IRX3 is linked to predisposition to obesity through the FTO locus and is upregulated during early adipogenesis in risk-allele carriers, shifting adipocyte fate toward fat storage. However, how this elevated IRX3 expression influences later developmental stages remains unclear. Here we show that IRX3 regulates adipocyte fate by modulating epigenetic reprogramming. ChIP-sequencing in preadipocytes identifies over 300 IRX3 binding sites, predominantly at promoters of genes involved in SUMOylation and chromatin remodeling. IRX3 knockout alters expression of SUMO pathway genes, increases global SUMOylation, and inhibits PPARγ activity and adipogenesis. Pharmacological SUMOylation inhibition rescues these effects. IRX3 KO also reduces SUMO occupancy at Wnt-related genes, enhancing Wnt signaling and promoting osteogenic fate in 3D cultures. This fate switch is partially reversible by SUMOylation inhibition. We identify IRX3 as a key transcriptional regulator of epigenetic programs, acting upstream of SUMOylation to maintain mesenchymal identity and support adipogenesis while suppressing osteogenesis in mouse embryonic fibroblasts.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 208
IRX3 controls a SUMOylation-dependent differentiation switch in adipocyte precursor cells.
In Nature Communications on 6 August 2025 by Bjune, J. I., Laber, S., et al.
In Redox Biology on 14 July 2025 by Heuser, S. K., Li, J., et al.
In humans and other primates, red blood cells (RBCs) constitutively express high levels of liver-type arginase 1 (Arg1), which regulates systemic l-arginine and nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability, particularly under pathological conditions such as sickle cell disease. In contrast, the role of RBC Arg1 in mice in vivo remains poorly defined. Here, we investigated the contribution of RBC Arg1 to systemic l-arginine metabolism, NO bioavailability, and cardioprotection following acute myocardial infarction in vivo. Comparative analyses of human blood fractions revealed that arginase activity in RBCs is comparable to that in white blood cells and is predominantly localized to the RBC membrane. In contrast, arginase activity in mouse RBC membranes was 13,500-fold lower as compared to human RBC membranes as measured by 13C-l-ornithine formation. To assess the in vivo relevance of RBC Arg1, we generated RBC-specific Arg1 knockout (KO) mice using the Cre/loxP technology. RBC Arg1 KO mice exhibited normal erythropoiesis and hematologic parameters. Moreover, systemic l-arginine and l-citrulline levels were preserved, while l-ornithine levels were lower in plasma of RBC Arg1 KO mice as compared to wildtype controls; whereas circulating NO metabolites, systemic hemodynamics, cardiac function, and infarct size post-acute myocardial infarction were preserved. These findings demonstrate that, unlike in humans, in mice RBC Arg1 plays a negligible role in regulating systemic l-arginine homeostasis and cardioprotection, underscoring critical interspecies differences and the need for human studies to evaluate the pathophysiological relevance of RBC arginase.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
In Biomolecules on 28 May 2025 by Walker, W. P., Ratz-Mitchem, M. L., et al.
Endosomal dysfunction is one of the earliest cellular signs in Alzheimer's disease. Tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein (TSG101) is a component of the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT)-I, which plays a key role in sorting ubiquitinated cell surface proteins and lipids onto intraluminal vesicles of multivesicular bodies for trafficking to lysosomes or autophagosomes for degradation, or to the plasma membrane for exosomal secretion. TSG101-dependent trafficking has been implicated in the propagation and spread of misfolded proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases. We used transgenesis mice to study the in vivo consequences of disrupting TSG101-dependent trafficking in adult neurons. Mice lacking Tsg101 in forebrain neurons (Tsg101ck2-null) showed rapid loss of hippocampal neurons and progressive forebrain atrophy. Astrogliosis was apparent in the dentate gyrus within 1 week of deleting Tsg101, followed by apoptosis of hippocampal CA3 neurons and accumulation of the autophagy adapter P62/SQSTM1 and ubiquitinated proteins. Failure to detect lipidated LC3 indicated autophagy was impaired rather than upregulated. Endosomal markers (RAB5 and RAB7) and amyloid protein also accumulated in hippocampal neurons of Tsg101ck2-null mice. Our data establish a critical role for TSG101 in neuronal survival and demonstrate the importance of the in vivo assessment of gene and protein functions.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Neuroscience
Low extracellular pH protects cancer cells from ammonia toxicity.
In Cell Death Discovery on 3 April 2025 by Dravecka, M., Mikkola, I., et al.
Ammonia is a natural waste product of cellular metabolism which, through its lysosomotropic ability, can have detrimental effects on various cellular functions. Increased levels of ammonia were recently detected in the interstitial fluid of various tumours, substantiating that high ammonia concentrations are a pathophysiological condition in the tumour microenvironment, alongside hypoxia and acidosis. Since little is known about how cancer cells respond to elevated levels of ammonia in the tumour microenvironment, we investigated how a panel of cancer cell lines derived from solid tumours behaved when exposed to increasing concentrations of ammonia. We found that ammonia represses cell growth, induces genome instability, and inhibits lysosome-mediated proteolysis in a dose-dependent manner. Unexpectedly, we also found that small fluctuations in the pH of the extracellular environment, had a significant impact on the cytotoxic effects of ammonia. In summary, our data show that the balance of pH and ammonia within the interstitial fluids of cancerous tumours significantly impacts the behaviour and fate of cells residing in the tumour microenvironment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Cancer Research
Advanced Lung-on-a-Chip Technology: Mimicking the Complex Human Lung Microenvironment.
In International Journal of Biological Sciences on 2 January 2025 by Min, E. K., Lee, C. M., et al.
Intricate crosstalk among various lung cell types is crucial for orchestrating diverse physiological processes. Traditional two-dimensional and recent three-dimensional (3D) assay platforms fail to precisely replicate these complex communications. Many in vitro lung models do not effectively reflect the multicellular complexity of lung tissue. Here, we fabricated an advanced multicellular 3D lung-on-a-chip system that properly replicates the dynamic pulmonary microenvironment and its intricate microarchitecture. Diverse lung cells were incorporated into a microstructure formed from a mixture of natural polymers, including collagen and hyaluronic acid, and blood coagulation factors acting as natural crosslinking agents. The system accurately reflects the complex 3D architecture of the lung. Biomarkers demonstrate more rapid and sensitive responses to toxic substances than functional indicators, such as cell proliferation and apoptosis. SERPINB2 was identified as a biomarker of lung toxicity; it was activated in small airway epithelial cells exposed to various toxic substances. We then developed a fluorescence-linked toxicity biomarker screening platform that enables both intuitive and quantitative evaluation of lung toxicity by measuring the converted fluorescent signal strength. This fluorescent tagging system was incorporated into small airway epithelial cells within a fabricated chip platform; enabling lung-on-a-chip enabled evaluation of the lung toxicity of prospective drug candidates.
© The author(s).
-
WB
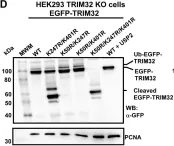
In PLoS One on 18 May 2021 by Garcia-Garcia, J., Overå, K. S., et al.
Fig.1.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
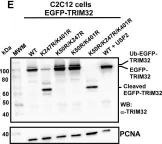
In PLoS One on 18 May 2021 by Garcia-Garcia, J., Overå, K. S., et al.
Fig.1.E

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
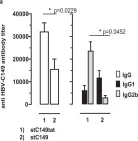
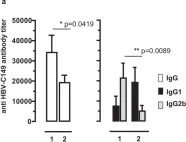
In Sci Rep on 2 October 2018 by Krieger, J., Stifter, K., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
ELISA
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
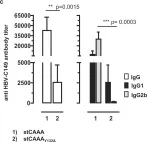
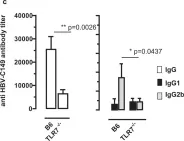
In Sci Rep on 2 October 2018 by Krieger, J., Stifter, K., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
ELISA
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
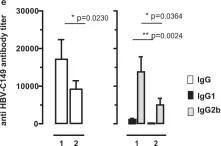
In Sci Rep on 2 October 2018 by Krieger, J., Stifter, K., et al.
Fig.6.C

-
ELISA
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In Sci Rep on 2 October 2018 by Krieger, J., Stifter, K., et al.
Fig.7.A

-
ELISA
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In Sci Rep on 2 October 2018 by Krieger, J., Stifter, K., et al.
Fig.7.C

-
ELISA
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
In Sci Rep on 2 October 2018 by Krieger, J., Stifter, K., et al.
Fig.7.E

-
ELISA
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
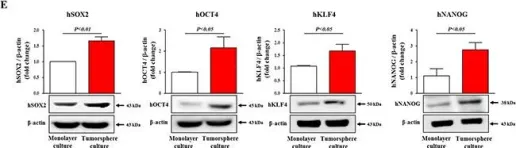
In Oncotarget on 12 April 2016 by Kim, J. Y., Lee, H. Y., et al.
Fig.2.E

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10
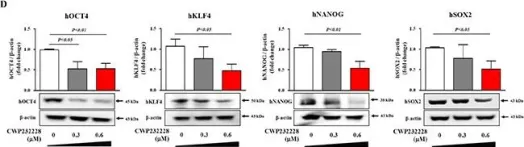
In Oncotarget on 12 April 2016 by Kim, J. Y., Lee, H. Y., et al.
Fig.5.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 10