Homozygous knockout of scavenger receptor class B type I (SR-B1) in mice with atherogenic mutations (such as knockout of the apolipoprotein E or low density lipoprotein receptor genes) results in spontaneous or diet-induced coronary heart disease characterized by atherosclerosis development in the aortic sinus and coronary arteries, platelet accumulation in coronary artery plaques, myocardial fibrosis, and early death. However, the extent of coronary artery atherothrombosis and myocardial fibrosis in mice lacking SR-B1 alone (homozygous SR-B1 knockout mice) has not been examined. Although age is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease, few studies directly examine the effects of age on susceptibility to atherosclerosis or coronary artery atherothrombosis and myocardial fibrosis in mice. Therefore, we set out to examine the effects of age on diet-induced atherosclerosis in female homozygous SR-B1 knockout mice.
SR-B1 knockout mice exhibited little-to-no aortic sinus or coronary artery atherosclerosis at 52 weeks of age, when fed a normal diet. However when fed a high-fat, high-cholesterol, cholate-containing (HFCC) diet for 12 weeks from either 14 weeks of age (26-week-old at analysis) or 40 weeks of age (52-week-old at analysis), they developed similar degrees of atherosclerosis in their aortic sinuses. Interestingly, the older aged SR-B1 knockout mice exhibited increased coronary artery atherosclerosis, increased vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 levels and platelet accumulation in coronary arteries, and increased myocardial fibrosis and plasma levels of cardiac troponin I compared to the younger aged mice. Older-aged HFCC diet-fed SR-B1 knockout mice also exhibited reduced survival to humane endpoint. Moreover, older-aged HFCC diet-fed SR-B1 knockout mice exhibited a greater inflammatory state with increased levels of circulating interleukin-6, tumour necrosis factor alpha, and neutrophils, despite plasma lipid levels being unchanged. Consistent with the increased circulating neutrophils, older-aged HFCC diet-fed SR-B1 knockout mice exhibited increased accumulation of the neutrophil marker myeloperoxidase and increased neutrophil extracellular traps in atherosclerotic plaques in the aortic sinus and increased abundance of atherosclerotic coronary arteries containing neutrophil extracellular traps.
HFCC diet-fed homozygous SR-B1 knockout mice develop occlusive coronary artery atherothrombosis and myocardial fibrosis in an age-dependent manner, and exhibit an increased inflammatory state with older age. Therefore, aged SR-B1 knockout mice may prove to be an attractive mouse model to analyze age-dependent mechanisms associated with coronary artery disease development, which may facilitate the discovery of more effective therapeutics to treat cardiovascular disease.
Copyright: © 2025 Lee et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Product Citations: 116
In PLoS ONE on 22 May 2025 by Lee, S. K., Xiong, T., et al.
-
Cardiovascular biology
In Transfusion on 1 December 2024 by Loriamini, M., Lewis-Bakker, M. M., et al.
The characteristic feature of immune cytopenias involves the process of extravascular phagocytosis, wherein macrophages in the spleen and/or liver engage in the destruction of blood cells that have been opsonized by auto- or alloantibodies. Therefore, new treatments that prevent phagocytosis will be advantageous, especially for short-term usage along with alternative options.
KB-208, a small molecule drug, previously shown to be efficacious for the in vitro inhibition of phagocytosis was synthesized. A passive antibody mouse model of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) was used. Three different mouse strains (BALB/c, C57BL/6, CD1) were used to determine the efficacy of KB-208 compared with IVIG to ameliorate the ITP. Toxicity was investigated after 60-day chronic administration of KB-208 by a biochemistry panel, gross necroscopy and histopathology.
KB-208 showed similar efficacy to ameliorate the thrombocytopenia compared with IVIG in all three mouse strains. This small molecule drug was effective at 1 mg/kg in ameliorating ITP, in comparison with IVIG at 1000-2500 mg/kg. KB-208 did not affect other blood parameters or elevate serum biochemistry markers of toxicity nor were any abnormal histopathological findings found.
KB-208 is similar to IVIG for the amelioration of ITP in multiple mouse strains. Chronic administration of KB-208 for 60 days did not demonstrate in vivo toxicity. These findings indicate that KB-208 is efficacious, without significant in vivo toxicities in mice, and is a potential small molecule candidate for further evaluation to be used in the treatment of ITP and possibly all immune cytopenias where phagocytosis is responsible for the pathophysiology.
© 2024 The Author(s). Transfusion published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of AABB.
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 12 July 2024 by Wang, Y., Moura, A. K., et al.
Accumulating evidence indicates that coronary microvascular dysfunction (CMD) caused by hypercholesterolemia can lead to myocardial ischemia, with or without obstructive atherosclerotic coronary artery disease (CAD). However, the molecular pathways associated with compromised coronary microvascular function prior to the development of myocardial ischemic injury remain poorly defined. In this study, we investigated the effects of hypercholesterolemia on the function and integrity of the coronary microcirculation in mice and the underlying mechanisms. Mice were fed with a hypercholesterolemic Paigen's diet (PD) for 8 weeks. Echocardiography data showed that PD caused CMD, characterized by significant reductions in coronary blood flow and coronary flow reserve (CFR), but did not affect cardiac remodeling or dysfunction. Immunofluorescence studies revealed that PD-induced CMD was associated with activation of coronary arterioles inflammation and increased myocardial inflammatory cell infiltration. These pathological changes occurred in parallel with the upregulation of lysosomal signaling pathways in endothelial cells (ECs). Treating hypercholesterolemic mice with the cholesterol-lowering drug ezetimibe significantly ameliorated PD-induced adverse effects, including hypercholesterolemia, steatohepatitis, reduced CFR, coronary EC inflammation, and myocardial inflammatory cell infiltration. In cultured mouse cardiac endothelial cells (MCECs), 7-ketocholesterol (7K) increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammatory responses. Meanwhile, 7K induced the activation of TFEB and lysosomal signaling in MCECs, whereas the lysosome inhibitor bafilomycin A1 blocked 7K-induced TFEB activation and exacerbated 7K-induced inflammation and cell death. Interestingly, ezetimibe synergistically enhanced 7K-induced TFEB activation and attenuated 7K-induced mitochondrial ROS and inflammatory responses in MCECs. These results suggest that CMD can develop and precede detectable cardiac functional or structural changes in the setting of hypercholesterolemia, and that upregulation of TFEB-mediated lysosomal signaling in ECs plays a protective role against CMD.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cell Biology
Neutrophil-derived migrasomes are an essential part of the coagulation system.
In Nature Cell Biology on 1 July 2024 by Jiang, D., Jiao, L., et al.
Migrasomes are organelles that are generated by migrating cells. Here we report the key role of neutrophil-derived migrasomes in haemostasis. We found that a large number of neutrophil-derived migrasomes exist in the blood of mice and humans. Compared with neutrophil cell bodies and platelets, these migrasomes adsorb and enrich coagulation factors on the surface. Moreover, they are highly enriched with adhesion molecules, which enable them to preferentially accumulate at sites of injury, where they trigger platelet activation and clot formation. Depletion of neutrophils, or genetic reduction of the number of these migrasomes, significantly decreases platelet plug formation and impairs coagulation. These defects can be rescued by intravenous injection of purified neutrophil-derived migrasomes. Our study reveals neutrophil-derived migrasomes as a previously unrecognized essential component of the haemostasis system, which may shed light on the cause of various coagulation disorders and open therapeutic possibilities.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Cell Biology
In Thrombosis and Haemostasis on 1 July 2024 by Zhu, H., Auten, R. L., et al.
Increased adhesivity of red blood cells (RBCs) to endothelial cells (ECs) may contribute to organ dysfunction in malaria, sickle cell disease, and diabetes. RBCs normally export nitric oxide (NO)-derived vascular signals, facilitating blood flow. S-nitrosothiols (SNOs) are thiol adducts formed in RBCs from precursor NO upon the oxygenation-linked allosteric transition in hemoglobin. RBCs export these vasoregulatory SNOs on demand, thereby regulating regional blood flow and preventing RBC-EC adhesion, and the large (system L) neutral amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1; SLC7A5) appears to mediate SNO export by RBCs.
To determine the role of LAT1-mediated SNO import by ECs generally and of LAT1-mediated SNO import by ECs in RBC SNO-dependent modulation of RBC sequestration and blood oxygenation in vivo, we engineered LAT1fl/fl; Cdh5-Cre+ mice, in which the putative SNO transporter LAT1 can be inducibly depleted (knocked down, KD) specifically in ECs ("LAT1ECKD").
We show that LAT1 in mouse lung ECs mediates cellular SNO uptake. ECs from LAT1ECKD mice (tamoxifen-induced LAT1fl/fl; Cdh5-Cre+) import SNOs poorly ex vivo compared with ECs from wild-type (tamoxifen-treated LAT1fl/fl; Cdh5-Cre-) mice. In vivo, endothelial depletion of LAT1 increased RBC sequestration in the lung and decreased blood oxygenation after RBC transfusion.
This is the first study showing a role for SNO transport by LAT1 in ECs in a genetic mouse model. We provide the first direct evidence for the coordination of RBC SNO export with EC SNO import via LAT1. SNO flux via LAT1 modulates RBC-EC sequestration in lungs after transfusion, and its disruption impairs blood oxygenation by the lung.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cardiovascular biology
In Nat Commun on 10 August 2023 by Ding, Y., Gui, X., et al.
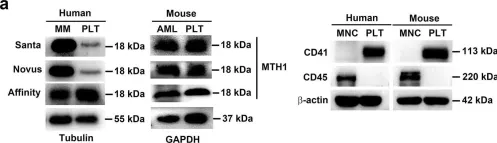
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
In Front Pediatr on 27 August 2022 by Huang, Z., Lin, B., et al.
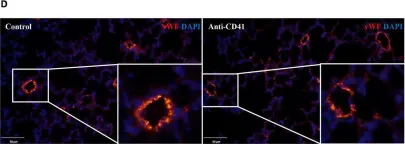
Fig.3.D

-
IHC-IF
-
Collected and cropped from Front Pediatr by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2