MRTX1133 is currently being evaluated in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) tumors harboring a KRASG12D mutation. Combination strategies have the potential to enhance the efficacy of MRTX1133 to further promote cell death and tumor regression. In this study, we demonstrated that MRTX1133 increased the levels of the proapoptotic protein BIM in PDAC cells and conferred sensitivity to the FDA-approved BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax. Combined treatment with MRTX1133 and venetoclax resulted in cell death and growth suppression in 3D cultures. BIM was required for apoptosis induced by the combination treatment. Consistently, BIM was induced in tumors treated with MRTX1133, and venetoclax enhanced the efficacy of MRTX1133 in vivo. Venetoclax could also resensitize MRTX1133-resistant PDAC cells to MRTX1133 in 3D cultures, and tumors established from resistant cells responded to the combination of MRTX1133 and venetoclax. These results provide a rationale for the clinical testing of MRTX1133 and venetoclax in patients with PDAC. Significance: The combination of MRTX1133 and the FDA-approved drug venetoclax promotes cancer cell death and tumor regression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, providing rationale for testing venetoclax with KRASG12D inhibitors in patients with pancreatic cancer.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Product Citations: 79
In Cancer Research on 4 November 2024 by Becker, J. H., Metropulos, A. E., et al.
-
Cancer Research
In Children (Basel, Switzerland) on 23 August 2024 by Sahyon, H. A., Alharbi, N. S., et al.
Background/Objectives: Wilms tumor (WT) is the most common form of pediatric renal tumor, accounting for over 90% of cases followed by hypernephroma. Some pediatric patients with WT (10%) experience relapse or metastasis and have poor survival rates. PD-L1 assists cancer cells in escaping damage from the immune system. P53 mutations are found in relapsed WT tumor samples. We hypothesized that testing circulating PD-1 and PD-L1 and P53 expression levels could offer a simple method to predict patient relapse and explore novel treatments for pediatric WTs and hypernephroma. Methods: Flow cytometric detection of cPD-1, cPD-L1, and P53 expression in relapsed and in-remission WT and hypernephroma before and after one year of chemotherapy was performed. Results: Our data shows increased levels of cPD-L1 in relapsed pediatric patients with WT or hypernephroma before and after chemotherapy. There were also slight and significant increases in cPD-1 levels in relapsed groups before chemotherapy. Additionally, we observed significant decreases in P53 expression after one year of chemotherapy in relapsed pediatric patients. Conclusions: Our study found that circulating PD-L1 can be used as a predictor marker for WT and hypernephroma relapse. In conclusion, these circulating markers can assist in monitoring relapse in WT and hypernephroma patients without the need for several biopsies.
-
Cancer Research
Anti-apoptotic MCL-1 promotes long-chain fatty acid oxidation through interaction with ACSL1.
In Molecular Cell on 4 April 2024 by Wright, T., Turnis, M. E., et al.
MCL-1 is essential for promoting the survival of many normal cell lineages and confers survival and chemoresistance in cancer. Beyond apoptosis regulation, MCL-1 has been linked to modulating mitochondrial metabolism, but the mechanism(s) by which it does so are unclear. Here, we show in tissues and cells that MCL-1 supports essential steps in long-chain (but not short-chain) fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO) through its binding to specific long-chain acyl-coenzyme A (CoA) synthetases of the ACSL family. ACSL1 binds to the BH3-binding hydrophobic groove of MCL-1 through a non-conventional BH3-domain. Perturbation of this interaction, via genetic loss of Mcl1, mutagenesis, or use of selective BH3-mimetic MCL-1 inhibitors, represses long-chain FAO in cells and in mouse livers and hearts. Our findings reveal how anti-apoptotic MCL-1 facilitates mitochondrial metabolism and indicate that disruption of this function may be associated with unanticipated cardiac toxicities of MCL-1 inhibitors in clinical trials.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
In Haematologica on 1 August 2022 by Schmid, V. K., Khadour, A., et al.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a frequent lymphoproliferative disorder of B cells. Although inhibitors targeting signal proteins involved in B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) signaling constitute an important part of the current therapeutic protocols for CLL patients, the exact role of BCR signaling, as compared to genetic aberration, in the development and progression of CLL is controversial. In order to investigate whether BCR expression per se is pivotal for the development and maintenance of CLL B cells, we used the TCL1 mouse model. By ablating the BCR in CLL cells from TCL1 transgenic mice, we show that CLL cells cannot survive without BCR signaling and are lost within 8 weeks in diseased mice. Furthermore, we tested whether mutations augmenting B-cell signaling influence the course of CLL development and its severity. The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway is an integral part of the BCR signaling machinery and its activity is indispensable for B-cell survival. It is negatively regulated by the lipid phosphatase PTEN, whose loss mimics PI3K pathway activation. Herein, we show that PTEN has a key regulatory function in the development of CLL, as deletion of the Pten gene resulted in greatly accelerated onset of the disease. By contrast, deletion of the gene TP53, which encodes the tumor suppressor p53 and is highly mutated in CLL, did not accelerate disease development, confirming that development of CLL was specifically triggered by augmented PI3K activity through loss of PTEN and suggesting that CLL driver consequences most likely affect BCR signaling. Moreover, we could show that in human CLL patient samples, 64% and 81% of CLL patients with a mutated and unmutated IgH VH, respectively, show downregulated PTEN protein expression in CLL B cells if compared to healthy donor B cells. Importantly, we found that B cells derived from CLL patients had higher expression levels of the miRNA-21 and miRNA-29, which suppresses PTEN translation, compared to healthy donors. The high levels of miRNA-29 might be induced by increased PAX5 expression of the B-CLL cells. We hypothesize that downregulation of PTEN by increased expression levels of miR-21, PAX5 and miR-29 could be a novel mechanism of CLL tumorigenesis that is not established yet. Together, our study demonstrates the pivotal role for BCR signaling in CLL development and deepens our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the genesis of CLL and for the development of new treatment strategies.
-
Cancer Research
-
Cardiovascular biology
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Long- term safety of Eruca sativa leaf ethanolic extract on Male Rats
Preprint on Research Square on 9 March 2022 by El-Gayar, H. A., Derbala, S., et al.
The present study was performed to evaluate the safe dose of ethanolic Eruca sativa leaves extract in healthy adult male rats. Twenty-five male Wister rats were divided into 5 groups: Group I (Control): received no treatment, groups 2, 3, 4, and 5 received 1, 3, 5, and 6 g/kg BW orally per day for 35 days. On the 36 day, rats were euthanized. Body weights were recorded. Serum biochemical analysis and the expression level of liver and kidney p53 and Bcl-2 were determined. Histopathology of liver and kidney, and TNF-α immunohistochemistry were examined. The ethanolic extract revealed the content of phenols, flavonoids, and fatty acids. Determination of biochemical parameters showed no significant difference in the estimated parameters between control and treated groups. While the treated groups did not show any significant changes expressions of p53 and Bcl-2 as observed by histopathological and immunohistochemical examination as compared to the control group, liver and kidney toxicity occurred for the rat groups administered 6g/kg. In conclusion, Eruca sativa is not toxic and there were no structural and functional changes in the liver and kidney when administered the doses of 1–5 g/Kg BW over a 35-day period through its potent antioxidant activity in rats and that toxicity that occurred in the 6g/kg-day group may be caused by a high concentration of glucosinolates.
-
FC/FACS
-
Plant Science
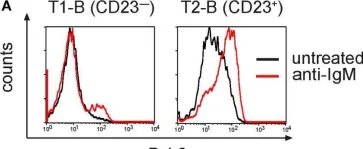
In Front Immunol on 22 August 2018 by Hobeika, E., Dautzenberg, M., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Front Immunol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 6
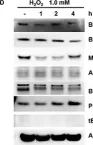
In Oncotarget on 11 April 2017 by Yang, H., Xie, Y., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 6
In Oncotarget on 11 April 2017 by Yang, H., Xie, Y., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 6
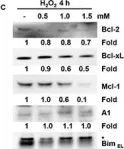
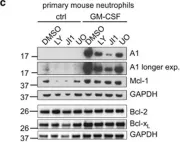
In Cell Death Dis on 18 February 2016 by Vier, J., Groth, M., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 6
In Cell Death Dis on 18 February 2016 by Vier, J., Groth, M., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 6
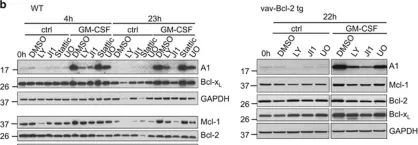
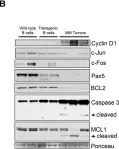
In Cancer Cell on 1 April 2007 by Carrasco, D. R., Sukhdeo, K., et al.
Fig.6.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cancer Cell by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 6