Ninjury-induced protein 1 (Ninj1) is associated with inflammation and tumor progression and shows increased expression in various cancers. This study aimed to investigate the role of Ninj1 in colitis-associated colorectal cancer (CRC) by focusing on its interaction with 17β-estradiol (E2).
Using an azoxymethane (AOM)/dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) mouse model of colitis-associated CRC, wild-type (WT) and Ninj1 knockout (KO) male mice were treated with or without E2.
At week 2, Ninj1 KO mice exhibited attenuated colitis symptoms than WT mice following AOM/DSS treatment. E2 administration significantly alleviated these symptoms in both WT and Ninj1 KO mice, with reductions in the disease activity index (DAI), colon length shortening, and histopathological damage. The levels of pro-inflammatory mediators were reduced by E2 treatment in both groups, with the Ninj1 KO group showing a more pronounced response. At week 13, tumor development in Ninj1 KO mice was significantly lower than that in WT mice, particularly in the distal colon. E2 treatment inhibited tumor formation in WT mice and had a stronger inhibitory effect on distal colon tumorigenesis in Ninj1 KO mice. Immune cell populations, including the populations of macrophages and T cells, were also modulated by E2 in WT mice; however, these effects were diminished in Ninj1 KO mice.
These findings suggest that Ninj1 plays a role in modulating colitis and CRC progression, with E2 exerting anti-inflammatory and anti-tumorigenic effects that are influenced by Ninj1 status.
Product Citations: 127
In Cancer Research and Treatment : Official Journal of Korean Cancer Association on 13 January 2025 by Song, C. H., Kim, N., et al.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
Epi-microRNA mediated metabolic reprogramming counteracts hypoxia to preserve affinity maturation.
In Nature Communications on 3 December 2024 by Nakagawa, R., Llorian, M., et al.
To increase antibody affinity against pathogens, positively selected GC-B cells initiate cell division in the light zone (LZ) of germinal centers (GCs). Among these, higher-affinity clones migrate to the dark zone (DZ) and vigorously proliferate by utilizing energy provided by oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). However, it remains unknown how positively selected GC-B cells adapt their metabolism for cell division in the glycolysis-dominant, cell cycle arrest-inducing, hypoxic LZ microenvironment. Here, we show that microRNA (miR)-155 mediates metabolic reprogramming during positive selection to protect high-affinity clones. Mechanistically, miR-155 regulates H3K36me2 levels in hypoxic conditions by directly repressing the histone lysine demethylase, Kdm2a, whose expression increases in response to hypoxia. The miR-155-Kdm2a interaction is crucial for enhancing OXPHOS through optimizing the expression of vital nuclear mitochondrial genes under hypoxia, thereby preventing excessive production of reactive oxygen species and subsequent apoptosis. Thus, miR-155-mediated epigenetic regulation promotes mitochondrial fitness in high-affinity GC-B cells, ensuring their expansion and consequently affinity maturation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cell Biology
In Nature Communications on 18 November 2024 by Park, H. B., Kim, K. H., et al.
Chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells show remarkable efficacy for some hematological malignancies. However, CAR targets that are expressed at high level and selective to tumors are scarce. Several strategies have been proposed to tackle the on-target off-tumor toxicity of CAR-T cells that arise from suboptimal selectivity, but these are complicated, with many involving dual gene expression for specificity. In this study, we show that switchable CAR-T cells with a tumor targeting adaptor can mitigate on-target off-tumor toxicity against a low selectivity tumor antigen that cannot be targeted by conventional CAR-T cells, such as CD40. Our system is composed of anti-cotinine murine CAR-T cells and cotinine-labeled anti-CD40 single chain variable fragments (scFv), with which we show selective tumor killing while sparing CD40-expressing normal cells including macrophages in a mouse model of lymphoma. Simple replacement of the tumor-targeting adaptor with a suicidal drug-conjugated tag may further enhance safety by enabling permanent in vivo depletion of the switchable CAR-T cells when necessary. In summary, our switchable CAR system can control CAR-T cell toxicity while maintaining therapeutic efficacy, thereby expanding the range of CAR targets.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Molecular Therapy. Nucleic Acids on 12 March 2024 by Lin, W. T., Wu, H. H., et al.
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a life-threatening condition with limited treatment options. The pathogenesis of ALI involves macrophage-mediated disruption and subsequent repair of the alveolar barriers, which ultimately results in lung damage and regeneration, highlighting the pivotal role of macrophage polarization in ALI. Although exosomes derived from mesenchymal stromal cells have been established as influential modulators of macrophage polarization, the specific role of exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) remains underexplored. This study aimed to elucidate the role of specific exosomal miRNAs in driving macrophage polarization, thereby providing a reference for developing novel therapeutic interventions for ALI. We found that miR-7704 is the most abundant and efficacious miRNA for promoting the switch to the M2 phenotype in macrophages. Mechanistically, we determined that miR-7704 stimulates M2 polarization by inhibiting the MyD88/STAT1 signaling pathway. Notably, intra-tracheal delivery of miR-7704 alone in a lipopolysaccharide-induced murine ALI model significantly drove M2 polarization in lung macrophages and remarkably restored pulmonary function, thus increasing survival. Our findings highlight miR-7704 as a valuable tool for treating ALI by driving the beneficial M2 polarization of macrophages. Our findings pave the way for deeper exploration into the therapeutic potential of exosomal miRNAs in inflammatory lung diseases.
© 2023 The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
GDF15 mediates inflammation-associated bone loss through a brain-bone axis
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 23 November 2023 by Van der Cruyssen, R., Devan, J., et al.
SUMMARY Metabolic mediators play an important role in regulating chronic inflammation in the body. Here we report an unexpected role for GDF15 (Growth Differentiation Factor 15), a central mediator of food intake, in inflammation-associated bone loss. GDF15 serum levels were found to be elevated in arthritis patients and inversely correlated with bone density. Despite being associated with inflammation, we found that GDF15 itself does not cause, nor contribute to, clinical or histopathological arthritis. Rather, under inflammatory conditions, GDF15 mediates trabecular bone loss through its receptor GFRAL, which is exclusively expressed in the hindbrain. GDF15-GFRAL binding results in β-adrenergic activation of MALPs (Marrow Adipocytic Lineage Precursors) in the bone marrow, which stimulate osteoclasts and trigger bone loss. These data suggest a metabolic mediator-controlled brain-bone axis in inflammation, through which bone loss is induced in a contextual rather than general manner. These findings may lead to more specific therapeutic interventions to protect bone.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
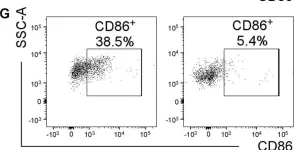
In J Neuroinflammation on 31 January 2019 by Funk, K. E. & Klein, R. S.
Fig.5.G

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from J Neuroinflammation by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
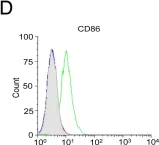
In PLoS One on 7 October 2014 by Bhowmick, R., Pore, D., et al.
Fig.8.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2