Hematopoietic aging is characterized by diminished stem cell regenerative capacity and an increased risk of hematologic dysfunction. We previously identified that the prostaglandin-degrading enzyme 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) regulates hematopoietic stem cell activity. Here, we expand on this work and demonstrate that in aged mice, (1) 15-PGDH expression and activity remain conserved in the bone marrow and spleen, suggesting it remains a viable therapeutic target in aging, (2) prolonged PGDH inhibition (PGDHi) significantly increases the frequency and number of phenotypic hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells across multiple compartments, with transcriptional changes indicative of enhanced function, (3) PGDHi-treated bone marrow enhances short-term hematopoietic recovery following transplantation, leading to improved peripheral blood output and accelerated multilineage reconstitution, and (4) PGDHi confers a competitive advantage in primary hematopoietic transplantation while mitigating age-associated myeloid bias in secondary transplants. Notably, these effects occur without perturbing steady-state blood production, suggesting that PGDHi enhances hematopoiesis under regenerative conditions while maintaining homeostasis. Our work identifies PGDHi as a translatable intervention to rejuvenate aged HSCs and mitigate hematopoietic decline. Significance Statement We identify 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase inhibition (PGDHi) as a strategy to enhance hematopoietic stem cell function in aging. In aged mice, PGDHi expands stem and progenitor populations, accelerates hematopoietic recovery after transplantation, and reduces myeloid bias while maintaining steady-state blood production. These findings highlight a potential therapeutic approach to restore hematopoietic resilience and improve regenerative outcomes in aging. Graphical Abstract 15-prostaglandin dehydrogenase inhibition ameliorates multiple facets of age-related hematopoietic decline. Schematic made using BioRender.com.
Product Citations: 114
15-PGDH inhibition promotes hematopoietic recovery and enhances HSC function during aging
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 17 April 2025 by Chaudhary, R., Cordova, B. A., et al.
In PLoS Computational Biology on 1 March 2025 by Wang, G., Zhang, D., et al.
Neutrophils, an essential innate immune cell type with a short lifespan, rely on continuous replenishment from bone marrow (BM) precursors. Although it is established that neutrophils are derived from the granulocyte-macrophage progenitor (GMP), the molecular regulators involved in the differentiation process remain poorly understood. Here we developed a random forest-based machine-learning pipeline, NeuRGI (Neutrophil Regulatory Gene Identifier), which utilized Positive-Unlabeled Learning (PU-learning) and neural network-based in silico gene knockout to identify neutrophil regulators. We interrogated features including gene expression dynamics, physiological characteristics, pathological relatedness, and gene conservation for the model training. Our identified pipeline leads to identifying Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-4 (MAP4K4) as a novel neutrophil differentiation regulator. The loss of MAP4K4 in hematopoietic stem cells and progenitors in mice induced neutropenia and impeded the differentiation of neutrophils in the bone marrow. By modulating the phosphorylation level of proteins involved in cell apoptosis, such as STAT5A, MAP4K4 delicately regulates cell apoptosis during the process of neutrophil differentiation. Our work presents a novel regulatory mechanism in neutrophil differentiation and provides a robust prediction model that can be applied to other cellular differentiation processes.
Copyright: © 2025 Wang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Endothelial LATS2 is a suppressor of bone marrow fibrosis.
In Nat Cardiovasc Res on 19 August 2024 by Sivaraj, K. K., Majev, P. G., et al.
Myelofibrosis and osteosclerosis are fibrotic diseases disrupting bone marrow function that occur in various leukemias but also in response to non-malignant alterations in hematopoietic cells. Here we show that endothelial cell-specific inactivation of the Lats2 gene, encoding Hippo kinase large tumor suppressor kinase 2, or overexpression of the downstream effector YAP1 induce myofibroblast formation and lead to extensive fibrosis and osteosclerosis, which impair bone marrow function and cause extramedullary hematopoiesis in the spleen. Mechanistically, loss of LATS2 induces endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition, resulting in increased expression of extracellular matrix and secreted signaling molecules. Changes in endothelial cells involve increased expression of serum response factor target genes, and, strikingly, major aspects of the LATS2 mutant phenotype are rescued by inactivation of the Srf gene. These findings identify the endothelium as a driver of bone marrow fibrosis, which improves understanding of myelofibrotic and osteosclerotic diseases, for which drug therapies are currently lacking.
© The Author(s) 2024.
In Blood Advances on 23 April 2024 by Wake, M. S., Palin, A., et al.
Iron plays a major role in the deterioration of β-thalassemia. Indeed, the high levels of transferrin saturation and iron delivered to erythroid progenitors are associated with production of α-globin precipitates that negatively affect erythropoiesis. Matriptase-2/TMPRSS6, a membrane-bound serine protease expressed in hepatocytes, negatively modulates hepcidin production and thus is a key target to prevent iron overload in β-thalassemia. To address safety concerns raised by the suppression of Tmprss6 by antisense oligonucleotides or small interfering RNA, we tested a fully human anti-matriptase-2 antibody, RLYB331, which blocks the protease activity of matriptase-2. When administered weekly to Hbbth3/+ mice, RLYB331 induced hepcidin expression, reduced iron loading, prevented the formation of toxic α-chain/heme aggregates, reduced ros oxygen species formation, and improved reticulocytosis and splenomegaly. To increase the effectiveness of RLYB331 in β-thalassemia treatment even further, we administered RLYB331 in combination with RAP-536L, a ligand-trapping protein that contains the extracellular domain of activin receptor type IIB and alleviates anemia by promoting differentiation of late-stage erythroid precursors. RAP-536L alone did not prevent iron overload but significantly reduced apoptosis in the erythroid populations of the bone marrow, normalized red blood cell counts, and improved hemoglobin and hematocrit levels. Interestingly, the association of RLYB331 with RAP-536L entirely reversed the β-thalassemia phenotype in Hbbth3/+ mice and simultaneously corrected iron overload, ineffective erythropoiesis, splenomegaly, and hematological parameters, suggesting that a multifunctional molecule consisting of the fusion of RLYB331 with luspatercept (human version of RAP-536L) would allow administration of a single medication addressing simultaneously the different pathophysiological aspects of β-thalassemia.
© 2024 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In The EMBO Journal on 1 April 2024 by Zhu, J., Yang, W., et al.
Pericytes and endothelial cells (ECs) constitute the fundamental components of blood vessels. While the role of ECs in tumor angiogenesis and the tumor microenvironment is well appreciated, pericyte function in tumors remains underexplored. In this study, we used pericyte-specific deletion of the nitric oxide (NO) receptor, soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC), to investigate via single-cell RNA sequencing how pericytes influence the vascular niche and the tumor microenvironment. Our findings demonstrate that pericyte sGC deletion disrupts EC-pericyte interactions, impairing Notch-mediated intercellular communication and triggering extensive transcriptomic reprogramming in both pericytes and ECs. These changes further extended their influence to neighboring cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) through paracrine signaling, collectively suppressing tumor growth. Inhibition of pericyte sGC has minimal impact on quiescent vessels but significantly increases the vulnerability of angiogenic tumor vessels to conventional anti-angiogenic therapy. In conclusion, our findings elucidate the role of pericytes in shaping the tumor vascular niche and tumor microenvironment and support pericyte sGC targeting as a promising strategy for improving anti-angiogenic therapy for cancer treatment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
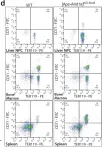
In Elife on 21 October 2020 by Riou, R., Ladli, M., et al.
Fig.3.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Elife by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
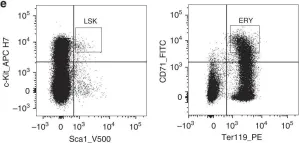
In Nat Commun on 22 May 2020 by Yang, L., Chen, Z., et al.
Fig.2.E

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
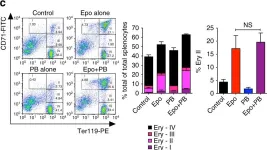
In Nat Commun on 1 September 2017 by Pasricha, S. R., Lim, P. J., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
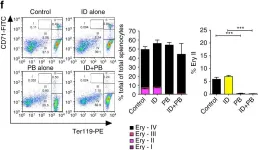
In Nat Commun on 1 September 2017 by Pasricha, S. R., Lim, P. J., et al.
Fig.4.F

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4