Background/Objectives: Enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) function in diverse modes and increasing studies have shown that they play important roles in normal development and disease. However, their role in erythropoiesis is not fully understood. Methods: We analyzed published RNA-seq and Promoter Capture Hi-C data from mouse E14.5 fetal liver cells to identify enhancer RNAs in erythroid cells with long-range interactions. Results: We discovered an erythroid-specific enhancer RNA (CpoxeRNA) transcribed from an enhancer region upstream of Cpox, an enzyme important for heme synthesis. CpoxeRNA is important for erythropoiesis, as the knockdown of CpoxeRNA by shRNA results in impaired enucleation and cell proliferation during terminal differentiation. CpoxeRNA interacts with cohesin and acts both in cis and trans to regulate erythroid genes. Conclusions: we have identified a trans-acting eRNA, CpoxeRNA, as a potential regulator of terminal erythropoiesis.
Product Citations: 56
In Genes on 28 March 2025 by Xie, B. & Dean, A.
-
Genetics
Preprint on Research Square on 4 June 2024 by Mukherjee, S., Elia, A., et al.
Abstract Tumor evolution is one of the major mechanisms responsible for acquiring therapy-resistant and more aggressive cancer clones. Whether the tumor microenvironment through immune-mediated mechanisms might promote the development of more aggressive cancer types is crucial for the identification of additional therapeutical opportunities. Here, we identified a novel subset of tumor-associated neutrophils, defined as tumor-associated neutrophil precursors (PreNeu). These PreNeu are enriched in highly proliferative hormone-dependent breast cancers and impair DNA repair capacity. Mechanistically, succinate secreted by tumor-associated PreNeu inhibits homologous recombination, promoting error-prone DNA repair through non-homologous end-joining regulated by PARP-1. Consequently, breast cancer cells acquire genomic instability, promoting tumor editing and progression. Selective inhibition of these pathways induces increased tumor cell killing in vitro and in vivo. Tumor-associated PreNeu score correlates with copy number alterations in highly proliferative hormone-dependent tumors from breast cancer patients. Treatment with PARP-1 inhibitors counteract the pro-tumorigenic effect of these neutrophils and synergize with combined immunotherapeutic approaches.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 5 December 2023 by Xie, B. & Dean, A.
ABSTRACT Super enhancers are important regulators of gene expression that often overlap with protein-coding genes. However, it is unclear whether the overlapping protein-coding genes and the mRNA derived from them contribute to enhancer activity. Using an erythroid-specific super enhancer that overlaps the Cpox gene as a model, we found that Cpox mRNA has a non-coding function in regulating neighboring protein-coding genes, eRNA expression and TAD interactions. Depletion of Cpox mRNA leads to accumulation of H3K27me3 and release of p300 from the Cpox locus, activating an intra-TAD enhancer and gene expression. Additionally, we identified a head-to-tail interaction between the TAD boundary genes Cpox and Dcbld2 that is facilitated by a novel type of repressive loop anchored by p300 and PRC2/H3K27me3. Our results uncover a regulatory role for mRNA transcribed within a super enhancer context and provide insight into head-to-tail inter-gene interaction in the regulation of gene expression and oncogene activation.
-
Genetics
In Blood Advances on 28 November 2023 by Liang, R., Lin, M., et al.
β-thalassemias are common hemoglobinopathies due to mutations in the β-globin gene that lead to hemolytic anemias. Premature death of β-thalassemic erythroid precursors results in ineffective erythroid maturation, increased production of erythropoietin (EPO), expansion of erythroid progenitor compartment, extramedullary erythropoiesis, and splenomegaly. However, the molecular mechanism of erythroid apoptosis in β-thalassemia is not well understood. Using a mouse model of β-thalassemia (Hbbth3/+), we show that dysregulated expression of the FOXO3 transcription factor is implicated in β-thalassemia erythroid apoptosis. In Foxo3-/-/Hbbth3/+ mice, erythroid apoptosis is significantly reduced, whereas erythroid cell maturation, and red blood cell and hemoglobin production are substantially improved even with elevated reactive oxygen species in double-mutant erythroblasts. However, persistence of elevated reticulocytes and splenomegaly suggests that ineffective erythropoiesis is not resolved in Foxo3-/-/Hbbth3/+. We found the cell cycle inhibitor Cdkn1a (cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21), a FOXO3 target gene, is markedly upregulated in both mouse and patient-derived β-thalassemic erythroid precursors. Double-mutant p21/Hbbth3/+ mice exhibited embryonic lethality with only a fraction of mice surviving to weaning. Notably, studies in adult mice displayed greatly reduced apoptosis and circulating Epo in erythroid compartments of surviving p21-/-/Hbbth3/+ mice relative to Hbbth3/+ mice, whereas ineffective erythroid cell maturation, extramedullary erythropoiesis, and splenomegaly were not modified. These combined results suggest that mechanisms that control β-thalassemic erythroid cell survival and differentiation are uncoupled from ineffective erythropoiesis and involve a molecular network including FOXO3 and P21. Overall, these studies provide a new framework for investigating ineffective erythropoiesis in β-thalassemia.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Monomeric agonist peptide/MHCII complexes activate T-cells in an autonomous fashion.
In EMBO Reports on 6 November 2023 by Platzer, R., Hellmeier, J., et al.
Molecular crowding of agonist peptide/MHC class II complexes (pMHCIIs) with structurally similar, yet per se non-stimulatory endogenous pMHCIIs is postulated to sensitize T-cells for the recognition of single antigens on the surface of dendritic cells and B-cells. When testing this premise with the use of advanced live cell microscopy, we observe pMHCIIs as monomeric, randomly distributed entities diffusing rapidly after entering the APC surface. Synaptic TCR engagement of highly abundant endogenous pMHCIIs is low or non-existent and affects neither TCR engagement of rare agonist pMHCII in early and advanced synapses nor agonist-induced TCR-proximal signaling. Our findings highlight the capacity of single freely diffusing agonist pMHCIIs to elicit the full T-cell response in an autonomous and peptide-specific fashion with consequences for adaptive immunity and immunotherapeutic approaches.
© 2023 The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
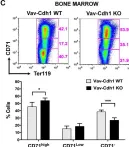
In Sci Rep on 21 June 2022 by Cuadrado, M., Garzón, J., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
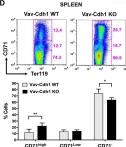
In Sci Rep on 21 June 2022 by Cuadrado, M., Garzón, J., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
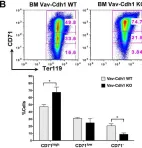
In Sci Rep on 21 June 2022 by Cuadrado, M., Garzón, J., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
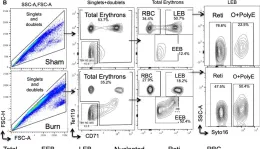
In Front Med (Lausanne) on 12 December 2019 by Hasan, S., Johnson, M. C., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Med (Lausanne) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4