The disease burden of sepsis continues to increase, with intraabdominal contamination being a significant source of infection. Sepsis is a syndrome involving both an increase in systemic inflammation as well as a regulatory component. We have previously demonstrated that neutrophils are significant IL-10 producers in the abdomen during sepsis. Here, we sought to further characterize these neutrophils and elucidate potential underlying mechanisms resulting in IL-10 generation. Using transcriptional reporter mice, we observed that IL-10 producing neutrophils were activated, non-apoptotic, and expressed C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4-expressing. Further, we observed that active Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 1 expression was significantly increased in IL-10 producing versus non-IL-10 producing neutrophils. During sepsis, IFN-γ blockade lead to a decrease of neutrophil IL-10 production, while peritoneal CD4 T cells were found to be the most numerous acute producers of IFN-γ. Altogether, this report demonstrates that during sepsis, mature neutrophils can potentially dampen local inflammation by IL-10 production and this can be orchestrated by CD4 T cells through an IFN-γ dependent manner.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 60
In Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications on 10 September 2020 by Bergmann, C. B., Salyer, C. E., et al.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
In Cancers on 10 July 2020 by Khou, S., Popa, A., et al.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) development has been linked to immune dysfunctions but the mechanisms are still unclear. Here, we report a progressive infiltration of tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) in precancerous and established cSCC lesions from chemically induced skin carcinogenesis. Comparative in-depth gene expression analyses identified a predominant protumor gene expression signature of TANs in lesions compared to their respective surrounding skin. In addition, in vivo depletion of neutrophils delayed tumor growth and significantly increased the frequency of proliferating IFN-γ (interferon-γ)-producing CD8+ T cells. Mechanisms that limited antitumor responses involved high arginase activity, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitrite (NO), and the expression of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) on TAN, concomitantly with an induction of PD-1 on CD8+ T cells, which correlated with tumor size. Our data highlight the relevance of targeting neutrophils and PD-L1-PD-1 (programmed death-1) interaction in the treatment of cSCC.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Distinct Neutrophil Populations in the Spleen During PICS.
In Frontiers in Immunology on 6 June 2020 by Sengupta, S., Caldwell, C. C., et al.
While mortality after acute sepsis has decreased, the long-term recovery for survivors is still poor, particularly those developing persistent inflammation, immunosuppression, and catabolism syndrome (PICS). While previously thought that activated neutrophils responding to the acute phase of sepsis migrate to the spleen to undergo cell death and contribute to immunosuppression, our data show a significant accumulation of distinct, yet functional, neutrophil populations in the spleen in a murine model of PICS. The exact role and function of neutrophils in this response is still unclear. The objective of our study was to better define the immune function of splenic neutrophils to determine if this could give insight into the pathogenesis of PICS. Using a murine model of cecal ligation and puncture (CLP), which demonstrates all characteristics of PICS by 8 days, spleens were harvested, and neutrophils were identified by Ly6G and CD11b expression via flow cytometry. Nearly all splenic neutrophils expressed CD54, but there were distinct CD54hi and CD54lo cells, with the majority being CD54lo cells during PICS. The CD54hi population showed traditional, proinflammatory properties, but a relatively decreased chemotactic response, while CD54lo cells had significantly higher chemotaxis, yet significantly decreased proinflammatory functions. Using 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) incorporation, we found that the CD54hi population on day 2 after CLP may be participating in emergency myelopoiesis. However, the vast majority of the CD54lo population were paused in the G1 phase at this time point and not proliferating. By day 8 after CLP, most of the CD54hi cells in the spleen were no longer proliferating, while the CD54lo cells were, indicating that CD54lo dominate in extramedullary myelopoiesis at later time points. Almost none of the neutrophils produced arginase or inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), indicating that these are not suppressor cells. Overall, our data demonstrate that neutrophil accumulation in the spleen during PICS is related to extramedullary myelopoiesis, leading to the production of immature neutrophils. While not suppressor cells, the majority have greater chemotactic function but less inflammatory responsiveness, which may contribute to the immunosuppression seen in PICS. Attention to these distinct neutrophil populations after septic or other systemic inflammatory responses is therefore critical to understanding the mechanisms of PICS.
Copyright © 2020 Sengupta, Caldwell and Nomellini.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nature Protocols on 1 June 2020 by Uroda, T., Chillón, I., et al.
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are recently discovered transcripts that regulate vital cellular processes, such as cellular differentiation and DNA replication, and are crucially connected to diseases. Although the 3D structures of lncRNAs are key determinants of their function, the unprecedented molecular complexity of lncRNAs has so far precluded their 3D structural characterization at high resolution. It is thus paramount to develop novel approaches for biochemical and biophysical characterization of these challenging targets. Here, we present a protocol that integrates non-denaturing lncRNA purification with in-solution hydrodynamic analysis and single-particle atomic force microscopy (AFM) imaging to produce highly homogeneous lncRNA preparations and visualize their 3D topology at ~15-Å resolution. Our protocol is suitable for imaging lncRNAs in biologically active conformations and for measuring structural defects of functionally inactive mutants that have been identified by cell-based functional assays. Once optimized for the specific target lncRNA of choice, our protocol leads from cloning to AFM imaging within 3-4 weeks and can be implemented using state-of-the-art biochemical and biophysical instrumentation by trained researchers familiar with RNA handling and supported by AFM and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) experts.
-
Genetics
Th1 Cells Rolling on Selectins Trigger DAP12-Dependent Signals That Activate Integrin αLβ2.
In The Journal of Immunology on 1 January 2020 by Shao, B., Yago, T., et al.
During inflammation, both neutrophils and effector T cells use selectins to roll and integrins to arrest in postcapillary venules. In both cell types, chemokines can transduce signals that convert integrin αLβ2 to a high-affinity conformation, which interacts with ICAM-1 to mediate arrest. In neutrophils, selectins also trigger an immunoreceptor-like signaling cascade that converts integrin αLβ2 to an intermediate-affinity conformation, which interacts with ICAM-1 to slow rolling. It is not known whether selectins induce similar signaling events in T cells. Ag engagement causes phosphorylation of ITAMs on the TCR; these motifs recruit kinases and adaptors that lead to the activation of αLβ2. We found that mouse Th1 cells rolling on P- or E-selectin triggered signals that promoted αLβ2-dependent slow rolling on ICAM-1 in vitro and in vivo. The selectin signaling cascade resembled that used by the TCR, except that unexpectedly, Th1 cells employed the ITAM-bearing protein DAP12, which was not known to be expressed in these cells. Importantly, outside-in signaling through ligand-occupied αLβ2 also required DAP12. Cooperative selectin and chemokine signaling in Th1 cells promoted αLβ2-dependent slow rolling and arrest in vitro and in vivo and migration into Ag-challenged tissues in vivo. Our findings reveal an important function for DAP12 in Th1 cells and a new mechanism to recruit effector T cells to sites of inflammation.
Copyright © 2019 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In PLoS Pathog on 1 October 2018 by Heyde, S., Philipsen, L., et al.
Fig.1.D

-
ICC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
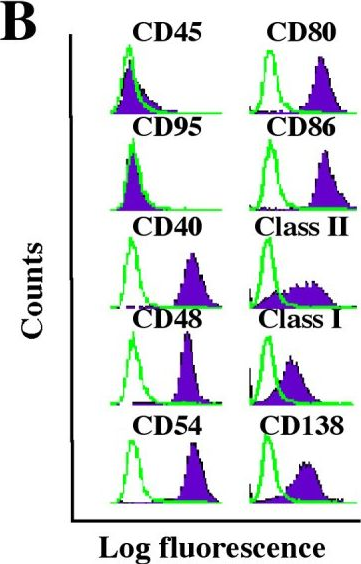
In Mol Cancer on 9 November 2005 by Han, S. S., Shaffer, A. L., et al.
Fig.1.B
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Mol Cancer by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2