Immunosenescence refers to the multifaceted and profound alterations in the immune system brought about by aging, exerting complex influences on the pathophysiological processes of diseases that manifest upon it. Using a combination of single-cell RNA sequencing, cytometry by time of flight, and various immunological assays, we investigated the characteristics of immunosenescence in the peripheral blood of aged mice and its impact on the cerebral immune environment after ischemic stroke. Our results revealed some features of immunosenescence. We observed an increase in neutrophil counts, concurrent with accelerated neutrophil aging, characterized by altered expression of aging-associated markers like CD62L and consequential changes in neutrophil-mediated immune functions. Monocytes/macrophages in aged mice exhibited enhanced antigen-presentation capabilities. T cell profiles shifted from naive to effector or memory states, with a specific rise in T helper 1 cells and T helper 17 cells subpopulations and increased regulatory T cell activation in CD4 T cells. Furthermore, regulatory CD8 T cells marked by Klra decreased with aging, while a subpopulation of exhausted-like CD8 T cells expanded, retaining potent immunostimulatory and proinflammatory functions. Critically, these inherent disparities not only persisted but were further amplified within the ischemic hemispheres following stroke. In summary, our comprehensive insights into the key attributes of peripheral immunosenescence provide a vital theoretical foundation for understanding not only ischemic strokes but also other age-associated diseases.
Copyright © 2023 Jianan Lu et al.
Product Citations: 23
Age-Related Alterations in Peripheral Immune Landscape with Magnified Impact on Post-Stroke Brain.
In Research (Washington, D.C.) on 13 December 2023 by Lu, J., Li, H., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In JCI Insight on 8 November 2021 by Prakhar, P., Alvarez-DelValle, J., et al.
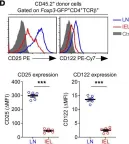
Foxp3+ Tregs are potent immunosuppressive CD4+ T cells that are critical to maintain immune quiescence and prevent autoimmunity. Both the generation and maintenance of Foxp3+ Tregs depend on the cytokine IL-2. Hence, the expression of the IL-2 receptor α-chain (CD25) is not only considered a specific marker, but also a nonredundant requirement for Tregs. Here, we report that Foxp3+ Tregs in the small intestine (SI) epithelium, a critical barrier tissue, are exempt from such an IL-2 requirement, since they had dramatically downregulated CD25 expression, showed minimal STAT5 phosphorylation ex vivo, and were unable to respond to IL-2 in vitro. Nonetheless, SI epithelial Tregs survived and were present at the same frequency as in other lymphoid organs, and they retained potent suppressor function that was associated with high levels of CTLA-4 expression and the production of copious amounts of IL-10. Moreover, adoptive transfer experiments of Foxp3+ Tregs revealed that such IL-2-independent survival and effector functions were imposed by the SI epithelial tissue, suggesting that tissue adaptation is a mechanism that tailors the effector function and survival requirements of Foxp3+ Tregs specific to the tissue environment.
-
FC/FACS
-
Immunology and Microbiology
MEK inhibition reprograms CD8+ T lymphocytes into memory stem cells with potent antitumor effects.
In Nature Immunology on 1 January 2021 by Verma, V., Jafarzadeh, N., et al.
Regenerative stem cell-like memory (TSCM) CD8+ T cells persist longer and produce stronger effector functions. We found that MEK1/2 inhibition (MEKi) induces TSCM that have naive phenotype with self-renewability, enhanced multipotency and proliferative capacity. This is achieved by delaying cell division and enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis and fatty acid oxidation, without affecting T cell receptor-mediated activation. DNA methylation profiling revealed that MEKi-induced TSCM cells exhibited plasticity and loci-specific profiles similar to bona fide TSCM isolated from healthy donors, with intermediate characteristics compared to naive and central memory T cells. Ex vivo, antigenic rechallenge of MEKi-treated CD8+ T cells showed stronger recall responses. This strategy generated T cells with higher efficacy for adoptive cell therapy. Moreover, MEKi treatment of tumor-bearing mice also showed strong immune-mediated antitumor effects. In conclusion, we show that MEKi leads to CD8+ T cell reprogramming into TSCM that acts as a reservoir for effector T cells with potent therapeutic characteristics.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In Scientific Reports on 8 November 2019 by Satake, K., Amano, T., et al.
A topical medication combining calcipotriol (Cal) and betamethasone dipropionate (BDP) has proven effective in a number of randomized controlled trials performed in patients with psoriasis, but its mechanism of action has not been fully elucidated. We investigated whether the combination of Cal and BDP (Cal/BDP) in this topical medication had a synergistic effect on psoriasis-like dermatitis and explored the underlying immunological mechanisms in a murine psoriasis model induced by application of imiquimod. Cal/BDP synergistically inhibited ear thickening induced by imiquimod compared to monotherapy with either Cal or BDP. In addition, Cal/BDP significantly suppressed the interleukin (IL)-23/IL-17-producing T (T17) pathogenic axis, including expression of IL-17a, IL-23a, IL-22 and TNF-α mRNA in skin lesions and expansion of CCR6+ γδ T17 cells in the draining lymph nodes. Notably, Cal/BDP synergistically induced regulatory CD8+ T cells and also improved the balance between regulatory CD8+ or CD4+ T cells and proinflammatory CCR6+ γδ T17 cells in the draining lymph nodes. These results suggest synergistic anti-psoriatic activity of Cal/BDP with normalization of the imbalance between regulatory CD8+ or CD4+ T cells and proinflammatory CCR6+ γδ T17 cells, which contributes to successful control of psoriasis by Cal-BDP combination therapy.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
A functional subset of CD8+ T cells during chronic exhaustion is defined by SIRPα expression.
In Nature Communications on 15 February 2019 by Myers, L. M., Tal, M. C., et al.
Prolonged exposure of CD8+ T cells to antigenic stimulation, as in chronic viral infections, leads to a state of diminished function termed exhaustion. We now demonstrate that even during exhaustion there is a subset of functional CD8+ T cells defined by surface expression of SIRPα, a protein not previously reported on lymphocytes. On SIRPα+ CD8+ T cells, expression of co-inhibitory receptors is counterbalanced by expression of co-stimulatory receptors and it is only SIRPα+ cells that actively proliferate, transcribe IFNγ and show cytolytic activity. Furthermore, target cells that express the ligand for SIRPα, CD47, are more susceptible to CD8+ T cell-killing in vivo. SIRPα+ CD8+ T cells are evident in mice infected with Friend retrovirus, LCMV Clone 13, and in patients with chronic HCV infections. Furthermore, therapeutic blockade of PD-L1 to reinvigorate CD8+ T cells during chronic infection expands the cytotoxic subset of SIRPα+ CD8+ T cells.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In JCI Insight on 8 November 2021 by Prakhar, P., Alvarez-DelValle, J., et al.
Fig.4.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1