The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic highlighted the potential of mRNA vaccines in rapidly responding to emerging pathogens. However, immunity induced by conventional mRNA vaccines wanes quickly, requiring frequent boosters. Self-amplifying RNA (saRNA) vaccines, which extend antigen expression via self-replication, offer a promising strategy to induce more durable immune responses. In this study, we developed an saRNA vaccine encoding Zika virus (ZIKV) membrane and envelope proteins and evaluated its efficacy in mice. A single vaccination elicited strong humoral and cellular immune responses and reduced viral loads but only for 28 days. By day 84, antibody titers and T cell responses had significantly declined, resulting in reduced efficacy. To address this, we evaluated agonist antibodies targeting the T cell costimulatory molecules OX40 and 4-1BB. Coadministration of agonist antibodies enhanced CD8+ T cell responses to vaccination, resulting in sustained immunity and reduced viral loads at day 84. Depletion and passive transfer studies verified that long-term antiviral immunity was primarily CD8+ T cell dependent, with minimal contributions from antibody responses. These findings suggest that agonists targeting members of the tumor necrosis receptor superfamily, such as OX40 and 4-1BB, might enhance the durability of saRNA vaccine-induced protection, addressing a key limitation of current mRNA vaccine platforms.
Product Citations: 39
In JCI Insight on 22 May 2025 by Lu, H. H., dos Santos Alves, R. P., et al.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Conserved role of hnRNPL in alternative splicing of epigenetic modifiers enables B cell activation.
In EMBO Reports on 1 June 2024 by Subramani, P. G., Fraszczak, J., et al.
The multifunctional RNA-binding protein hnRNPL is implicated in antibody class switching but its broader function in B cells is unknown. Here, we show that hnRNPL is essential for B cell activation, germinal center formation, and antibody responses. Upon activation, hnRNPL-deficient B cells show proliferation defects and increased apoptosis. Comparative analysis of RNA-seq data from activated B cells and another eight hnRNPL-depleted cell types reveals common effects on MYC and E2F transcriptional programs required for proliferation. Notably, while individual gene expression changes are cell type specific, several alternative splicing events affecting histone modifiers like KDM6A and SIRT1, are conserved across cell types. Moreover, hnRNPL-deficient B cells show global changes in H3K27me3 and H3K9ac. Epigenetic dysregulation after hnRNPL loss could underlie differential gene expression and upregulation of lncRNAs, and explain common and cell type-specific phenotypes, such as dysfunctional mitochondria and ROS overproduction in mouse B cells. Thus, hnRNPL is essential for the resting-to-activated B cell transition by regulating transcriptional programs and metabolism, at least in part through the alternative splicing of several histone modifiers.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
T-bet+ B cells accumulate in adipose tissue and exacerbate metabolic disorder during obesity.
In Cell Metabolism on 2 August 2022 by Hägglöf, T., Vanz, C., et al.
Obesity is accompanied by inflammation in adipose tissue, impaired glucose tolerance, and changes in adipose leukocyte populations. These studies of adipose tissue from humans and mice revealed that increased frequencies of T-bet+ B cells in adipose tissue depend on invariant NKT cells and correlate with weight gain during obesity. Transfer of B cells enriched for T-bet+ cells exacerbates metabolic disorder in obesity, while ablation of Tbx21 specifically in B cells reduces serum IgG2c levels, inflammatory cytokines, and inflammatory macrophages in adipose tissue, ameliorating metabolic symptoms. Furthermore, transfer of serum or purified IgG from HFD mice restores metabolic disease in T-bet+ B cell-deficient mice, confirming T-bet+ B cell-derived IgG as a key mediator of inflammation during obesity. Together, these findings reveal an important pathological role for T-bet+ B cells that should inform future immunotherapy design in type 2 diabetes and other inflammatory conditions.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports on 22 March 2022 by Stienne, C., Virgen-Slane, R., et al.
The Btla inhibitory receptor limits innate and adaptive immune responses, both preventing the development of autoimmune disease and restraining anti-viral and anti-tumor responses. It remains unclear how the functions of Btla in diverse lymphocytes contribute to immunoregulation. Here, we show that Btla inhibits activation of genes regulating metabolism and cytokine signaling, including Il6 and Hif1a, indicating a regulatory role in humoral immunity. Within mucosal Peyer's patches, we find T-cell-expressed Btla-regulated Tfh cells, while Btla in T or B cells regulates GC B cell numbers. Treg-expressed Btla is required for cell-intrinsic Treg homeostasis that subsequently controls GC B cells. Loss of Btla in lymphocytes results in increased IgA bound to intestinal bacteria, correlating with altered microbial homeostasis and elevations in commensal and pathogenic bacteria. Together our studies provide important insights into how Btla functions as a checkpoint in diverse conventional and regulatory lymphocyte subsets to influence systemic immune responses.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America on 30 November 2021 by McCorkell, K. A., Jayachandran, N., et al.
Global inactivation of IκB kinase (IKK)-α results in defective lymph node (LN) formation and B cell maturation, and loss of IKK-α-dependent noncanonical NF-κB signaling in stromal organizer and hematopoietic cells is thought to underlie these distinct defects. We previously demonstrated that this pathway is also activated in vascular endothelial cells (ECs). To determine the physiologic function of EC-intrinsic IKK-α, we crossed IkkαF/F mice with Tie2-cre or Cdh5-cre mice to ablate IKK-α in ECs. Notably, the compound defects of global IKK-α inactivation were recapitulated in IkkαTie2 and IkkαCdh5 mice, as both lacked all LNs and mature follicular and marginal zone B cell numbers were markedly reduced. However, as Tie2-cre and Cdh5-cre are expressed in all ECs, including blood forming hemogenic ECs, IKK-α was also absent in hematopoietic cells (HC). To determine if loss of HC-intrinsic IKK-α affected LN development, we generated IkkαVav mice lacking IKK-α in only the hematopoietic compartment. While mature B cell numbers were significantly reduced in IkkαVav mice, LN formation was intact. As lymphatic vessels also arise during development from blood ECs, we generated IkkαLyve1 mice lacking IKK-α in lymphatic ECs (LECs) to determine if IKK-α in lymphatic vessels impacts LN development. Strikingly, while mature B cell numbers were normal, LNs were completely absent in IkkαLyve1 mice. Thus, our findings reveal that IKK-α in distinct EC-derived compartments is uniquely required to promote B cell homeostasis and LN development, and we establish that LEC-intrinsic IKK-α is absolutely essential for LN formation.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
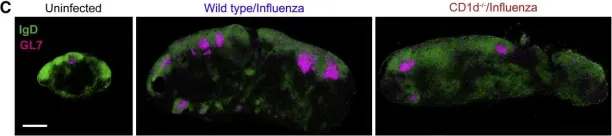
In Cell on 25 January 2018 by Gaya, M., Barral, P., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cell by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1