Mutations that negatively impact mitochondrial function are highly prevalent in humans and lead to disorders with a wide spectrum of disease phenotypes, including deficiencies in immune cell development and/or function. Previous analyses of mice with a hepatocyte-specific cytochrome c oxidase (COX) deficiency revealed an unexpected peripheral blood leukopenia associated with splenic and thymic atrophy. Here, we use mice with a hepatocyte-specific deletion of the COX assembly factor Sco1 to show that metabolic defects extrinsic to the hematopoietic compartment lead to a pan-lymphopenia represented by severe losses in both B and T cells. We further demonstrate that immune defects in these mice are associated with the loss of bone marrow lymphoid progenitors common to both lineages and early signs of autoantibody-mediated autoimmunity. Our findings collectively identify hepatocyte dysfunction as a potential instigator of immunodeficiency in patients with congenital mitochondrial defects who suffer from chronic or recurrent infections.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Product Citations: 125
In IScience on 18 April 2025 by Pioli, K. T., Ghosh, S., et al.
Preprint on BioRxiv : the Preprint Server for Biology on 22 January 2025 by Miller, C. M., Morrison, J. H., et al.
SUMMARY Sensing of viral double-stranded RNA by MDA5 triggers abundant but transient interferon-stimulated gene (ISGs) expression. If dsRNA synthesis is made persistent by transgenically expressing a picornaviral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) in mice, lifelong MDA5 activation and marked, global ISG upregulation result. This confers robust protection from viral diseases but in contrast to numerous other chronic MDA5 hyperactivation states, the mice suffer no autoimmune consequences. Here we find they further confound expectations by being resistant to a strong autoimmunity (lupus) provocation. However, knockout of one allele of Adar , which by itself is also well-tolerated, breaks the protective state and results in a severe disease that resembles interferonopathies caused by MDA5 gain-of-function mutations. In Adar +/- RdRp transgenic mice, A-to-I editing is both dysregulated and increased (numbers of genes and sites). This dsRNA-driven, MDA5-wild type model establishes that viral polymerase-sourced dsRNA can drive interferonopathy pathogenesis and illuminates the autoimmunity preventing role of ADAR1, while the ADAR1-intact viral RdRp model distinctively uncouples chronic MDA5 hyperactivity and autoinflammatory disease.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Genetics
-
Immunology and Microbiology
Tumor stage-driven disruption of NK cell maturation in human and murine tumors.
In IScience on 15 November 2024 by Russick, J., Torset, C., et al.
Natural killer (NK) cells play a pivotal role against cancer, both by direct killing of malignant cells and by promoting adaptive immune response though cytokine and chemokine secretion. In the lung tumor microenvironment (TME), NK cells are scarce and dysfunctional. By conducting single-cell transcriptomic analysis of lung tumors, and exploring pseudotime, we uncovered that the intratumoral maturation trajectory of NK cells is disrupted in a tumor stage-dependent manner, ultimately resulting in the selective exclusion of the cytotoxic subset. Using functional assays, we observed intratumoral NK cell death and a reduction in cytotoxic capacities depending on the tumor stage. Finally, our analyses of human public dataset on lung cancer corroborate these findings, revealing a parallel dysfunctional maturation process of NK cells during tumor progression. These results highlight additional mechanisms by which tumor cells escape from NK cell cytotoxicity, therefore paving the way for tailored therapeutic strategies.
© 2024 The Author(s).
-
Cancer Research
In IScience on 18 October 2024 by Fahlquist-Hagert, C., Wittenborn, T. R., et al.
Autoantibodies generated in germinal centers (GCs) contribute to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. GCs are controlled by specialized FoxP3+ T-follicular regulatory cells (Tfr), but their role in established autoimmunity is unclear. We generated autoimmune bone marrow chimeras in which Tfr could be specifically ablated by diphtheria toxin. Furthermore, we tracked the clonal persistence and evolution of Tfr populations using Confetti reporters. Ablation of Tfr caused increased early plasma cell output, but longer-term ablation did not increase plasma cell levels beyond those of Tfr-sufficient controls, suggesting that Tfr fail to contain chronic autoreactive GC responses. In agreement, Tfr were robustly induced in early autoreactive GCs but then waned. Moreover, we observed polyclonal Tfr expansion when ablating part of the Tfr subset. Hence, under homeostatic conditions, a polyclonal population of Tfr operates to control autoreactivity by limiting the output of plasma cells from GCs, but in chronic autoimmunity, this mechanism fails.
© 2024 The Author(s).
CD14 is a decision-maker between Fas-mediated death and inflammation.
In Cell Reports on 24 September 2024 by Magri, Z., Jetton, D., et al.
Signaling through classical death receptor Fas was mainly appreciated as a pro-death pathway until recent reports characterized pro-inflammatory outcomes of Fas-mediated activation in pathological contexts. How Fas signaling can switch to pro-inflammatory activation is poorly understood. Herein, we report that in macrophages and neutrophils, the Toll-like receptor (TLR) adapter CD14 determines the inflammatory output of Fas-mediated signaling. Our findings propose CD14 as a crucial chaperone of Fas receptor internalization in macrophages and neutrophils, resulting in Cd14-/- myeloid cells that are protected from FasL-induced apoptosis, activate nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), and release cytokines in response. As in TLR signaling, CD14 is also required for Fas to signal through the adaptor TRIF (TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β) and induce a pro-death complex. Our findings demonstrate that CD14 availability can determine the switch between Fas-mediated pro-death and pro-inflammatory outcomes by internalizing the receptor.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
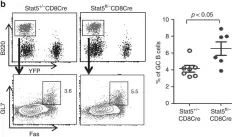
In Nat Commun on 27 September 2019 by Chen, Y., Yu, M., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2
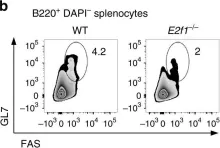
In Nat Commun on 12 October 2017 by Béguelin, W., Rivas, M. A., et al.
Fig.7.B

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 2