Group 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3s) are important for maintaining gut homeostasis. Upon stimulation, ILC3s can rapidly produce cytokines to protect against infections and colitis. However, the regulation of ILC3 quick response is still unclear. Here, we find that eIF6 aggregates with Nsun2 and cytokine mRNA in ILC3s at steady state, which inhibits the methyltransferase activity of Nsun2 and the nuclear export of cytokine mRNA, resulting in the nuclear reservation of cytokine mRNA. Upon stimulation, phosphorylated p38α phosphorylates eIF6, which in turn releases Nsun2 activity, and promotes the nuclear export of cytokine mRNA and rapid cytokine production. Genetic disruption of p38α, Nsun2, or eIF6 in ILC3s influences the mRNA nuclear export and protein expression of the protective cytokines, thus leading to increased susceptibility to colitis. Together, our data identify a crucial role of the p38α-eIF6-Nsun2 axis in regulating rapid ILC3 immune response at the posttranscriptional level, which is critical for gut homeostasis maintenance and protection against gut inflammation.
© 2024 Huang et al.
Product Citations: 13
p38α-eIF6-Nsun2 axis promotes ILC3's rapid response to protect host from intestinal inflammation.
In The Journal of Experimental Medicine on 6 January 2025 by Huang, J., Zhang, J., et al.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In The Journal of Immunology on 15 November 2022 by Matter, A. L., Liggitt, D., et al.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory, demyelinating CNS disease believed to be mediated by CD4 T cells specific for CNS self-antigens. CD8 T cells are also implicated in MS but their function is not well understood. MS lesions are heterogeneous and may reflect variation in the contribution of different types of lymphocytes. Understanding how lymphocytes with different effector functions contribute to MS is essential to develop effective therapies. We investigated how T cells expressing an MHC class I-restricted transgenic TCR specific for myelin basic protein (MBP) contribute to CNS autoimmunity using the mouse model of MS, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Virus infection triggered cytotoxic TCR-transgenic CD8 T cells to initiate acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in an IFN-γ- and perforin-dependent manner. Unexpectedly, spontaneous CNS autoimmunity developed in the TCR-transgenic mice that was accelerated by IFN-γ-deficiency. Spontaneous disease was associated with CD4 T cells that develop via endogenous TCR rearrangements but retain specificity for the MHC class I-restricted MBP epitope. The CD4 T cells produced TNF-α without other inflammatory cytokines and caused lesions with striking similarity to active MS lesions. Surprisingly, B cells were the predominant cell type that cross-presented MBP, and their depletion halted disease progression. This work provides a new model of spontaneous CNS autoimmunity with unique similarities to MS that is mediated by T cells with a distinct effector phenotype.
Copyright © 2022 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Cell Reports on 25 October 2022 by Mudalagiriyappa, S., Sharma, J., et al.
GM-CSF co-expressing T17 cells instigate pathologic inflammation during autoimmune disorders, but their function in immunity to infections is unclear. Here, we demonstrate the role of GM-CSF+Tc17 cells for vaccine immunity against lethal fungal pneumonia and the cytokine requirements for their induction and memory homeostasis. Vaccine-induced GM-CSF+ Tc17 cells are necessary to bolster pulmonary fungal immunity without inflating pathology. Although GM-CSF expressing Tc17 cells preferentially elevate during the memory phase, their phenotypic attributes strongly suggest they are more like Tc17 cells than IFNγ-producing Tc1 cells. IL-1 and IL-23, but not GM-CSF, are necessary to elicit GM-CSF+ Tc17 cells following vaccination. IL-23 is dispensable for memory Tc17 and GM-CSF+ Tc17 cell maintenance, but recall responses of effector or memory Tc17 cells in the lung require it. Our study reveals the beneficial, nonpathological role of GM-CSF+ Tc17 cells during fungal vaccine immunity.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
-
Pathology
In Vaccines on 14 June 2022 by Bommireddy, R., Stone, S., et al.
Several approaches have produced an effective vaccine against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Since millions of people are exposed to influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2, it is of great interest to develop a two-in-one vaccine that will be able to protect against infection of both viruses. We have developed a hybrid vaccine for SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses using influenza virus-like particles (VLP) incorporated by protein transfer with glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored SARS-CoV-2 RBD fused to GM-CSF as an adjuvant. GPI-RBD-GM-CSF fusion protein was expressed in CHO-S cells, purified and incorporated onto influenza VLPs to develop the hybrid vaccine. Our results show that the hybrid vaccine induced a strong antibody response and protected mice from both influenza virus and mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 challenges, with vaccinated mice having significantly lower lung viral titers compared to naive mice. These results suggest that a hybrid vaccine strategy is a promising approach for developing multivalent vaccines to prevent influenza A and SARS-CoV-2 infections.
-
FC/FACS
-
COVID-19
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Nature Communications on 16 July 2021 by Zhao, Z., Wang, H., et al.
Mucosal-associated Invariant T (MAIT) cells are recognized for their antibacterial functions. The protective capacity of MAIT cells has been demonstrated in murine models of local infection, including in the lungs. Here we show that during systemic infection of mice with Francisella tularensis live vaccine strain results in evident MAIT cell expansion in the liver, lungs, kidney and spleen and peripheral blood. The responding MAIT cells manifest a polarised Th1-like MAIT-1 phenotype, including transcription factor and cytokine profile, and confer a critical role in controlling bacterial load. Post resolution of the primary infection, the expanded MAIT cells form stable memory-like MAIT-1 cell populations, suggesting a basis for vaccination. Indeed, a systemic vaccination with synthetic antigen 5-(2-oxopropylideneamino)-6-D-ribitylaminouracil in combination with CpG adjuvant similarly boosts MAIT cells, and results in enhanced protection against both systemic and local infections with different bacteria. Our study highlights the potential utility of targeting MAIT cells to combat a range of bacterial pathogens.
© 2021. The Author(s).
-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Immunity on 19 June 2018 by Hirota, K., Hashimoto, M., et al.
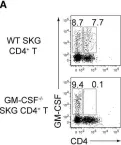
Fig.4.A

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Immunity by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
In Immunity on 19 June 2018 by Hirota, K., Hashimoto, M., et al.
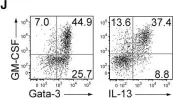
Fig.4.J

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Immunity by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
In Immunity on 19 June 2018 by Hirota, K., Hashimoto, M., et al.
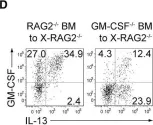
Fig.5.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Immunity by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
In Immunity on 19 June 2018 by Hirota, K., Hashimoto, M., et al.
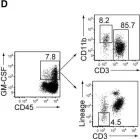
Fig.7.D

-
FC/FACS
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Immunity by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4