Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a heterogeneous disease with limited treatment options. To characterize TNBC heterogeneity, we defined transcriptional, epigenetic, and metabolic subtypes and subtype-driving super-enhancers and transcription factors by combining functional and molecular profiling with computational analyses. Single-cell RNA sequencing revealed relative homogeneity of the major transcriptional subtypes (luminal, basal, and mesenchymal) within samples. We found that mesenchymal TNBCs share features with mesenchymal neuroblastoma and rhabdoid tumors and that the PRRX1 transcription factor is a key driver of these tumors. PRRX1 is sufficient for inducing mesenchymal features in basal but not in luminal TNBC cells via reprogramming super-enhancer landscapes, but it is not required for mesenchymal state maintenance or for cellular viability. Our comprehensive, large-scale, multiplatform, multiomics study of both experimental and clinical TNBC is an important resource for the scientific and clinical research communities and opens venues for future investigation.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 17
Heterogeneity and transcriptional drivers of triple-negative breast cancer.
In Cell Reports on 26 December 2023 by Jovanovic, B., Temko, D., et al.
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
In Cell Reports Medicine on 21 March 2023 by Fischer, J. R., Jackson, H. W., et al.
Although breast cancer mortality is largely caused by metastasis, clinical decisions are based on analysis of the primary tumor and on lymph node involvement but not on the phenotype of disseminated cells. Here, we use multiplex imaging mass cytometry to compare single-cell phenotypes of primary breast tumors and matched lymph node metastases in 205 patients. We observe extensive phenotypic variability between primary and metastatic sites and that disseminated cell phenotypes frequently deviate from the clinical disease subtype. We identify single-cell phenotypes and spatial organizations of disseminated tumor cells that are associated with patient survival and a weaker survival association for high-risk phenotypes in the primary tumor. We show that p53 and GATA3 in lymph node metastases provide prognostic information beyond clinical classifiers and can be measured with standard methods. Molecular characterization of disseminated tumor cells is an untapped source of clinically applicable prognostic information for breast cancer.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
JAK-STAT Signaling in Inflammatory Breast Cancer Enables Chemotherapy-Resistant Cell States.
In Cancer Research on 18 January 2023 by Stevens, L. E., Peluffo, G., et al.
Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a difficult-to-treat disease with poor clinical outcomes due to high risk of metastasis and resistance to treatment. In breast cancer, CD44+CD24- cells possess stem cell-like features and contribute to disease progression, and we previously described a CD44+CD24-pSTAT3+ breast cancer cell subpopulation that is dependent on JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Here we report that CD44+CD24- cells are the most frequent cell type in IBC and are commonly pSTAT3+. Combination of JAK2/STAT3 inhibition with paclitaxel decreased IBC xenograft growth more than either agent alone. IBC cell lines resistant to paclitaxel and doxorubicin were developed and characterized to mimic therapeutic resistance in patients. Multi-omic profiling of parental and resistant cells revealed enrichment of genes associated with lineage identity and inflammation in chemotherapy-resistant derivatives. Integrated pSTAT3 chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analyses showed pSTAT3 regulates genes related to inflammation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in resistant cells, as well as PDE4A, a cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase. Metabolomic characterization identified elevated cAMP signaling and CREB as a candidate therapeutic target in IBC. Investigation of cellular dynamics and heterogeneity at the single cell level during chemotherapy and acquired resistance by CyTOF and single cell RNA-seq identified mechanisms of resistance including a shift from luminal to basal/mesenchymal cell states through selection for rare preexisting subpopulations or an acquired change. Finally, combination treatment with paclitaxel and JAK2/STAT3 inhibition prevented the emergence of the mesenchymal chemo-resistant subpopulation. These results provide mechanistic rational for combination of chemotherapy with inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 signaling as a more effective therapeutic strategy in IBC.
Chemotherapy resistance in inflammatory breast cancer is driven by the JAK2/STAT3 pathway, in part via cAMP/PKA signaling and a cell state switch, which can be overcome using paclitaxel combined with JAK2 inhibitors.
©2022 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
-
Cancer Research
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cancers on 4 August 2021 by Luan, H., Bailey, T. A., et al.
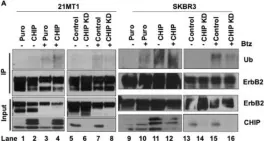
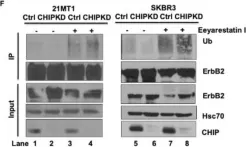
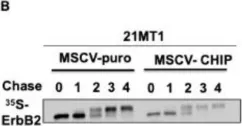
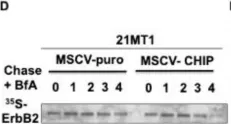
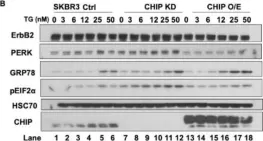
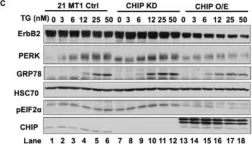
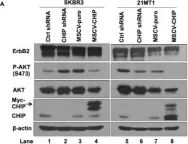
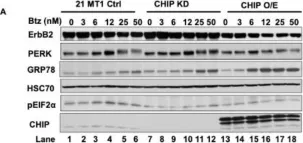
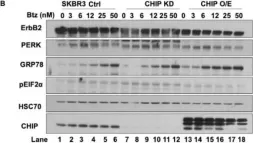
Overexpression of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family member ErbB2 (HER2) drives oncogenesis in up to 25% of invasive breast cancers. ErbB2 expression at the cell surface is required for oncogenesis but mechanisms that ensure the optimal cell surface display of overexpressed ErbB2 following its biosynthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum are poorly understood. ErbB2 is dependent on continuous association with HSP90 molecular chaperone for its stability and function as an oncogenic driver. Here, we use knockdown and overexpression studies to show that the HSP90/HSC70-interacting negative co-chaperone CHIP (C-terminus of HSC70-Interacting protein)/STUB1 (STIP1-homologous U-Box containing protein 1) targets the newly synthesized, HSP90/HSC70-associated, ErbB2 for ubiquitin/proteasome-dependent degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi, thus identifying a novel mechanism that negatively regulates cell surface ErbB2 levels in breast cancer cells, consistent with frequent loss of CHIP expression previously reported in ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancers. ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells with low CHIP expression exhibited higher endoplasmic reticulum stress inducibility. Accordingly, the endoplasmic reticulum stress-inducing anticancer drug Bortezomib combined with ErbB2-targeted humanized antibody Trastuzumab showed synergistic inhibition of ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cell proliferation. Our findings reveal new insights into mechanisms that control the surface expression of overexpressed ErbB2 and suggest that reduced CHIP expression may specify ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancers suitable for combined treatment with Trastuzumab and ER stress inducing agents.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
Preprint on Research Square on 7 May 2020 by Penachiotti, G., Valdez, F., et al.
h4>Background: /h4> The oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) affects more than 300,000 patients annually worldwide with a high morbidity rate (37.8%). Several tumor biomarkers have been suggested to anticipate outcome but results were poor. Changes of SPINK7 and associated proteins in precancerous oral lesions could lead to genomic instability and promote oncogenesis. Our aim was to evaluate SPINK7as apotential molecular biomarkerpredictive of OSCC stages, compared with well-known molecules altered in cancer: HER2,TP53, RB1, NFKB and CYP4B1. h4>Methods: /h4>. Oral biopsies from patientswith dysplasia (n=33), less invasive(n=28) andhighly invasiveOSCC (n=18) were collected. 20 cases with a clinical suspicion but normal mucosa confirmedwere included ascontrol. Gene expression of SPINK7, P53,RB, NFKB and CYP4B1 were quantified by qPCR. SPINK7 levels were correlated with a cohort of 330 patients from the TCGA. Also,SPINK7, HER2, TP53, and RB1, were evaluated by immunohistofluorescence. One-way Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn's post-hoc with a p0.05 significance were used to data analyze. h4>Results: /h4>. In OSCC, SPINK7 wasdown regulated and P53, RB, NFKB and CYP4B1 were up regulatedrespect tothe others groups (p0.001). Also, SPINK7 expressionwasdiminished in patients of TCGA(p=2.10e-6). In less invasive OSCC,SPINK7 and HER2 proteinswere decreasedandTP53 and RB1 significantly increasedrespect todysplasia and highly invasivegroups (p0.05). h4>Conclusion: /h4> Our results suggest that SPINK7changes accompanied of HER2, P53 and RB1 can be used to classify the molecular stage of epithelial oral lesion inthe OSCC, allowing a more accuratediagnosis to molecular and histopathological level.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
In Cancers (Basel) on 4 August 2021 by Luan, H., Bailey, T. A., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Cancers (Basel) on 4 August 2021 by Luan, H., Bailey, T. A., et al.
Fig.2.F

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Cancers (Basel) on 4 August 2021 by Luan, H., Bailey, T. A., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Cancers (Basel) on 4 August 2021 by Luan, H., Bailey, T. A., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Cancers (Basel) on 4 August 2021 by Luan, H., Bailey, T. A., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Cancers (Basel) on 4 August 2021 by Luan, H., Bailey, T. A., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Cancers (Basel) on 4 August 2021 by Luan, H., Bailey, T. A., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Cancers (Basel) on 4 August 2021 by Luan, H., Bailey, T. A., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9
In Cancers (Basel) on 4 August 2021 by Luan, H., Bailey, T. A., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 9