The integrins and G protein-coupled receptors are both fundamental in cell biology. The cross talk between these two, however, is unclear. Here we show that β3 integrins negatively regulate G protein-coupled signaling by directly inhibiting the Gα13-p115RhoGEF interaction. Furthermore, whereas β3 deficiency or integrin antagonists inhibit integrin-dependent platelet aggregation and exocytosis (granule secretion), they enhance G protein-coupled RhoA activation and integrin-independent secretion. In contrast, a β3-derived Gα13-binding peptide or Gα13 knockout inhibits G protein-coupled RhoA activation and both integrin-independent and dependent platelet secretion without affecting primary platelet aggregation. In a mouse model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo, the β3-derived Gα13-binding peptide inhibits platelet secretion of granule constituents, which exacerbates inflammation and ischemia/reperfusion injury. These data establish crucial integrin-G protein crosstalk, providing a rationale for therapeutic approaches that inhibit exocytosis in platelets and possibly other cells without adverse effects associated with loss of cell adhesion.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Product Citations: 9
In Nature Communications on 16 August 2023 by Zhang, Y., Zhao, X., et al.
In Science Advances on 1 August 2021 by Neufeld, L., Yeini, E., et al.
Many drugs show promising results in laboratory research but eventually fail clinical trials. We hypothesize that one main reason for this translational gap is that current cancer models are inadequate. Most models lack the tumor-stroma interactions, which are essential for proper representation of cancer complexed biology. Therefore, we recapitulated the tumor heterogenic microenvironment by creating fibrin glioblastoma bioink consisting of patient-derived glioblastoma cells, astrocytes, and microglia. In addition, perfusable blood vessels were created using a sacrificial bioink coated with brain pericytes and endothelial cells. We observed similar growth curves, drug response, and genetic signature of glioblastoma cells grown in our 3D-bioink platform and in orthotopic cancer mouse models as opposed to 2D culture on rigid plastic plates. Our 3D-bioprinted model could be the basis for potentially replacing cell cultures and animal models as a powerful platform for rapid, reproducible, and robust target discovery; personalized therapy screening; and drug development.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
-
FC/FACS
-
Cancer Research
Influenza A virus directly modulates mouse eosinophil responses.
In Journal of Leukocyte Biology on 1 July 2020 by LeMessurier, K. S., Rooney, R., et al.
Allergic asthma and influenza are common respiratory diseases with a high probability of co-occurrence. During the 2009 influenza pandemic, hospitalized patients with influenza experienced lower morbidity if asthma was an underlying condition. We have previously demonstrated that acute allergic asthma protects mice from severe influenza and have implicated eosinophils in the airways of mice with allergic asthma as participants in the antiviral response. However, very little is known about how eosinophils respond to direct exposure to influenza A virus (IAV) or the microenvironment in which the viral burden is high. We hypothesized that eosinophils would dynamically respond to the presence of IAV through phenotypic, transcriptomic, and physiologic changes. Using our mouse model of acute fungal asthma and influenza, we showed that eosinophils in lymphoid tissues were responsive to IAV infection in the lungs and altered surface expression of various markers necessary for cell activation in a niche-specific manner. Siglec-F expression was altered in a subset of eosinophils after virus exposure, and those expressing high Siglec-F were more active (IL-5Rαhi CD62Llo ). While eosinophils exposed to IAV decreased their overall transcriptional activity and mitochondrial oxygen consumption, transcription of genes encoding viral recognition proteins, Ddx58 (RIG-I), Tlr3, and Ifih1 (MDA5), were up-regulated. CD8+ T cells from IAV-infected mice expanded in response to IAV PB1 peptide-pulsed eosinophils, and CpG methylation in the Tbx21 promoter was reduced in these T cells. These data offer insight into how eosinophils respond to IAV and help elucidate alternative mechanisms by which they regulate antiviral immune responses during IAV infection.
©2020 Society for Leukocyte Biology.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Platelets in Amyloidogenic Mice Are Activated and Invade the Brain.
In Frontiers in Neuroscience on 21 March 2020 by Kniewallner, K. M., de Sousa, D. M. B., et al.
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease with a complex and not fully understood pathogenesis. Besides brain-intrinsic hallmarks such as abnormal deposition of harmful proteins, i.e., amyloid beta in plaques and hyperphosphorylated Tau in neurofibrillary tangles, blood-derived elements, in particular, platelets have been discussed to be involved in AD pathogenesis. The underlying mechanisms, however, are rather unexplored. Here, we investigate a potential role of platelets in an AD transgenic animal model with severe amyloid plaque formation, the APP-PS1 transgenic mice, and analyzed the presence, spatial location and activation status of platelets within the brain. In APP-PS1 mice, a higher number of platelets were located within the brain parenchyma, i.e., outside the cerebral blood vessels compared to WT controls. Such platelets were activated according to the expression of the platelet activation marker CD62P and to morphological hallmarks such as membrane protrusions. In the brain, platelets were in close contact exclusively with astrocytes suggesting an interaction between these two cell types. In the bloodstream, although the percentage of activated platelets did not differ between transgenic and age-matched control animals, APP-PS1 blood-derived platelets showed remarkable ultrastructural peculiarities in platelet-specific organelles such as the open canalicular system (OCS). This work urges for further investigations on platelets and their yet unknown functional roles in the brain, which might go beyond AD pathogenesis and be relevant for various age-related neurodegenerative diseases.
Copyright © 2020 Kniewallner, de Sousa, Unger, Mrowetz and Aigner.
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Neuroscience
In Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis : JTH on 1 September 2018 by Zhu, W., Buffa, J. A., et al.
Essentials Microbe-dependent production of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) contributes to thrombosis risk. The impact of host flavin monooxygenase 3 (FMO3) modulation on platelet function is unknown. Genetic manipulation of FMO3 in mice alters systemic TMAO levels and thrombosis potential. Genetic manipulation of FMO3 is associated with alteration of gut microbial community structure.
Background Gut microbes play a critical role in the production of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), an atherogenic metabolite that impacts platelet responsiveness and thrombosis potential. Involving both microbe and host enzymatic machinery, TMAO generation utilizes a metaorganismal pathway, beginning with ingestion of trimethylamine (TMA)-containing dietary nutrients such as choline, phosphatidylcholine and carnitine, which are abundant in a Western diet. Gut microbial TMA lyases use these nutrients as substrates to produce TMA, which upon delivery to the liver via the portal circulation, is converted into TMAO by host hepatic flavin monooxygenases (FMOs). Gut microbial production of TMA is rate limiting in the metaorganismal TMAO pathway because hepatic FMO activity is typically in excess. Objectives FMO3 is the major FMO responsible for host generation of TMAO; however, a role for FMO3 in altering platelet responsiveness and thrombosis potential in vivo has not yet been explored. Methods The impact of FMO3 suppression (antisense oligonucleotide-targeting) and overexpression (as transgene) on plasma TMAO levels, platelet responsiveness and thrombosis potential was examined using a murine FeCl3 -induced carotid artery injury model. Cecal microbial composition was examined using 16S analyses. Results Modulation of FMO3 directly impacts systemic TMAO levels, platelet responsiveness and rate of thrombus formation in vivo. Microbial composition analyses reveal taxa whose proportions are associated with both plasma TMAO levels and in vivo thrombosis potential. Conclusions The present studies demonstrate that host hepatic FMO3, the terminal step in the metaorganismal TMAO pathway, participates in diet-dependent and gut microbiota-dependent changes in both platelet responsiveness and thrombosis potential in vivo.
© 2018 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
-
FC/FACS
-
Cardiovascular biology
In Front Neurosci on 21 March 2020 by Kniewallner, K. M., de Sousa, D. M. B., et al.
Fig.2.B
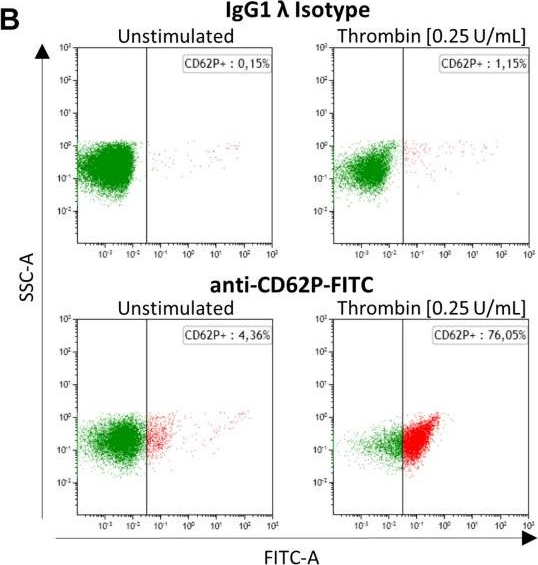
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Front Neurosci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 1