Pancreatic islet transplantation (PITx) is a promising treatment option for patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Previously, we demonstrated that therapy with alloantigen-specific immunomodulatory cells (IMCs) generated ex vivo in the presence of anti-CD80 and CD86 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), successfully induced tolerance following clinical liver transplantation. To extend IMC therapy to PITx, it is crucial to address the strong inflammatory and innate immune responses that occur immediately after PITx. In this study, we investigated the efficacy of IMCs in modulating macrophage activation and mitigating inflammatory damage of pancreatic islets. IMCs were induced using mouse splenocytes in the presence of anti-mouse anti-CD80 (RM80) and anti-CD86 (GL-1) mAbs. IMCs exerted donor-specific immunosuppressive effects in a mixed lymphocyte reaction. During lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation, the addition of IMCs suppressed conversion to the M1 phenotype and promoted a shift toward the M2 phenotype, particularly under direct cell-cell contact conditions. Nitric oxide production, a hallmark of M1 polarized macrophages, was significantly reduced in LPS-stimulated RAW264 macrophages by IMC treatment. These findings were associated with reduced secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, tumoral necrosis factor α, and interleukin-6, and increased interleukin-10 production by macrophages. IMCs effectively prevented macrophage-mediated islet destruction after 12 h of co-culture with LPS-stimulated macrophages and significantly inhibited macrophage migration toward allogeneic islets in vitro. Intraportal co-infusion of IMCs with syngeneic islets in a mouse PITx model resulted in reduced messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the recipient liver. Immunohistochemical staining revealed a significantly lower number of F4/80+ macrophages at the transplantation site in IMCs-treated mice. These results demonstrate that IMCs modulate macrophage polarization, promoting a shift toward the M2 phenotype and protecting islets from macrophage-mediated damage. These effects combined with its intrinsic donor antigen-specific immunosuppressive capacity make IMC therapy a promising strategy for improving outcomes after PITx.
Product Citations: 204
In Cell Transplantation on 21 February 2025 by Forgioni, A., Watanabe, M., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Journal of Neuroinflammation on 1 September 2024 by Hong, H., Wang, Y., et al.
Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterized by neuroinflammation, progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons, and accumulation of α-synuclein (α-Syn) into insoluble aggregates called Lewy pathology. The Line 61 α-Syn mouse is an established preclinical model of PD; Thy-1 is used to promote human α-Syn expression, and features of sporadic PD develop at 9-18 months of age. To accelerate the PD phenotypes, we injected sonicated human α-Syn preformed fibrils (PFFs) into the striatum, which produced phospho-Syn (p-α-Syn) inclusions in the substantia nigra pars compacta and significantly increased MHC Class II-positive immune cells. Additionally, there was enhanced infiltration and activation of innate and adaptive immune cells in the midbrain. We then used this new model, Line 61-PFF, to investigate the effect of inhibiting the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, which is critical for regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses. After administration of the JAK1/2 inhibitor AZD1480, immunofluorescence staining showed a significant decrease in p-α-Syn inclusions and MHC Class II expression. Flow cytometry showed reduced infiltration of CD4+ T-cells, CD8+ T-cells, CD19+ B-cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, and endogenous microglia into the midbrain. Importantly, single-cell RNA-Sequencing analysis of CD45+ cells from the midbrain identified 9 microglia clusters, 5 monocyte/macrophage (MM) clusters, and 5 T-cell (T) clusters, in which potentially pathogenic MM4 and T3 clusters were associated with neuroinflammatory responses in Line 61-PFF mice. AZD1480 treatment reduced cell numbers and cluster-specific expression of the antigen-presentation genes H2-Eb1, H2-Aa, H2-Ab1, and Cd74 in the MM4 cluster and proinflammatory genes such as Tnf, Il1b, C1qa, and C1qc in the T3 cluster. Together, these results indicate that inhibiting the JAK/STAT pathway suppresses the activation and infiltration of innate and adaptive cells, reducing neuroinflammation in the Line 61-PFF mouse model.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Neuroscience
In Frontiers in Immunology on 7 August 2024 by Jackson, K. J., Buhl, C., et al.
Atopic diseases have been steadily increasing over the past decades and effective disease-modifying treatment options are urgently needed. These studies introduce a novel synthetic Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) agonist, INI-2004, with remarkable efficacy as a therapeutic intranasal treatment for seasonal allergic rhinitis.
Using a murine airway allergic sensitization model, the impact of INI-2004 on allergic responses was assessed.
One or two intranasal doses of INI-2004 significantly reduced airway resistance, eosinophil influx, and Th2 cytokine production - providing strong evidence of allergic desensitization. Further investigations revealed that a liposomal formulation of INI-2004 exhibited better safety and efficacy profiles compared to aqueous formulations. Importantly, the liposomal formulation demonstrated a 1000-fold increase in the maximum tolerated intravenous dose in pigs. Pre-clinical GLP toxicology studies in rats and pigs confirmed the safety of liposomal INI-2004, supporting its selection for human clinical trials.
These findings lay the groundwork for the ongoing clinical evaluation of INI-2004 in allergic rhinitis as a stand-alone therapy for individuals poly-sensitized to multiple seasonal allergens. The study underscores the significance of innovative immunotherapy approaches in reshaping the landscape of allergic rhinitis management.
Copyright © 2024 Jackson, Buhl, Miller, Khalaf, Ward, Sands, Walsh, Whitacre, Burkhart, Bazin-Lee and Evans.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Death Discovery on 19 June 2024 by Krug, A., Mhaidly, R., et al.
Cancer metabolic reprogramming has been recognized as one of the cancer hallmarks that promote cell proliferation, survival, as well as therapeutic resistance. Up-to-date regulation of metabolism in T-cell lymphoma is poorly understood. In particular, for human angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) the metabolic profile is not known. Metabolic intervention could help identify new treatment options for this cancer with very poor outcomes and no effective medication. Transcriptomic analysis of AITL tumor cells, identified that these cells use preferentially mitochondrial metabolism. By using our preclinical AITL mouse model, mimicking closely human AITL features, we confirmed that T follicular helper (Tfh) tumor cells exhibit a strong enrichment of mitochondrial metabolic signatures. Consistent with these results, disruption of mitochondrial metabolism using metformin or a mitochondrial complex I inhibitor such as IACS improved the survival of AITL lymphoma-bearing mice. Additionally, we confirmed a selective elimination of the malignant human AITL T cells in patient biopsies upon mitochondrial respiration inhibition. Moreover, we confirmed that diabetic patients suffering from T-cell lymphoma, treated with metformin survived longer as compared to patients receiving alternative treatments. Taking together, our findings suggest that targeting the mitochondrial metabolic pathway could be a clinically efficient approach to inhibit aggressive cancers such as peripheral T-cell lymphoma.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
The trogocytosis of neutrophils on initial transplanted tumor in mice.
In IScience on 17 May 2024 by Zhu, M., Wang, S., et al.
The role of neutrophils in tumor initiation stage is rarely reported because of the lack of suitable models. We found that neutrophils recruited in early tumor nodules induced by subcutaneous inoculation of B16 melanoma cells were able to attack tumor cells by trogocytosis. The anti-tumor immunotherapy like peritoneal injection with TLR9 agonist CpG oligodeoxynucleotide combined with transforming growth factor β2 inhibitor TIO3 could increase the trogocytic neutrophils in the nodules, as well as CD8+ T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and their interferon-γ production. Local use of Cxcl2 small interfering RNA significantly reduced the number of neutrophils and trogocytic neutrophils in tumor nodules, as well as CD8+ T and NK cells, and also enlarged the nodules. These results suggest that neutrophils recruited early to the inoculation site of tumor cells are conducive to the establishment of anti-tumor immune microenvironment. Our findings provide a useful model system for studying the effect of neutrophils on tumors and anti-tumor immunotherapy.
© 2024 The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
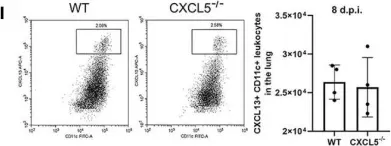
In Front Immunol on 7 December 2021 by Guo, L., Li, N., et al.
Fig.6.I

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
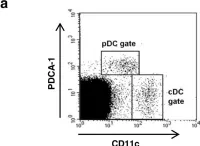
In Vet Res on 10 August 2013 by Correia, A., Ferreirinha, P., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Vet Res by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2