B cell adapter for PI 3-kinase (BCAP) is an adaptor molecule associated with signaling through multiple immune receptors, including the B cell receptor (BCR). However, B cell-intrinsic role of BCAP in antibody responses is unclear. We investigated the role of BCAP in B cell response to viral particles and found a previously unidentified mechanism by which BCAP regulates antigen-specific responses. B cell-specific deletion of BCAP in mice leads to decreases in antigen-specific responses through defects in BCR-antigen endocytosis. BCAP is necessary to orchestrate actin reorganization around the antigen for efficient endocytosis through BCR and intracellular processing of antigens. Therefore, loss of BCAP from B cells leads to defects in antigen endocytosis, hampering the propagation of antigen-derived signals and decreasing the ability of B cells to present antigens to T cells. Thus, our study clarifies how BCAP regulates B cell responses to complex antigens and elucidates that antigen positioning inside B cells determines different B cell activation outcomes.
Product Citations: 72
In Science Advances on 15 November 2024 by Lagos, J., Holder, U., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In The Journal of Experimental Medicine on 1 April 2024 by Liu, S., Lagos, J., et al.
Genome-wide association studies in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have linked loss-of-function mutations in phagocytic NADPH oxidase complex (NOX2) genes, including NCF1 and NCF2, to disease pathogenesis. The prevailing model holds that reduced NOX2 activity promotes SLE via defective efferocytosis, the immunologically silent clearance of apoptotic cells. Here, we describe a parallel B cell-intrinsic mechanism contributing to breaks in tolerance. In keeping with an important role for B cell Toll-like receptor (TLR) pathways in lupus pathogenesis, NOX2-deficient B cells exhibit enhanced signaling downstream of endosomal TLRs, increased humoral responses to nucleic acid-containing antigens, and the propensity toward humoral autoimmunity. Mechanistically, TLR-dependent NOX2 activation promotes LC3-mediated maturation of TLR-containing endosomes, resulting in signal termination. CRISPR-mediated disruption of NCF1 confirmed a direct role for NOX2 in regulating endosomal TLR signaling in primary human B cells. Together, these data highlight a new B cell-specific mechanism contributing to autoimmune risk in NCF1 and NCF2 variant carriers.
© 2024 Liu et al.
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Host & Microbe on 13 March 2024 by Ngo, V. L., Lieber, C. M., et al.
Susceptibility to respiratory virus infections (RVIs) varies widely across individuals. Because the gut microbiome impacts immune function, we investigated the influence of intestinal microbiota composition on RVI and determined that segmented filamentous bacteria (SFB), naturally acquired or exogenously administered, protected mice against influenza virus (IAV) infection. Such protection, which also applied to respiratory syncytial virus and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), was independent of interferon and adaptive immunity but required basally resident alveolar macrophages (AMs). In SFB-negative mice, AMs were quickly depleted as RVI progressed. In contrast, AMs from SFB-colonized mice were intrinsically altered to resist IAV-induced depletion and inflammatory signaling. Yet, AMs from SFB-colonized mice were not quiescent. Rather, they directly disabled IAV via enhanced complement production and phagocytosis. Accordingly, transfer of SFB-transformed AMs into SFB-free hosts recapitulated SFB-mediated protection against IAV. These findings uncover complex interactions that mechanistically link the intestinal microbiota with AM functionality and RVI severity.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Developmental Cell on 18 December 2023 by Rowbotham, S. P., Pessina, P., et al.
The lung contains multiple progenitor cell types, but how their responses are choreographed during injury repair and whether this changes with age is poorly understood. We report that histone H3 lysine 9 di-methylation (H3K9me2), mediated by the methyltransferase G9a, regulates the dynamics of distal lung epithelial progenitor cells and that this regulation deteriorates with age. In aged mouse lungs, H3K9me2 loss coincided with fewer alveolar type 2 (AT2) cell progenitors and reduced alveolar regeneration but increased the frequency and activity of multipotent bronchioalveolar stem cells (BASCs) and bronchiolar progenitor club cells. H3K9me2 depletion in young mice decreased AT2 progenitor activity and impaired alveolar injury repair. Conversely, H3K9me2 depletion increased chromatin accessibility of bronchiolar cell genes, increased BASC frequency, and accelerated bronchiolar cell injury repair. These findings indicate that during aging, the epigenetic regulation that coordinates lung progenitor cells' regenerative responses becomes dysregulated, aiding our understanding of age-related susceptibility to lung disease.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In Science Signaling on 9 May 2023 by Choi, S., Lee, J., et al.
The T cell lineage-restricted protein THEMIS plays a critical role in T cell development at the positive selection stage. In the SHP1 activation model, THEMIS is proposed to enhance the activity of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP1 (encoded by Ptpn6), thereby dampening T cell antigen receptor (TCR) signaling and preventing the inappropriate negative selection of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes by positively selecting ligands. In contrast, in the SHP1 inhibition model, THEMIS is proposed to suppress SHP1 activity, rendering CD4+CD8+ thymocytes more sensitive to TCR signaling initiated by low-affinity ligands to promote positive selection. We sought to resolve the controversy regarding the molecular function of THEMIS. We found that the defect in positive selection in Themis-/- thymocytes was ameliorated by pharmacologic inhibition of SHP1 or by deletion of Ptpn6 and was exacerbated by SHP1 overexpression. Moreover, overexpression of SHP1 phenocopied the Themis-/- developmental defect, whereas deletion of Ptpn6, Ptpn11 (encoding SHP2), or both did not result in a phenotype resembling that of Themis deficiency. Last, we found that thymocyte negative selection was not enhanced but was instead impaired in the absence of THEMIS. Together, these results provide evidence favoring the SHP1 inhibition model, supporting a mechanism whereby THEMIS functions to enhance the sensitivity of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes to TCR signaling, enabling positive selection by low-affinity, self-ligand-TCR interactions.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
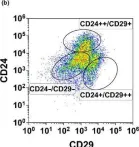
In Oral Dis on 1 January 2021 by Serrano Martinez, P., Cinat, D., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Oral Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1