In celiac disease (CeD), a gluten-dependent autoimmune disorder, transglutaminase 2 (TG2), deamidates selected glutamine residues in gluten peptides, while HLA-DQ2 presents deamidated antigens to inflammatory T cells. The cellular sources of pathogenic TG2 and DQ2 are unclear. Using chemical biology tools, we show that intestinal CD103+ dendritic cells (DCs) couple cell-surface TG2 to the endocytic LRP1 receptor to simultaneously deamidate gluten antigens and concentrate them in lysosomes. In DQ2-transgenic mice, CD103+ DCs loaded with deamidated antigens migrate from intestinal lamina propria and Peyer's patches into mesenteric lymph nodes, where they engage T cells. In turn, gluten antigen presentation upregulates intestinal TG2 activity. The tool (HB-230) used to establish a role of CD103+ DCs in gluten antigen presentation and TG2 activation in mice also revealed that the TG2/LRP1 pathway is active in human CD14+ monocytes. Within this population of circulating monocytes, a DC subset with the gut-homing β7-integrin marker is elevated in patients with CeD with active disease compared with nonceliac controls or patients on a gluten-free diet. Our findings not only inform the cellular basis for gluten toxicity in CeD, but they also highlight the immunologic role of an enigmatic protein of growing therapeutic relevance in CeD and other immune disorders.
Product Citations: 116
In JCI Insight on 8 October 2025 by Yang, F. C., Besser, H. A., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
CD138 and APRIL regulate plasma cell survival, competition, and retention in the bone marrow niche.
In Cell Reports on 26 August 2025 by Park, R., Benet, Z., et al.
Durable serological protection is maintained through the persistence of antigen-specific plasma cells (PCs), but key factors regulating the survival of nascent PCs remain unclear. Previously, we reported that bone marrow (BM) PCs partially organize into clusters that are enriched for long-lived PCs, suggesting that clusters are survival niches. Here, we report that acute blockade of a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) and B cell activating factor (BAFF) using transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI)-Fc rapidly disrupts clusters and mobilizes BM PCs. CD138, a surface co-receptor that is abundant on PCs and binds APRIL but not BAFF, regulates PC retention in the BM and adhesion and motility on fibronectin. Cell-intrinsic CD138 levels control competition for survival between nascent CD138low PCs and mature CD138high PCs, and enhanced survival of CD138high PCs correlates with retention in clusters. Collectively, these results indicate that PC clusters are survival niches and that dynamic competition between new and pre-existing PCs regulates the survival of new PCs and the durability of antibody responses.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
ICOS+CD4+ T cells define a high susceptibility to anti-PD-1 therapy-induced lung pathogenesis.
In JCI Insight on 22 May 2025 by Yokoi, M., Murakami, K., et al.
Managing immune-related adverse events (irAEs) caused by cancer immunotherapy is essential for developing effective and safer therapies. However, cellular mechanism(s) underlying organ toxicity during anti-PD-(L)1 therapy remain unclear. Here, we investigated the effect of chronological aging on anti-PD-(L)1 therapy-induced irAE-like lung toxicity, utilizing tumor-bearing aged mice. Anti-PD-(L)1 therapy facilitated ectopic infiltration of T and B cells, and antibody deposition in lungs of aged but not young mice. Adoptive transfer of aged lung-derived CD4+ T cells into TCR-deficient mice revealed that both pathogenic CD4+ T cells and an aged host environment were necessary for the irAE-inducible responses. Single-cell transcriptomics of lung-infiltrating cells in aged mice demonstrated that anti-PD-(L)1 therapy elicited ICOS+CD4+ T cell activation. Disruption of the ICOS-ICOSL interaction attenuated germinal center B cell differentiation and subsequent lung damage, which were overcome by local administration of IL-21 in the lungs of anti-PD-1 therapy-treated aged mice. Therefore, ICOS+CD4+ T cells elicited under an aged environment exacerbated aberrant immune responses and the subsequent lung dysfunction. Consistent with the findings from the mouse model, ICOS upregulation in CD4+ T cells was associated with later irAE incidence in patients with cancer. These finding will help development of useful strategies for irAE management in patients with cancer, many of whom are elderly.
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Lrba participates in the differentiation of IgA+ B lymphocytes through TGFβR signaling.
In Frontiers in Immunology on 8 July 2024 by Flores-Hermenegildo, J. M., Hernández-Cázares, F. J., et al.
Lrba is a cytoplasmic protein involved in vesicular trafficking. Lrba-deficient (Lrba-/-) mice exhibit substantially higher levels of IgA in both serum and feces than wild-type (WT) mice. Transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) and its receptors (TGFβR I and II) is essential for differentiating IgA+ B cells. Furthermore, increased IgA production suggests a potential connection between Lrba and the TGFβR signaling pathway in IgA production. However, the specific function of Lrba in B cell biology remains unknown.
Given the increased IgA levels in Lrba-/- mice, the goal in this work was to explore the lymph organs where the switch to IgA occurs, and if TGFβR function is affected.
Non-immunized Lrba-/- mice were compared with Lrba+/+ mice. IgA levels in the serum and feces, as well as during peripheral B cell development, were determined. IgA+ B cells and plasma cells were assessed in the small intestine and secondary lymphoid organs, such as the spleen, mesenteric lymph nodes, and Peyer's patches. The TGFβR signaling pathway was evaluated by determining the expression of TGFβR on B cells. Additionally, SMAD2 phosphorylation was measured under basal conditions and in response to recombinant TGFβ. Finally, confocal microscopy was performed to investigate a possible interaction between Lrba and TGFβR in B cells.
Lrba-/- mice exhibited significantly higher levels of circulating IgA, IgA+ B, and plasma cells than in peripheral lymphoid organs those in WT mice. TGFβR expression on the membrane of B cells was similar in both Lrba-/- and Lrba+/+ mice. However, intracellular TGFβR expression was reduced in Lrba-/- mice. SMAD2 phosphorylation showed increased levels under basal conditions; stimulation with recombinant TGFβ elicited a poorer response than in that in Lrba+/+ B cells. Finally, we found that Lrba colocalizes with TGFβR in B cells.
Lrba is essential in controlling TGFβR signaling, subsequently regulating SMAD2 phosphorylation on B cells. This mechanism may explain the increased differentiation of IgA+ B cells and production of IgA-producing plasma cells.
Copyright © 2024 Flores-Hermenegildo, Hernández-Cázares, Pérez-Pérez, Romero-Ramírez, Rodríguez-Alba, Licona-Limon, Kilimann, Santos-Argumedo and López-Herrera.
-
IHC-IF
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology on 17 July 2023 by Hernández-Cázares, F., Maqueda-Alfaro, R. A., et al.
Patients with Human Hyper IgM syndromes (HIGM) developed pulmonary and gastrointestinal infections since infancy and most patients have mutations in the CD40 ligand (CD40L) gene. Most HIGM patients compared to healthy subjects have higher/similar IgM and lower IgG, and IgA serum concentrations but gut antibody concentrations are unknown. CD40L on activated T-cells interacts with CD40 on B-cells, essential for the formation of germinal centres (GCs) inside secondary lymphoid organs (SLOs), where high-affinity antibodies, long-lived antibody-secreting plasma cells, and memory B-cells, are produced. C57BL6-CD40 ligand deficient mice (C57BL6-cd40l -/-), are a model of HIGM, because serum immunoglobulin concentrations parallel levels observed in HIGM patients and have higher faecal IgA concentrations. In mice, TGFβ and other cytokines induce IgA production.
To compare and evaluate B-cell populations and IgA-producing plasma cells in peritoneal lavage, non-gut-associated SLOs, spleen/inguinal lymph nodes (ILN), and gut-associated SLOs, mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN)/Peyer´s patches (PP) of unimmunised C57BL6-cd40l -/- and C57BL6-wild-type (WT) mice.
Peritoneal lavages, spleens, ILN, MLN, and PP from 8-10 weeks old C57BL6-cd40l -/- and WT mice, were obtained. Organ cryosections were analysed by immunofluorescence and B-cell populations and IgA-positive plasma cell suspensions by flow cytometry.
In unimmunised WT mice, GCs were only observed in the gut-associated SLOs, but GCs were absent in all C57BL6-cd40l -/- SLOs. PP and MLN of C57BL6-cd40l -/- mice exhibited a significantly higher number of IgA-producing cells than WT mice. In the spleen and ILN of C57BL6-cd40l- /- mice IgA-producing cells significantly decreased, while IgM-positive plasma cells increased. C57BL6-cd40l -/- B-1 cells were more abundant in all analysed SLOs, whereas in WT mice most B-1 cells were contained within the peritoneal cavity. C57BL6-cd40l -/- B-cells in MLN expressed a higher TGFβ receptor-1 than WT mice. Mouse strains small intestine microvilli (MV), have a similar frequency of IgA-positive cells.
Together our results confirm the role of PP and MLN as gut inductive sites, whose characteristic features are to initiate an IgA preferential immune response production in these anatomical sites even in the absence of GCs. IgA antibodies play a pivotal role in neutralising, eliminating, and regulating potential pathogens and microorganisms in the gut.
Copyright © 2023 Hernandez-Cazares, Maqueda-Alfaro, Lopez-Saucedo, Martinez-Barnetche, Yam-Puc, Estrada-Parra, Flores-Romo and Estrada-Garcia.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In JCI Insight on 22 September 2021 by Luo, S., Kwon, J., et al.
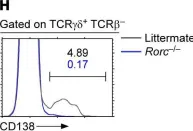
Fig.1.H
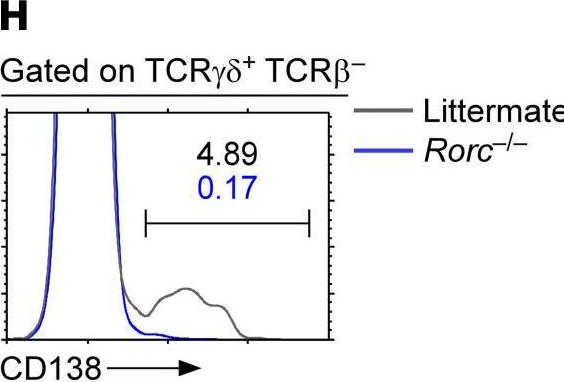
-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In JCI Insight on 22 September 2021 by Luo, S., Kwon, J., et al.
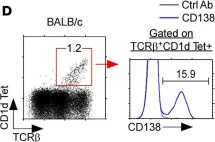
Fig.1.D
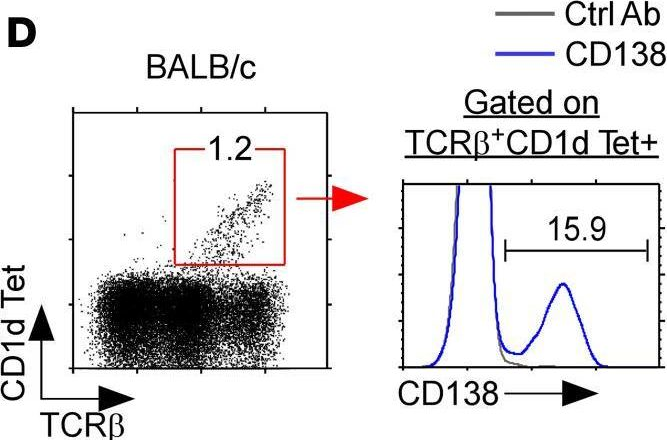
-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
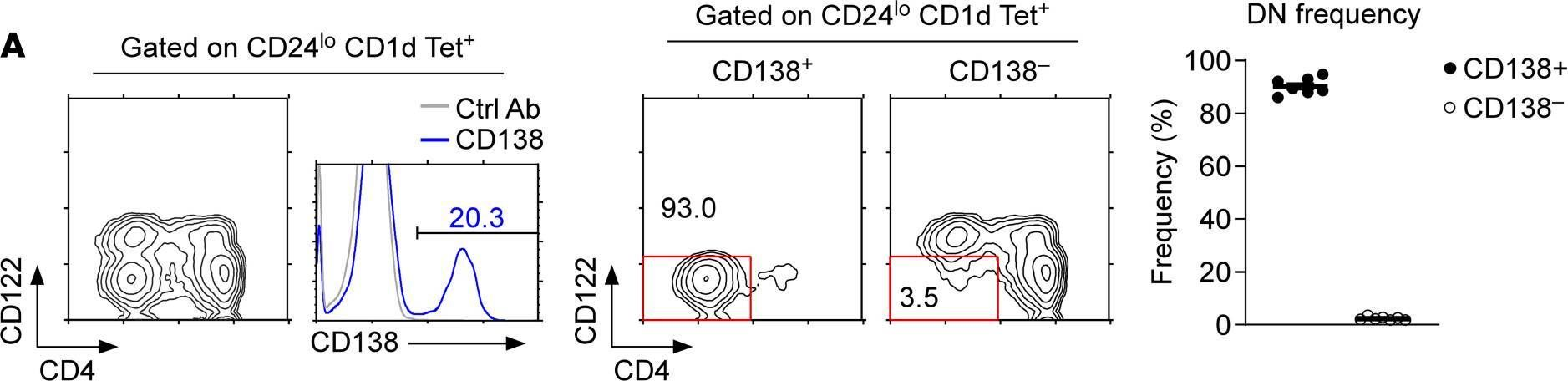
In JCI Insight on 22 September 2021 by Luo, S., Kwon, J., et al.
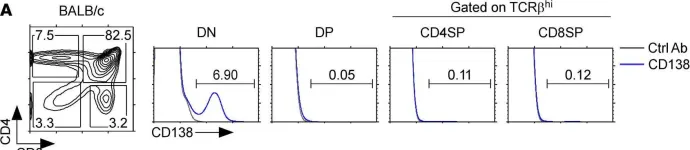
Fig.1.A
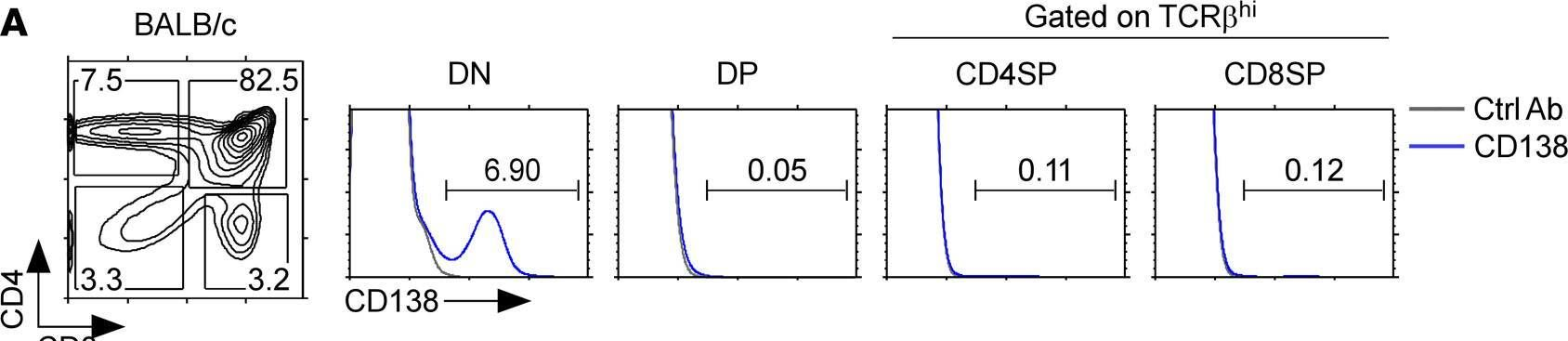
-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In JCI Insight on 22 September 2021 by Luo, S., Kwon, J., et al.
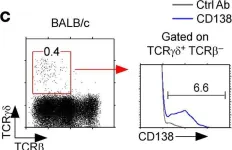
Fig.1.C
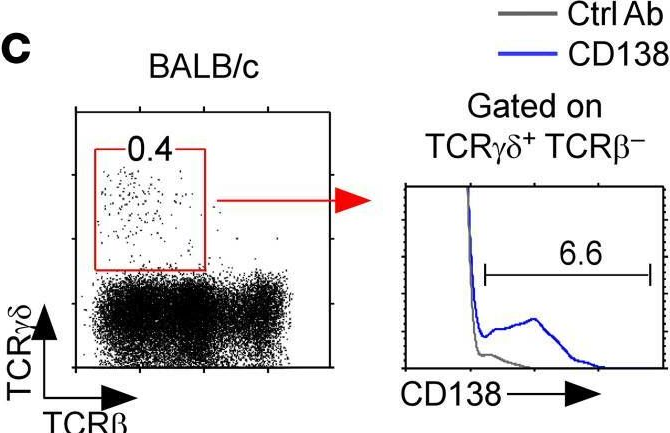
-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In JCI Insight on 22 September 2021 by Luo, S., Kwon, J., et al.
Fig.3.B
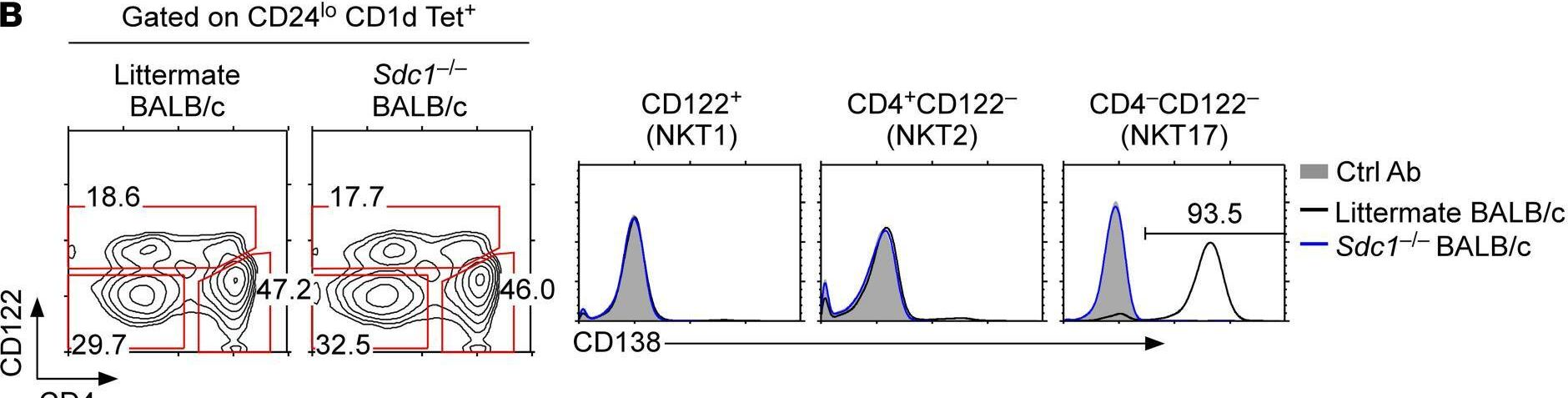
-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
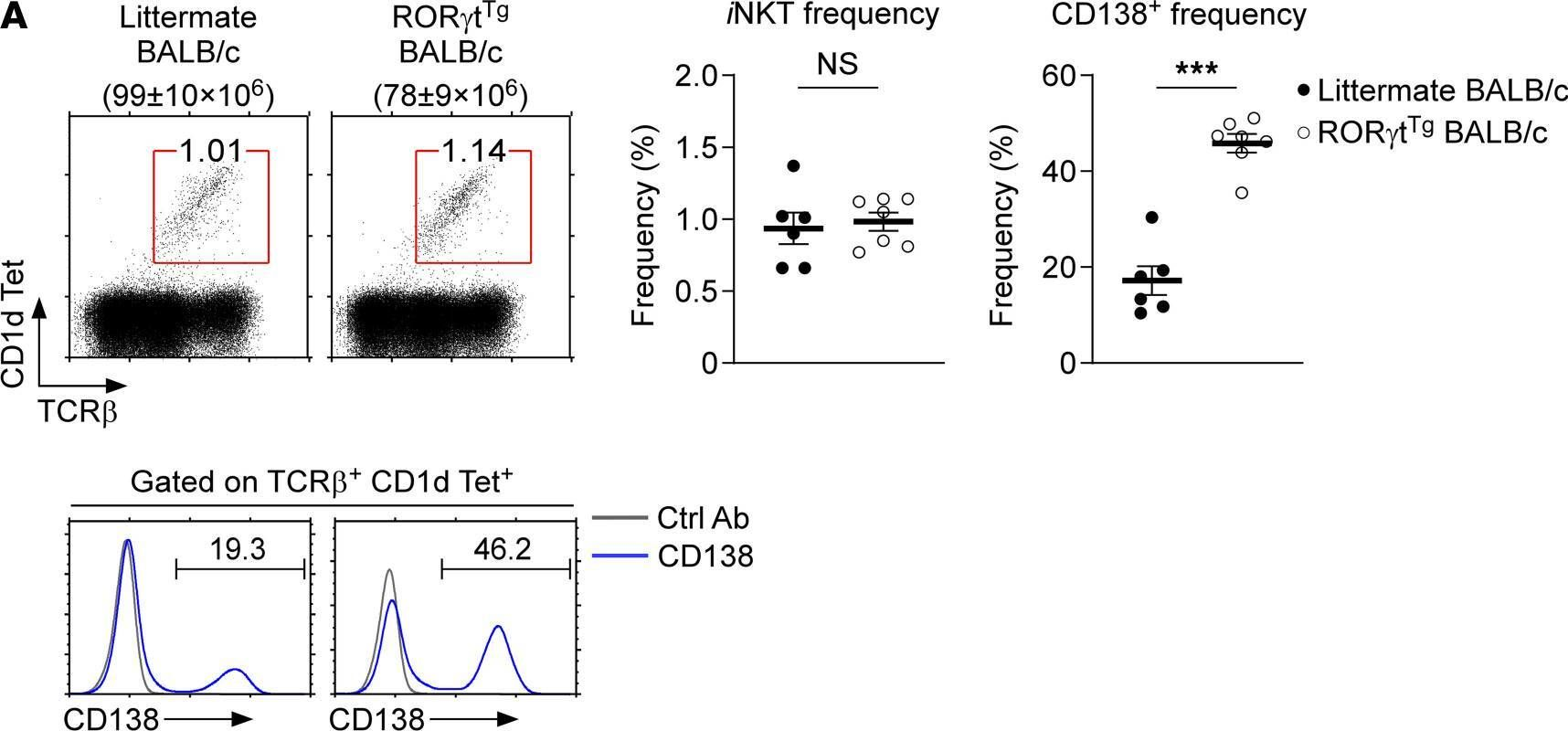
In JCI Insight on 22 September 2021 by Luo, S., Kwon, J., et al.
Fig.3.A
-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In JCI Insight on 22 September 2021 by Luo, S., Kwon, J., et al.
Fig.5.A
-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In JCI Insight on 22 September 2021 by Luo, S., Kwon, J., et al.
Fig.7.A
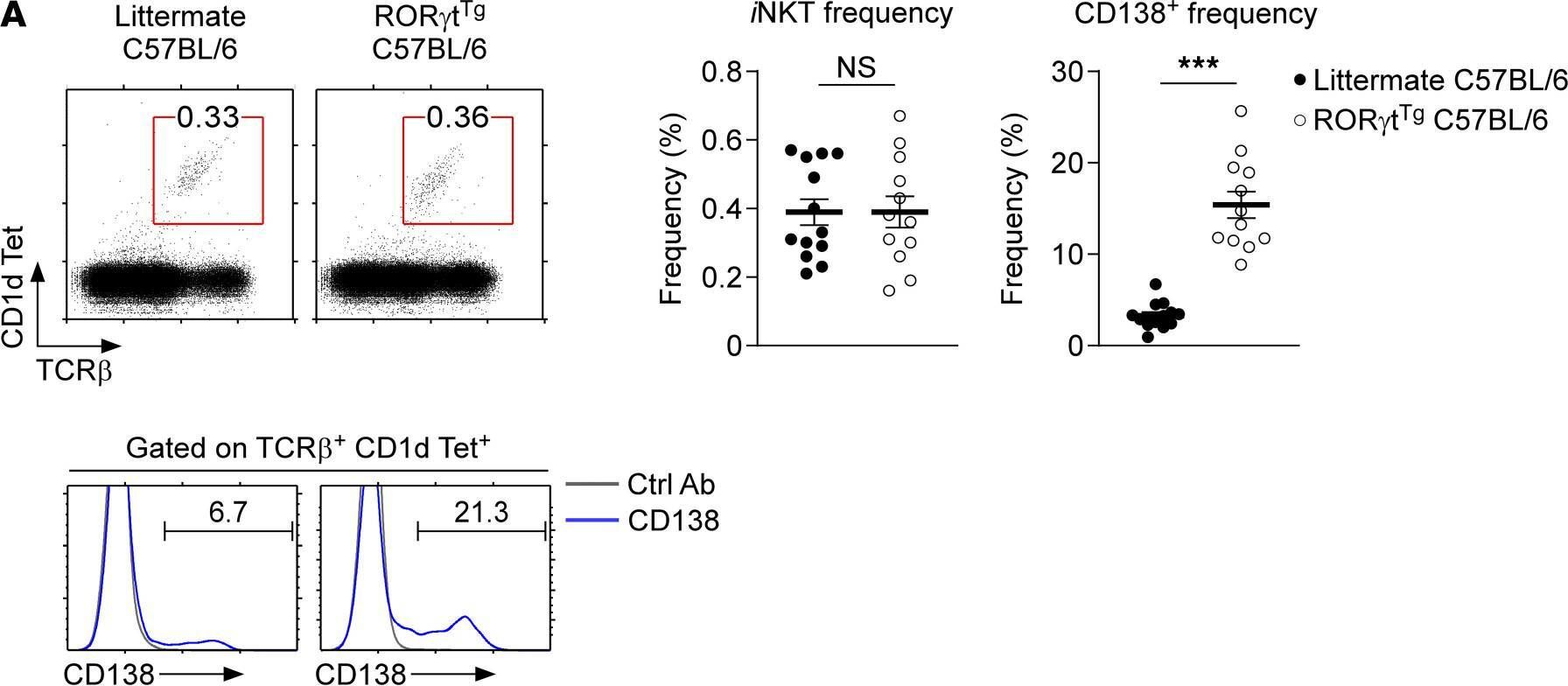
-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from JCI Insight by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
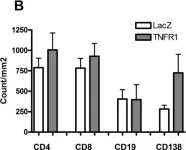
In Arthritis Res Ther on 17 December 2009 by Vosters, J. L., Yin, H., et al.
Fig.3.B
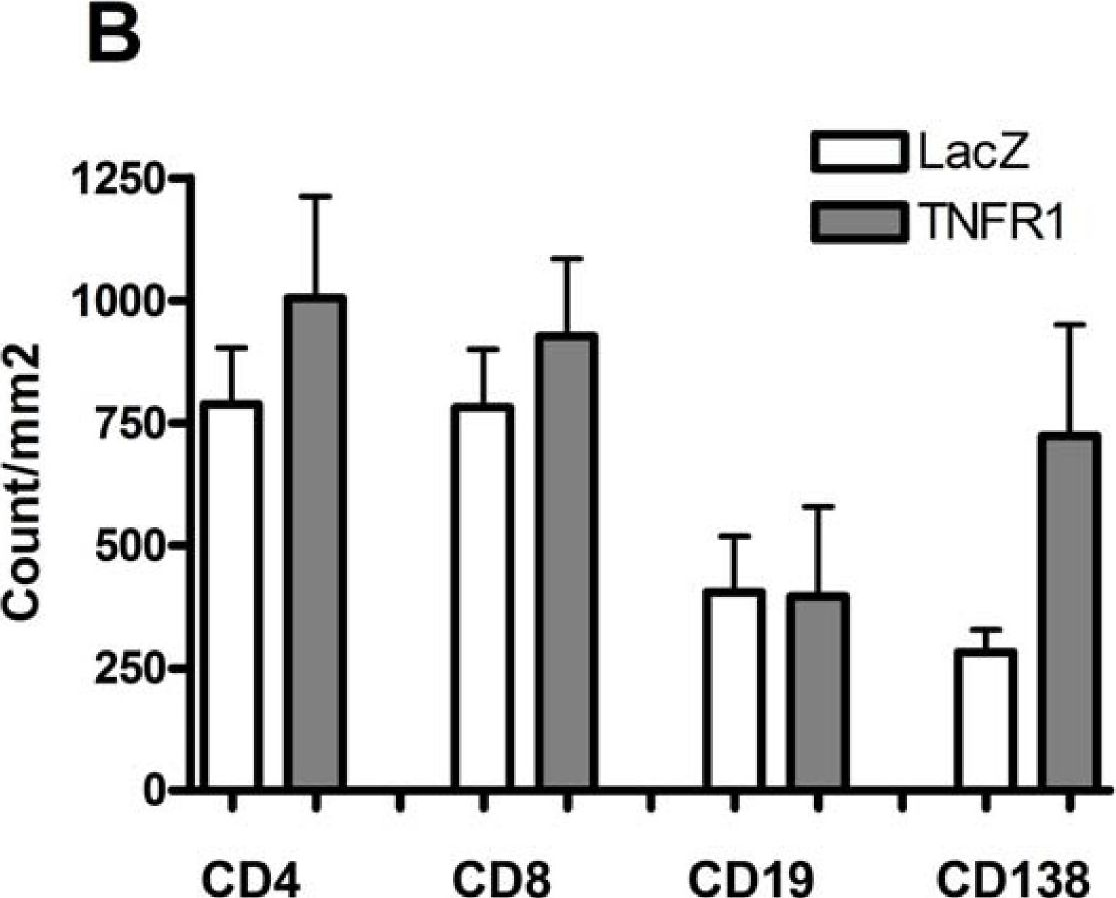
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Arthritis Research & Therapy by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In Mol Cancer on 9 November 2005 by Han, S. S., Shaffer, A. L., et al.
Fig.1.B
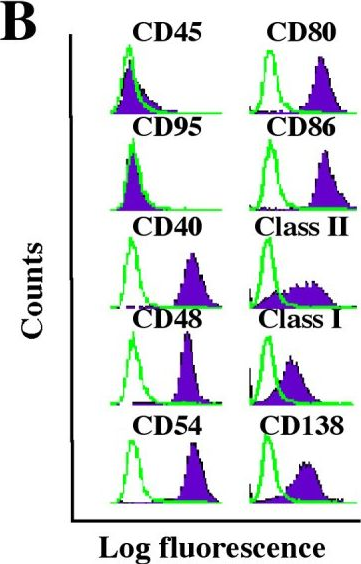
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Molecular Cancer by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10