Peters anomaly, the most common cause of congenital corneal opacity, stems from corneal-lenticular adhesion. Despite numerous identified mutations, a cohesive molecular framework of the disease’s etiology remains elusive. Here, we identified Abl kinases as pivotal regulators of FGF signaling, as genetic ablation of Abl kinases restores lens induction even in the absence of FGF signaling. Intriguingly, both Abl kinase deficiency and increased FGF-Ras activity result in Peters anomaly independent of ERK signaling, which can be rescued by allelic deletion of Abl substrate, Crk. However, contrary to the prevailing belief that Abl kinases regulate Crk proteins by direct phosphorylation, mutations at Abl kinase phosphorylation sites on Crk and CrkL did not yield any observable effects. Instead, our findings reveal that Abl kinases phosphorylate Ptpn12, which in turn inhibits p130Cas phosphorylation and Crk recruitment, crucial for Rho GTPases activation and cytoskeletal dynamics. Consequently, Abl kinase deficiency reduces actomyosin contractility within the lens vesicle and genetically interacts with RhoA inhibition. Conversely, Rac1 deletion mitigates Peters anomaly in models with aberrant FGF, Abl kinase and RhoA signaling. Our results demonstrate that Abl kinases regulate FGF signaling to balance RhoA and Rac1 activity via the Ptpn12-p130Cas pathway, suggesting that targeting tension-mediated lens vesicle separation could be a therapeutic strategy for Peters anomaly.
Product Citations: 58
Abl kinases regulate FGF signaling independent of Crk phosphorylation to prevent Peters anomaly
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 26 October 2024 by Wu, H., Mao, Y., et al.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
In Cancers on 8 August 2024 by Dubourg, A., Harnois, T., et al.
A major issue in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) is the persistence of quiescent leukemia stem cells (LSCs) in the hematopoietic niche under tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) treatment.
Here, using CFSE sorting, we show that low-proliferating CD34+ cells from CML patients in 3D co-culture hide under HS27A stromal cells during TKI treatment-a behavior less observed in untreated cells. Under the same conditions, Ba/F3p210 cells lose their spontaneous motility. In CML CD34+ and Ba/F3p210 cells, while Rac1 is completely inhibited by TKI, RhoA remains activated but is unable to signal to ROCK. Co-incubation of Ba/F3p210 cells with TKI, SKF-96365 (a calcium channel inhibitor), and EGF restores myosin II activation and amoeboid motility to levels comparable to untreated cells, sustaining the activation of ROCK. In CFSE+ CD34+ cells containing quiescent leukemic stem cells, co-incubation of TKI with SKF-96365 induced the expulsion of these cells from the HS27A niche.
This study underscores the role of RhoA in LSC behavior under TKI treatment and suggests that SKF-96365 could remobilize quiescent CML LSCs through reactivation of the RhoA/ROCK pathway.
-
Cancer Research
In Cancer Reports (Hoboken, N.J.) on 1 April 2024 by Takahashi, K., Nguyen, T. T. T., et al.
Adhesion of cancer cells to extracellular matrix laminin through the integrin superfamily reportedly induces drug resistance. Heterodimers of integrin α6 (CD49f) with integrin β1 (CD29) or β4 (CD104) are major functional receptors for laminin. Higher CD49f expression is reportedly associated with a poorer response to induction therapy in childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL). Moreover, a xenograft mouse model transplanted with primary BCP-ALL cells revealed that neutralized antibody against CD49f improved survival after chemotherapy.
Considering the poor outcomes in Philadelphia chromosome (Ph)-positive ALL treated with conventional chemotherapy without tyrosine kinase inhibitors, we sought to investigate an involvement of the laminin adhesion.
Ph-positive ALL cell lines expressed the highest levels of CD49f among the BCP-ALL cell lines with representative translocations, while CD29 and CD104 were ubiquitously expressed in BCP-ALL cell lines. The association of Ph-positive ALL with high levels of CD49f gene expression was also confirmed in two databases of childhood ALL cohorts. Ph-positive ALL cell lines attached to laminin and their laminin-binding properties were disrupted by blocking antibodies against CD49f and CD29 but not CD104. The cell surface expression of CD49f, but not CD29 and CD104, was downregulated by imatinib treatment in Ph-positive ALL cell lines, but not in their T315I-acquired sublines. Consistently, the laminin-binding properties were disrupted by the imatinib pre-treatment in the Ph-positive ALL cell line, but not in its T315I-acquired subline.
BCR::ABL1 plays an essential role in the laminin adhesion of Ph-positive ALL cells through upregulation of CD49f.
© 2024 The Authors. Cancer Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
In Bioorganic Chemistry on 1 February 2024 by Wang, X., Defilippis, R. A., et al.
Activating mutations within FLT3 make up 30 % of all newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cases, with the most common mutation being an internal tandem duplication (FLT3-ITD) in the juxtamembrane region (25 %). Currently, two generations of FLT3 kinase inhibitors have been developed, with three inhibitors clinically approved. However, treatment of FLT3-ITD mutated AML is limited due to the emergence of secondary clinical resistance, caused by multiple mechanism including on-target FLT3 secondary mutations - FLT3-ITD/D835Y and FLT3-ITD/F691L being the most common, as well as the off-target activation of alternative pathways including the BCR-ABL pathway. Through the screening of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivatives, N-(3-methoxyphenyl)-6-(7-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyridin-2-amine (compound 1) was identified as an inhibitor of both the FLT3-ITD and BCR-ABL pathways. Compound 1 potently inhibits clinically related leukemia cell lines driven by FLT3-ITD, FLT3-ITD/D835Y, FLT3-ITD/F691L, or BCR-ABL. Studies indicate that it mediates proapoptotic effects on cells by inhibiting FLT3 and BCR-ABL pathways, and other possible targets. Compound 1 is more potent against FLT3-ITD than BCR-ABL, and it may have other possible targets; however, compound 1 is first step for further optimization for the development of a balanced FLT3-ITD/BCR-ABL dual inhibitor for the treatment of relapsed FLT3-ITD mutated AML with multiple secondary clinical resistant subtypes such as FLT3-ITD/D835Y, FLT3-ITD/F691L, and cells co-expressing FLT3-ITD and BCR-ABL.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Inc.
ABL1 and ABL2 promote medulloblastoma leptomeningeal dissemination.
In Neuro-oncology Advances on 2 October 2023 by Jones, J. K., Zhang, H., et al.
Medulloblastoma is the most common malignant pediatric brain tumor, and leptomeningeal dissemination (LMD) of medulloblastoma both portends a poorer prognosis at diagnosis and is incurable at recurrence. The biological mechanisms underlying LMD are unclear. The Abelson (ABL) tyrosine kinase family members, ABL1 and ABL2, have been implicated in cancer cell migration, invasion, adhesion, metastasis, and chemotherapy resistance, and are upstream mediators of the oncogene c-MYC in fibroblasts and lung cancer cells. However, their role in medulloblastoma has not yet been explored. The purpose of this work was to elucidate the role of ABL1/2 in medulloblastoma LMD.
ABL1 and ABL2 mRNA expression of patient specimens was analyzed. shRNA knockdowns of ABL1/2 and pharmacologic inhibition of ABL1/2 were used for in vitro and in vivo analyses of medulloblastoma LMD. RNA sequencing of ABL1/2 genetic knockdown versus scrambled control medulloblastoma was completed.
ABL1/2 mRNA is highly expressed in human medulloblastoma and pharmacologic inhibition of ABL kinases resulted in cytotoxicity. Knockdown of ABL1/2 resulted in decreased adhesion of medulloblastoma cells to the extracellular matrix protein, vitronectin (P = .0013), and significantly decreased tumor burden in a mouse model of medulloblastoma LMD with improved overall survival (P = .0044). Furthermore, both pharmacologic inhibition of ABL1/2 and ABL1/2 knockdown resulted in decreased expression of c-MYC, identifying a putative signaling pathway, and genes/pathways related to oncogenesis and neurodevelopment were differentially expressed between ABL1/2 knockdown and control medulloblastoma cells.
ABL1 and ABL2 have potential roles in medulloblastoma LMD upstream of c-MYC expression.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press, the Society for Neuro-Oncology and the European Association of Neuro-Oncology.
-
WB
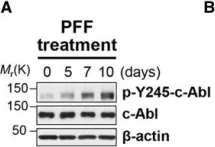
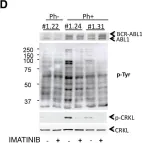
In Hum Mol Genet on 1 July 2018 by Lee, S., Kim, S., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Hum Mol Genet by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
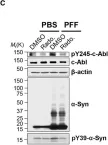
In Hum Mol Genet on 1 July 2018 by Lee, S., Kim, S., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Hum Mol Genet by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
In PLoS One on 23 October 2013 by Gordon, M., El-Kalla, M., et al.
Fig.9.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
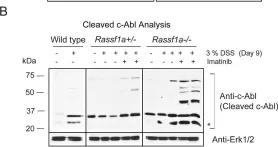
In PLoS One on 23 October 2013 by Gordon, M., El-Kalla, M., et al.
Fig.9.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5
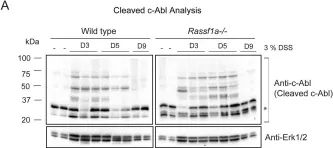
In PLoS One on 24 September 2013 by Bedel, A., Pasquet, J. M., et al.
Fig.3.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 5