitochondrial dysfunction and restore the cell cycle in GMECs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 185
In Stem Cell Research & Therapy on 20 December 2024 by Rui, Q., Li, C., et al.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cell Biology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In eLife on 22 November 2024 by Garnica, J., Solé, P., et al.
Chronic antigenic stimulation can trigger the formation of interleukin 10 (IL-10)-producing T-regulatory type 1 (TR1) cells in vivo. We have recently shown that murine T-follicular helper (TFH) cells are precursors of TR1 cells and that the TFH-to-TR1 cell transdifferentiation process is characterized by the progressive loss and acquisition of opposing transcription factor gene expression programs that evolve through at least one transitional cell stage. Here, we use a broad range of bulk and single-cell transcriptional and epigenetic tools to investigate the epigenetic underpinnings of this process. At the single-cell level, the TFH-to-TR1 cell transition is accompanied by both, downregulation of TFH cell-specific gene expression due to loss of chromatin accessibility, and upregulation of TR1 cell-specific genes linked to chromatin regions that remain accessible throughout the transdifferentiation process, with minimal generation of new open chromatin regions. By interrogating the epigenetic status of accessible TR1 genes on purified TFH and conventional T-cells, we find that most of these genes, including Il10, are already poised for expression at the TFH cell stage. Whereas these genes are closed and hypermethylated in Tconv cells, they are accessible, hypomethylated, and enriched for H3K27ac-marked and hypomethylated active enhancers in TFH cells. These enhancers are enriched for binding sites for the TFH and TR1-associated transcription factors TOX-2, IRF4, and c-MAF. Together, these data suggest that the TR1 gene expression program is genetically imprinted at the TFH cell stage.
© 2024, Garnica et al.
Effects of Perfluorohexane Sulfonate Exposure on Immune Cell Populations in Naive Mice.
In ImmunoHorizons on 1 August 2024 by Pierpont, T. M., Elmore, J., et al.
Perfluorohexane sulfonate (PFHxS) is a member of the per- and polyfluoroalkyls (PFAS) superfamily of molecules, characterized by their fluorinated carbon chains and use in a wide range of industrial applications. PFHxS and perfluorooctane sulfonate are able to accumulate in the environment and in humans with the approximated serum elimination half-life in the range of several years. More recently, some PFAS compounds have also been suggested as potential immunosuppressants. In this study, we analyze immune cell numbers in mice following 28-d repeated oral exposure to potassium PFHxS at 12, 120, 1,200, and 12,000 ng/kg/d, with resulting serum levels ranging up to ∼1,600 ng/ml, approximating ranges found in the general population and at higher levels in PFAS workers. The immunosuppressant cyclophosphamide was analyzed as a positive control. B cells, T cells, and granulocytes from the bone marrow, liver, spleen, lymph nodes, and thymus were evaluated. We found that at these exposures, there was no effect of PFHxS on major T or B cell populations, macrophages, dendritic cells, basophils, mast cells, eosinophils, neutrophils, or circulating Ab isotypes. By contrast, mice exposed to cyclophosphamide exhibited depletion of several granulocyte and T and B cell populations in the thymus, bone marrow, and spleen, as well as reductions in IgG1, IgG2b, IgG2c, IgG3, IgE, and IgM. These data indicate that exposures of up to 12,000 ng/kg of PFHxS for 28 d do not affect immune cell numbers in naive mice, which provides valuable information for assessing the risks and health influences of exposures to this compound.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In The Journal of Clinical Investigation on 11 June 2024 by Chung, Y. R., Awakoaiye, B., et al.
Viral vectors are being used for the treatment of cancer. Yet, their efficacy varies among tumors and their use poses challenges in immunosuppressed patients, underscoring the need for alternatives. We report striking antitumoral effects by a nonlytic viral vector based on attenuated lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (r3LCMV). We show in multiple tumor models that injection of tumor-bearing mice with this vector results in improved tumor control and survival. Importantly, r3LCMV improved tumor control in immunodeficient Rag1-/- mice and MyD88-/- mice, suggesting that multiple pathways contributed to the antitumoral effects. The antitumoral effects of r3LCMV were also observed when this vector was administered several weeks before tumor challenges, suggesting the induction of trained immunity. Single-cell RNA sequencing analyses, antibody blockade experiments, and knockout models revealed a critical role for host-intrinsic IFN-I in the antitumoral efficacy of r3LCMV vectors. Collectively, these data demonstrate potent antitumoral effects by r3LCMV vectors and unveil multiple mechanisms underlying their antitumoral efficacy.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Scientific Reports on 14 May 2024 by Lassoued, N., Yero, A., et al.
Researchers who aim to globally analyze the gastrointestinal immune system via flow cytometry have many protocol options to choose from, with specifics generally tied to gut wall layers of interest. To get a clearer idea of the approach we should use on full-thickness colon samples from mice, we first undertook a systematic comparison of three tissue dissociation techniques: two based on enzymatic cocktails and the other one based on manual crushing. Using flow cytometry panels of general markers of lymphoid and myeloid cells, we found that the presence of cell-surface markers and relative cell population frequencies were more stable with the mechanical method. Both enzymatic approaches were associated with a marked decrease of several cell-surface markers. Using mechanical dissociation, we then developed two minimally overlapping panels, consisting of a total of 26 antibodies, for serial profiling of lymphoid and myeloid lineages from the mouse colon in greater detail. Here, we highlight how we accurately delineate these populations by manual gating, as well as the reproducibility of our panels on mouse spleen and whole blood. As a proof-of-principle of the usefulness of our general approach, we also report segment- and life stage-specific patterns of immune cell profiles in the colon. Overall, our data indicate that mechanical dissociation is more suitable and efficient than enzymatic methods for recovering immune cells from all colon layers at once. Additionally, our panels will provide researchers with a relatively simple tool for detailed immune cell profiling in the murine gastrointestinal tract, regardless of life stage or experimental conditions.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
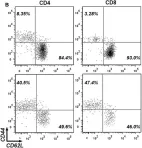
In Front Immunol on 7 April 2017 by Dai, K., Huang, L., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
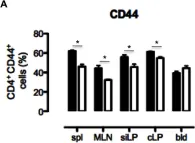
In PLoS One on 19 June 2013 by Radulovic, K., Rossini, V., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2