Legionella pneumophila is a pathogen which can lead to a severe form of pneumonia in humans known as Legionnaires disease after replication in alveolar macrophages. Viable L. pneumophila actively secrete effector molecules to modulate the host's immune response. Here, we report that L. pneumophila-derived factors reprogram macrophages into a tolerogenic state, a process to which the C-type lectin receptor Mincle (CLEC4E) markedly contributes. The underlying epigenetic state is characterized by increases of the closing mark H3K9me3 and decreases of the opening mark H3K4me3, subsequently leading to the reduced secretion of the cytokines TNF, IL-6, IL-12, the production of reactive oxygen species, and cell-surface expression of MHC-II and CD80 upon re-stimulation. In summary, these findings provide important implications for our understanding of Legionellosis and the contribution of Mincle to reprogramming of macrophages by L. pneumophila.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Product Citations: 63
In IScience on 20 September 2024 by Stegmann, F., Diersing, C., et al.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
NRF2 Mediates Cellular Resistance to Transformation, Radiation, and Inflammation in Mice.
In Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) on 25 August 2022 by Schaue, D., Micewicz, E. D., et al.
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) is recognized as a master transcription factor that regulates expression of numerous detoxifying and antioxidant cytoprotective genes. In fact, models of NRF2 deficiency indicate roles not only in redox regulation, but also in metabolism, inflammatory/autoimmune disease, cancer, and radioresistancy. Since ionizing radiation (IR) generates reactive oxygen species (ROS), it is not surprising it activates NRF2 pathways. However, unexpectedly, activation is often delayed for many days after the initial ROS burst. Here, we demonstrate that, as assayed by γ-H2AX staining, rapid DNA double strand break (DSB) formation by IR in primary mouse Nrf2-/- MEFs was not affected by loss of NRF2, and neither was DSB repair to any great extent. In spite of this, basal and IR-induced transformation was greatly enhanced, suggesting that NRF2 protects against late IR-induced genomic instability, at least in murine MEFs. Another possible IR- and NRF2-related event that could be altered is inflammation and NRF2 deficiency increased IR-induced NF-κB pro-inflammatory responses mostly late after exposure. The proclivity of NRF2 to restrain inflammation is also reflected in the reprogramming of tumor antigen-specific lymphocyte responses in mice where Nrf2 k.o. switches Th2 responses to Th1 polarity. Delayed NRF2 responses to IR may be critical for the immune transition from prooxidant inflammation to antioxidant healing as well as in driving cellular radioresistance and survival. Targeting NRF2 to reprogram immunity could be of considerable therapeutic benefit in radiation and immunotherapy.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Hif-1a suppresses ROS-induced proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts following myocardial infarction.
In Cell Stem Cell on 3 February 2022 by Janbandhu, V., Tallapragada, V., et al.
We report that cardiac fibroblasts (CFs) and mesenchymal progenitors are more hypoxic than other cardiac interstitial populations, express more hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α), and exhibit increased glycolytic metabolism. CF-specific deletion of Hif-1a resulted in decreased HIF-1 target gene expression and increased mesenchymal progenitors in uninjured hearts and increased CF activation without proliferation following sham injury, as demonstrated using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq). After myocardial infarction (MI), however, there was ∼50% increased CF proliferation and excessive scarring and contractile dysfunction, a scenario replicated in 3D engineered cardiac microtissues. CF proliferation was associated with higher reactive oxygen species (ROS) as occurred also in wild-type mice treated with the mitochondrial ROS generator MitoParaquat (MitoPQ). The mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant MitoTEMPO rescued Hif-1a mutant phenotypes. Thus, HIF-1α in CFs provides a critical braking mechanism against excessive post-ischemic CF activation and proliferation through regulation of mitochondrial ROS. CFs are potential cellular targets for designer antioxidant therapies in cardiovascular disease.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
In International Journal of Nanomedicine on 30 October 2021 by Barbosa, M. M. F., Kanno, A. I., et al.
The use of adjuvants can significantly strengthen a vaccine's efficacy. We sought to explore the immunization efficacy of bacterial outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) displaying the Schistosoma mansoni antigen, SmTSP-2, through a biotin-rhizavidin coupling approach. The rationale is to exploit the nanoparticulate structure and the adjuvant properties of OMVs to induce a robust antigen-specific immune response, in light of developing new vaccines against S. mansoni.
OMVs were obtained from Neisseria lactamica and conjugated with biotin. The recombinant SmTSP-2 in fusion with the biotin-binding protein rhizavidin (rRzvSmTSP-2) was produced in E. coli and coupled to biotinylated OMVs to generate an OMV complex displaying SmTSP-2 on the membrane surface (OMV:rSmTSP-2). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering analysis were used to determine particle charge and size. The immunogenicity of the vaccine complex was evaluated in C57BL/6 mice.
The rRzvSmTSP-2 protein was successfully coupled to biotinylated OMVs and purified by size-exclusion chromatography. The OMV:rSmTSP-2 nanoparticles showed an average size of 200 nm, with zeta potential around - 28 mV. Mouse Bone Marrow Dendritic Cells were activated by the nanoparticles as determined by increased expression of the co-stimulatory molecules CD40 and CD86, and the proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-12) or IL-10. Splenocytes of mice immunized with OMV:rSmTSP-2 nanoparticles reacted to an in vitro challenge with SmTSP-2 with an increased production of IL-6, IL-10 and IL-17 and displayed a higher number of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes expressing IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-2, compared to mice immunized with the antigen alone. Immunization of mice with OMV:rSmTSP-2 induced a 100-fold increase in specific anti-SmTSP-2 IgG antibody titers, as compared to the group receiving the recombinant rSmTSP-2 protein alone or even co-administered with unconjugated OMV.
Our results demonstrate that the SmTSP-2 antigen coupled with OMVs is highly immunogenic in mice, supporting the potential effectiveness of this platform for improved antigen delivery in novel vaccine strategies.
© 2021 Barbosa et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Lymph node-resident dendritic cells drive TH2 cell development involving MARCH1.
In Science Immunology on 15 October 2021 by Castellanos, C. A., Ren, X., et al.
Type 2 T helper (TH2) cells are protective against parasitic worm infections but also aggravate allergic inflammation. Although the role of dendritic cells (DCs) in TH2 cell differentiation is well established, the underlying mechanisms are largely unknown. Here, we show that DC induction of TH2 cells depends on membrane-associated RING-CH-1 (MARCH1) ubiquitin ligase. The pro-TH2 effect of MARCH1 relied on lymph node (LN)–resident DCs, which triggered T cell receptor (TCR) signaling and induced GATA-3 expression from naïve CD4+ T cells independent of tissue-driven migratory DCs. Mice with mutations in the ubiquitin acceptor sites of MHCII and CD86, the two substrates of MARCH1, failed to develop TH2 cells. These findings suggest that TH2 cell development depends on ubiquitin-mediated clearance of antigen-presenting and costimulatory molecules by LN-resident DCs and consequent control of TCR signaling.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
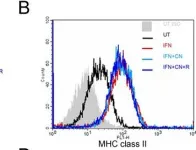
In J Neuroinflammation on 6 March 2009 by Lin, H. W., Jain, M. R., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from J Neuroinflammation by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
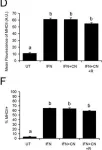
In J Neuroinflammation on 6 March 2009 by Lin, H. W., Jain, M. R., et al.
Fig.5.D,F

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from J Neuroinflammation by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In J Neuroinflammation on 6 March 2009 by Lin, H. W., Jain, M. R., et al.
Fig.6.B,D,F,H

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from J Neuroinflammation by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3