In systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), neutrophil dysregulation and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) formation contribute to disease pathogenesis, potentially worsening the autoimmune response. Although research indicates NETs' involvement in various autoimmune conditions, their relationship with regulatory T cells (Tregs) in SLE remains elusive. In this study, in vivo experiments were involved in administering NET injections to C57BL/6 and MRL/Ipr mice. In vitro, a co-culture system facilitated interaction between Tregs and NETs. Proteomic analysis elucidated NET composition, while RNA sequencing delineated their impact on Treg differentiation. We demonstrated that increased NET levels correlate inversely with Treg abundance in SLE patients, influencing both their proportion and functionality. NET administration reduced Treg levels and induced lupus-like symptoms in C57BL/6 mice, exacerbating symptoms in MRL/Ipr mice. DNase I treatment mitigated NET effects, restoring Treg levels and alleviating symptoms. RNA sequencing revealed altered gene expression in naïve CD4+ T cells exposed to NETs. Additionally, proteomic analysis showed S100A10 protein changes between SLE patients and healthy controls, hindering Treg differentiation. NETs influence TLR-4 of naïve CD4+ T cells via S100A10, thereby modulating Treg proportion and functionality. These findings highlight the critical role of NETs in Treg differentiation in SLE, suggesting that targeting NETs may provide a novel therapeutic approach.
© 2024 Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Product Citations: 209
In European Journal of Immunology on 1 January 2025 by Guo, H., Liang, Q., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Preprint on Research Square on 18 November 2024 by Chen, R., Ding, S., et al.
Abstract Bladder cancer is recognized as one of the most prevalent malignant tumors within the urinary system. The conventional treatment approach for bladder cancer typically involves a combination of surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy. However, the efficacy of current treatment modalities remains suboptimal, prompting ongoing efforts to develop novel and more effective therapeutic strategies to better address the clinical demands of bladder cancer management. In this study, we utilized the orthotopic mouse model to assess the effectiveness of intravesical conventional chemotherapy alone and in combination with immunotherapy for treating bladder cancer. The anti-tumor effect was analyzed by determining bioluminescence imaging (BLI), while histopathological analysis was conducted to evaluate the tumor proliferation and invasion capabilities upon treatment. Additionally, alterations in the immune microenvironment within different treatment methods were studied through flow cytometry for various T-cell markers. BLI and tumor weights analysis revealed that the intravesical route of doxorubicin administration produced better treatment efficacy than the conventional chemotherapy through the intraperitoneal route and combination of doxorubicin and anti-PD-L1 i.p administration. Histopathological analysis and proliferation markers (Ki-67 staining) revealed significant differences across the intravesical, conventional chemotherapy, and immune combination therapy groups. Importantly, intravesical treatment was more effective in reducing tumor cell proliferation compared to the other groups. FACS analysis revealed the route of administration significantly impacted the immune response in the tumor microenvironment. Our results demonstrate that both intravesical and conventional doxorubicin chemotherapy led to a significant decrease in CD8+ T cell expression (p < 0.01), while intravesical treatment exhibited a more pronounced activation of CD8+ T cells, as evidenced by increased CD69 expression. Treg cells also showed moderate reductions in the conventional chemotherapy and immune combination therapy groups. Notably, the intravesical approach activated CD8+ T cells more effectively and reduced the expression of the exhaustion marker PD-1 compared to immune combination therapy. Overall, these findings highlight the potential of intravesical doxorubicin delivery to activate CD8+ T cells and reduce immune exhaustion, enhancing its anti-tumor efficacy. These results suggest that intravesical administration may be a viable treatment option for bladder cancer in clinical settings.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Intrahepatic Exhausted Antiviral Immunity in an Immunocompetent Mouse Model of Chronic Hepatitis B.
In Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology on 1 October 2024 by Shigeno, S., Kodama, T., et al.
Targeting exhausted immune systems would be a promising therapeutic strategy to achieve a functional cure for HBV infection in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). However, animal models recapitulating the immunokinetics of CHB are very limited. We aimed to develop an immunocompetent mouse model of CHB for intrahepatic immune profiling.
CHB mice were created by intrahepatic delivery of the Sleeping Beauty transposon vector tandemly expressing the hepatitis B virus (HBV) genome and fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (FAH) cDNA into C57BL/6J congenic FAH knockout mice via hydrodynamic tail vein injection. We profiled the viral and intrahepatic immune kinetics in CHB mice with or without treatment with recombinant IFNα or the hepatotropic Toll-like receptor 7 agonist SA-5 using single-cell RNA-seq.
CHB mice exhibited sustained HBV viremia and persistent hepatitis. They showed intrahepatic expansion of exhausted CD8+ T (Tex) cells, the frequency of which was positively associated with viral load. Recruited macrophages increased in number but impaired inflammatory responses in the liver. The cytotoxicity of mature natural killer (NK) cells also increased in CHB mice. IFNα and SA-5 treatment both resulted in viral suppression with mild hepatic flares in CHB mice. Although both treatments activated NK cells, SA-5 had the capacity to revitalize the impaired function of Tex cells and liver-recruited macrophages.
Our novel CHB mouse model recapitulated the intrahepatic exhausted antiviral immunity in patients with CHB, which might be able to be reinvigorated by a hepatotropic TLR7 agonist.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Chronic High-Salt Diet Activates Tumor-Initiating Stem Cells Leading to Breast Cancer Proliferation.
In Cells on 25 May 2024 by Tucker, L., Ali, U., et al.
Several chronic inflammatory diseases have been linked to high-salt (HS) diets. Chronic inflammation is an established causative hallmark of cancer. However, a direct role of HS diets in tumorigenesis is yet to be defined. Previous orthotopic murine breast tumor studies have shown that short-term HS diets caused inhibition of tumor growth through the activation of cytotoxic adaptive immune responses. However, there have been experimental challenges in developing a viable chronic HS-diet-based murine tumor model. To address this, we have developed a novel chronic HS diet tumor model through the sequential passaging of tumor cells in mice under HS dietary conditions. Two orthotopic murine triple-negative breast cancer models, 4T1 tumor cells injected into BALB/c mice and Py230 tumor cells injected into C57Bl/6 mice, were utilized in our study. For the HS diet cohort, prior to orthotopic injection with tumor cells, the mice were kept on a 4% NaCl diet for 2 weeks. For the regular salt (RS) diet cohort, the mice were kept on a 1% NaCl diet. Following syngeneic cancer cell injection, tumors were allowed to grow for 28 days, following which they were collected to isolate immune cell-depleted cancer cells (passage 1, P1). The tumor cells from P1 were reinjected into the next set of non-tumor-bearing mice. This procedure was repeated for three cycles (P2-P4). In P1, compared to the RS diet cohort, we observed reduced tumor kinetics in both murine tumor models on the HS diet. In contrast, by P4, there was significantly higher tumor progression in the HS diet cohort over the RS diet cohort. Flow cytometry analysis demonstrated an 8-fold increase in tumor-initiating stem cells (TISCs) from P1 to P4 of the HS diet cohort, while there were no significant change in TISC frequency with sequential passaging in the RS diet cohort. Molecular studies showed enhanced expression of TGFβR2 and CD80 on TISCs isolated from the P4 HS diet cohort. In vitro studies demonstrated that TGFβ stimulation of these TISCs increased the cellular expression of CD80 molecules. Further, the chronic HS diet selectively induced the glycolytic metabolic phenotype over the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation phenotype in TISCs, which is needed for the production of metabolites during tumor cell differentiation and proliferation. The infiltrating CD8 and CD4 T-lymphocytes in P4 tumors demonstrated increased expression of the immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) CTLA4, a known binding partner of CD80, to cause immune exhaustion and pro-tumorigenic effects. Interestingly, anti-TGFβ monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) played a synergistic role in further enhancing the anti-tumor effect of anti-CTLA4 mAb. In summary, our findings demonstrated that chronic HS diet increased the frequency of TISCs in tumors leading to blunting of cytotoxic adaptive immune responses causing tumor proliferation. Furthermore, a combination of anti-TGFβ with current ICI-based immunotherapies could exert more favorable anti-cancer clinical outcomes.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Stem Cells and Developmental Biology
Enrichment of liver MAIT cells in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
In Journal of Neuroimmunology on 15 May 2024 by Wyatt-Johnson, S. K., Kersey, H. N., et al.
Emerging evidence has supported a role for the immune system and liver in Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, our understanding of how hepatic immune cells are altered in AD is limited. We previously found that brain mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cell numbers are increased in AD. Furthermore, loss of MAIT cells and their antigen-presenting molecule, MR1, reduced amyloid-β accumulation in the brain. MAIT cells are also significantly present in the liver. Therefore, we sought to analyze MAIT and other immune cells in the AD liver. Increased frequency of activated MAIT cells (but not conventional T cells) were found in 8-month-old 5XFAD mouse livers. Therefore, these data raise the possibility that there is a role for peripheral MAIT cells in AD pathology.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
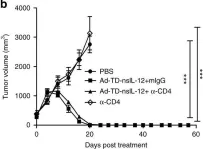
In Nat Commun on 9 November 2017 by Wang, P., Li, X., et al.
Fig.7.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
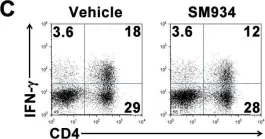
In PLoS One on 6 March 2012 by Hou, L. F., He, S. J., et al.
Fig.6.C

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
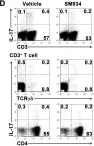
In PLoS One on 6 March 2012 by Hou, L. F., He, S. J., et al.
Fig.6.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3