The BRAF gene is mutated in a plethora of human cancers. The majority of such molecular lesions result in the expression of a constitutively active BRAF variant (BRAFV600E) which continuously bolsters cell proliferation. Although we recently addressed the early effects triggered by BRAFV600E-activation, the specific contribution of ERK1 and ERK2 in BRAFV600E-driven responses in vivo has never been explored. Here we describe the first murine model suitable for genetically dissecting the ERK1/ERK2 impact in multiple phenotypes induced by ubiquitous BRAFV600E-expression. We unveil that ERK1 is dispensable for BRAFV600E-dependent lifespan shortening and for BRAFV600E-driven tumor growth. We show that BRAFV600E-expression provokes an ERK1-independent lymphocyte depletion which does not rely on p21CIP1-induced cell cycle arrest and is unresponsive to ERK-chemical inhibition. Moreover, we also reveal that ERK1 is dispensable for BRAFV600E-triggered cytotoxicity in lungs and that ERK-chemical inhibition abrogates some of these detrimental effects, such as DNA damage, in Club cells but not in pulmonary lymphocytes. Our data suggest that ERK1/ERK2 contribution to BRAFV600E-driven phenotypes is dynamic and varies dependently on cell type, the biological function, and the level of ERK-pathway activation. Our findings also provide useful insights into the comprehension of BRAFV600E-driven malignancies pathophysiology as well as the consequences in vivo of novel ERK pathway-targeted anti-cancer therapies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 15
In Cell Death and Differentiation on 1 June 2024 by Bosso, G., Cintra Herpst, A. C., et al.
-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cell Biology
Kras oncogene ablation prevents resistance in advanced lung adenocarcinomas.
In The Journal of Clinical Investigation on 3 April 2023 by Salmón, M., Álvarez-Díaz, R., et al.
KRASG12C inhibitors have revolutionized the clinical management of patients with KRASG12C-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. However, patient exposure to these inhibitors leads to the rapid onset of resistance. In this study, we have used genetically engineered mice to compare the therapeutic efficacy and the emergence of tumor resistance between genetic ablation of mutant Kras expression and pharmacological inhibition of oncogenic KRAS activity. Whereas Kras ablation induces massive tumor regression and prevents the appearance of resistant cells in vivo, treatment of KrasG12C/Trp53-driven lung adenocarcinomas with sotorasib, a selective KRASG12C inhibitor, caused a limited antitumor response similar to that observed in the clinic, including the rapid onset of resistance. Unlike in human tumors, we did not observe mutations in components of the RAS-signaling pathways. Instead, sotorasib-resistant tumors displayed amplification of the mutant Kras allele and activation of xenobiotic metabolism pathways, suggesting that reduction of the on-target activity of KRASG12C inhibitors is the main mechanism responsible for the onset of resistance. In sum, our results suggest that resistance to KRAS inhibitors could be prevented by achieving a more robust inhibition of KRAS signaling mimicking the results obtained upon Kras ablation.
-
Cancer Research
KSR induces RAS-independent MAPK pathway activation and modulates the efficacy of KRAS inhibitors.
In Molecular Oncology on 1 September 2022 by Paniagua, G., Jacob, H. K. C., et al.
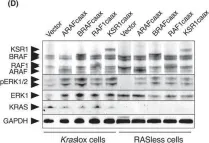
The kinase suppressor of rat sarcoma (RAS) proteins (KSR1 and KSR2) have long been considered as scaffolding proteins required for optimal mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway signalling. However, recent evidence suggests that they play a more complex role within this pathway. Here, we demonstrate that ectopic expression of KSR1 or KSR2 is sufficient to activate the MAPK pathway and to induce cell proliferation in the absence of RAS proteins. In contrast, the ectopic expression of KSR proteins is not sufficient to induce cell proliferation in the absence of either rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma (RAF) or MAPK-ERK kinase proteins, indicating that they act upstream of RAF. Indeed, KSR1 requires dimerization with at least one member of the RAF family to stimulate proliferation, an event that results in the translocation of the heterodimerized RAF protein to the cell membrane. Mutations in the conserved aspartic acid-phenylalanine-glycine motif of KSR1 that affect ATP binding impair the induction of cell proliferation. We also show that increased expression levels of KSR1 decrease the responsiveness to the KRASG12C inhibitor sotorasib in human cancer cell lines, thus suggesting that increased levels of expression of KSR may make tumour cells less dependent on KRAS oncogenic signalling.
© 2022 The Authors. Molecular Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
-
WB
KRAS4A induces metastatic lung adenocarcinomas in vivo in the absence of the KRAS4B isoform.
In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America on 27 July 2021 by Salmón, M., Paniagua, G., et al.
In mammals, the KRAS locus encodes two protein isoforms, KRAS4A and KRAS4B, which differ only in their C terminus via alternative splicing of distinct fourth exons. Previous studies have shown that whereas KRAS expression is essential for mouse development, the KRAS4A isoform is expendable. Here, we have generated a mouse strain that carries a terminator codon in exon 4B that leads to the expression of an unstable KRAS4B154 truncated polypeptide, hence resulting in a bona fide Kras4B-null allele. In contrast, this terminator codon leaves expression of the KRAS4A isoform unaffected. Mice selectively lacking KRAS4B expression developed to term but died perinatally because of hypertrabeculation of the ventricular wall, a defect reminiscent of that observed in embryos lacking the Kras locus. Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) obtained from Kras4B-/- embryos proliferated less than did wild-type MEFs, because of limited expression of KRAS4A, a defect that can be compensated for by ectopic expression of this isoform. Introduction of the same terminator codon into a KrasFSFG12V allele allowed expression of an endogenous KRAS4AG12V oncogenic isoform in the absence of KRAS4B. Exposure of Kras+/FSF4AG12V4B- mice to Adeno-FLPo particles induced lung tumors with complete penetrance, albeit with increased latencies as compared with control Kras+/FSFG12V animals. Moreover, a significant percentage of these mice developed proximal metastasis, a feature seldom observed in mice expressing both mutant isoforms. These results illustrate that expression of the KRAS4AG12V mutant isoform is sufficient to induce lung tumors, thus suggesting that selective targeting of the KRAS4BG12V oncoprotein may not have significant therapeutic consequences.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America on 29 September 2020 by Esteban-Burgos, L., Wang, H., et al.
KRAS mutant lung adenocarcinomas remain intractable for targeted therapies. Genetic interrogation of KRAS downstream effectors, including the MAPK pathway and the interphase CDKs, identified CDK4 and RAF1 as the only targets whose genetic inactivation induces therapeutic responses without causing unacceptable toxicities. Concomitant CDK4 inactivation and RAF1 ablation prevented tumor progression and induced complete regression in 25% of KRAS/p53-driven advanced lung tumors, yet a significant percentage of those tumors that underwent partial regression retained a population of CDK4/RAF1-resistant cells. Characterization of these cells revealed two independent resistance mechanisms implicating hypermethylation of several tumor suppressors and increased PI3K activity. Importantly, these CDK4/RAF1-resistant cells can be pharmacologically controlled. These studies open the door to new therapeutic strategies to treat KRAS mutant lung cancer, including resistant tumors.
-
Cancer Research
In Mol Oncol on 1 September 2022 by Paniagua, G., Jacob, H. K. C., et al.
Fig.4.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Mol Oncol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
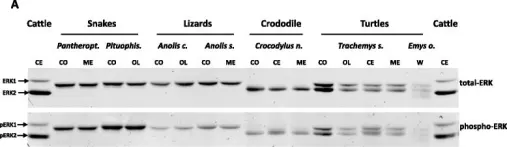
In BMC Evol Biol on 3 September 2015 by Busca, R., Christen, R., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from BMC Evol Biol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2