The most common hemoglobin disorder worldwide is sickle cell disease (SCD) caused by a point mutation in the adult β-globin gene. As a result, hemoglobin S production occurs leading to clinical symptoms including vaso-occlusive pain, organ damage, and a shortened lifespan. Hydroxyurea is the only FDA-approved fetal hemoglobin (HbF) inducer in the United States that ameliorates the clinical severity of SCD. Due to challenges with hydroxyurea, our study aimed to address the unmet need for the development of non-chemotherapeutic HbF inducers. We investigated the ability of CT-101, a Class 1 histone deacetylase inhibitor, to flip the γ-globin to β-globin switch in a humanized SCD mouse model. Pharmacokinetic parameters were assessed in CD-1 and Townes SCD mice after a single intraperitoneal drug dose. Similar drug uptake and half-life were observed in both animals. Subsequent studies in β-YAC mice expressing human γ-globin and β-globin genes established the optimal dose of CT-101 that induces HbF without peripheral blood toxicity. Subsequent confirmatory studies were conducted in the SCD mouse treated with intraperitoneal CT-101, demonstrating increases in F-cells, HbF, and γ-globin gene mRNA levels. Hydroxyurea combined with CT-101 significantly decreased spleen size and hemorrhagic infarcts and improved splenic extramedullary hematopoiesis. Our novel agent, CT-101, flipped the switch by activating γ-globin gene transcription and HbF protein synthesis in the preclinical SCD mouse model without significant toxicity in the peripheral blood. These findings support the development of an oral CT-101 formulation for clinical testing in SCD.
Copyright: © 2025 Takezaki et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Product Citations: 52
In PLoS ONE on 13 May 2025 by Takezaki, M., Li, B., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Genetics
Epidermal maintenance of Langerhans cells relies on autophagy-regulated lipid metabolism.
In The Journal of Cell Biology on 3 February 2025 by Arbogast, F., Sal-Carro, R., et al.
Macroautophagy (often-named autophagy), a catabolic process involving autophagy-related (Atg) genes, prevents the accumulation of harmful cytoplasmic components and mobilizes energy reserves in long-lived and self-renewing cells. Autophagy deficiency affects antigen presentation in conventional dendritic cells (DCs) without impacting their survival. However, previous studies did not address epidermal Langerhans cells (LCs). Here, we demonstrate that deletion of either Atg5 or Atg7 in LCs leads to their gradual depletion. ATG5-deficient LCs showed metabolic dysregulation and accumulated neutral lipids. Despite increased mitochondrial respiratory capacity, they were unable to process lipids, eventually leading them to ferroptosis. Finally, metabolically impaired LCs upregulated proinflammatory transcripts and showed decreased expression of neuronal interaction receptors. Altogether, autophagy represents a critical regulator of lipid storage and metabolism in LCs, allowing their maintenance in the epidermis.
© 2024 Arbogast et al.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
In Oncogene on 1 September 2023 by Pawlikowska, P., Delestré, L., et al.
Leukaemia is caused by the clonal evolution of a cell that accumulates mutations/genomic rearrangements, allowing unrestrained cell growth. However, recent identification of leukaemic mutations in the blood cells of healthy individuals revealed that additional events are required to expand the mutated clones for overt leukaemia. Here, we assessed the functional consequences of deleting the Fanconi anaemia A (Fanca) gene, which encodes a DNA damage response protein, in Spi1 transgenic mice that develop preleukaemic syndrome. FANCA loss increases SPI1-associated disease penetrance and leukaemic progression without increasing the global mutation load of leukaemic clones. However, a high frequency of leukaemic FANCA-depleted cells display heterozygous activating mutations in known oncogenes, such as Kit or Nras, also identified but at low frequency in FANCA-WT mice with preleukaemic syndrome, indicating that FANCA counteracts the emergence of oncogene mutated leukaemic cells. A unique transcriptional signature is associated with the leukaemic status of FANCA-depleted cells, leading to activation of MDM4, NOTCH and Wnt/β-catenin pathways. We show that NOTCH signalling improves the proliferation capacity of FANCA-deficient leukaemic cells. Collectively, our observations indicate that loss of the FANC pathway, known to control genetic instability, fosters the expansion of leukaemic cells carrying oncogenic mutations rather than mutation formation. FANCA loss may contribute to this leukaemogenic progression by reprogramming transcriptomic landscape of the cells.
© 2023. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
In BMC Immunology on 19 April 2022 by Wu, S., Wang, S., et al.
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) supplementation is beneficial for several chronic diseases; however, its effect on immune regulation is still debated. Given the prevalence of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection and because natural killer (NK) cells are a component of innate immunity critical for controlling CMV infection, the current study explored the effect of a DHA-enriched diet on susceptibility to murine (M) CMV infection and the NK cell effector response to MCMV infection.
Male C57BL/6 mice fed a control or DHA-enriched diet for 3 weeks were infected with MCMV and sacrificed at the indicated time points postinfection. Compared with control mice, DHA-fed mice had higher liver and spleen viral loads at day 7 postinfection, but final MCMV clearance was not affected. The total numbers of NK cells and their terminal mature cell subset (KLRG1+ and Ly49H+ NK cells) were reduced compared with those in control mice at day 7 postinfection but not day 21. DHA feeding resulted in higher IFN-γ and granzyme B expression in splenic NK cells at day 7 postinfection. A mechanistic analysis showed that the splenic NK cells of DHA-fed mice had enhanced glucose uptake, increased CD71 and CD98 expression, and higher mitochondrial mass than control mice. In addition, DHA-fed mice showed reductions in the total numbers and activation levels of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.
These results suggest that DHA supplementation represses the early response to CMV infection but preserves NK cell effector functions by improving mitochondrial activity, which may play critical roles in subsequent MCMV clearance.
© 2022. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Response of Astrocyte Subpopulations Following Spinal Cord Injury.
In Cells on 18 February 2022 by Allahyari, R. V., Heinsinger, N. M., et al.
There is growing appreciation for astrocyte heterogeneity both across and within central nervous system (CNS) regions, as well as between intact and diseased states. Recent work identified multiple astrocyte subpopulations in mature brain. Interestingly, one subpopulation (Population C) was shown to possess significantly enhanced synaptogenic properties in vitro, as compared with other astrocyte subpopulations of adult cortex and spinal cord. Following spinal cord injury (SCI), damaged neurons lose synaptic connections with neuronal partners, resulting in persistent functional loss. We determined whether SCI induces an enhanced synaptomodulatory astrocyte phenotype by shifting toward a greater proportion of Population C cells and/or increasing expression of relevant synapse formation-associated genes within one or more astrocyte subpopulations. Using flow cytometry and RNAscope in situ hybridization, we found that astrocyte subpopulation distribution in the spinal cord did not change to a selectively synaptogenic phenotype following mouse cervical hemisection-type SCI. We also found that spinal cord astrocytes expressed synapse formation-associated genes to a similar degree across subpopulations, as well as in an unchanged manner between uninjured and SCI conditions. Finally, we confirmed these astrocyte subpopulations are also present in the human spinal cord in a similar distribution as mouse, suggesting possible conservation of spinal cord astrocyte heterogeneity across species.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cell Biology
-
Neuroscience
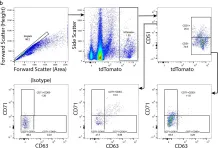
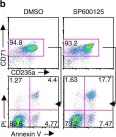
In Cells on 18 February 2022 by Allahyari, R. V., Heinsinger, N. M., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cells by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
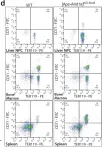
In Elife on 21 October 2020 by Riou, R., Ladli, M., et al.
Fig.3.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Elife by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
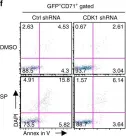
In Nat Commun on 29 August 2018 by Hu, P., Nebreda, A. R., et al.
Fig.7.F

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In Nat Commun on 29 August 2018 by Hu, P., Nebreda, A. R., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
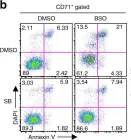
In Nat Commun on 29 August 2018 by Hu, P., Nebreda, A. R., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5